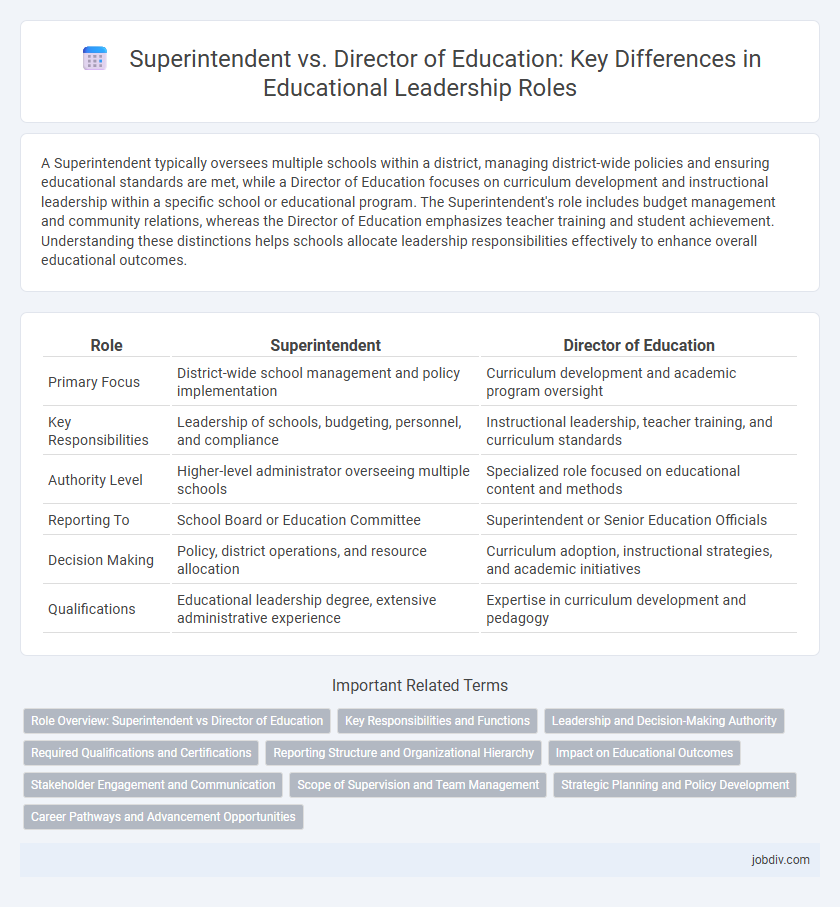
A Superintendent typically oversees multiple schools within a district, managing district-wide policies and ensuring educational standards are met, while a Director of Education focuses on curriculum development and instructional leadership within a specific school or educational program. The Superintendent's role includes budget management and community relations, whereas the Director of Education emphasizes teacher training and student achievement. Understanding these distinctions helps schools allocate leadership responsibilities effectively to enhance overall educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Superintendent | Director of Education |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | District-wide school management and policy implementation | Curriculum development and academic program oversight |
| Key Responsibilities | Leadership of schools, budgeting, personnel, and compliance | Instructional leadership, teacher training, and curriculum standards |
| Authority Level | Higher-level administrator overseeing multiple schools | Specialized role focused on educational content and methods |
| Reporting To | School Board or Education Committee | Superintendent or Senior Education Officials |
| Decision Making | Policy, district operations, and resource allocation | Curriculum adoption, instructional strategies, and academic initiatives |
| Qualifications | Educational leadership degree, extensive administrative experience | Expertise in curriculum development and pedagogy |
Role Overview: Superintendent vs Director of Education
The Superintendent oversees the implementation of educational policies and manages district-wide operations, ensuring compliance with state and federal regulations. The Director of Education focuses on developing curriculum standards, instructional programs, and professional development initiatives to enhance teaching quality. Both roles collaborate to improve student outcomes, with the Superintendent handling administrative leadership and the Director concentrating on educational strategies.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Superintendents oversee district-wide educational policies, manage budgets, and ensure compliance with state and federal regulations, while Directors of Education focus on curriculum development, staff training, and instructional quality improvements. Superintendents act as liaisons between school boards and individual schools, setting strategic goals and monitoring overall performance metrics. Directors of Education implement these strategies by coordinating professional development programs and evaluating educational outcomes to enhance student achievement.
Leadership and Decision-Making Authority
Superintendents hold higher leadership and decision-making authority within school districts, overseeing multiple schools and setting strategic policies to improve educational outcomes. Directors of Education typically focus on specific programs or departments, managing day-to-day operations and implementing policies established by superintendents and school boards. The superintendent's role involves broader governance responsibilities, including budget approval and community engagement, whereas directors concentrate on specialized educational initiatives and staff supervision.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Superintendent positions typically require a master's degree in education or administration and state-specific certification in school leadership, often demanding several years of prior teaching and administrative experience. Directors of Education may also need a master's degree, specialized certifications related to curriculum management or educational leadership, and demonstrated expertise in policy implementation. Both roles emphasize strong credentials in educational law, finance, and community relations to effectively oversee school systems.
Reporting Structure and Organizational Hierarchy
The Superintendent typically reports directly to the School Board or Superintendent's Office, overseeing the entire school district's operations, while the Director of Education usually reports to the Superintendent and focuses on curriculum development and instructional leadership. In the organizational hierarchy, the Superintendent holds a higher executive role responsible for broad policy implementation and district-wide administration, whereas the Director of Education is a senior manager specializing in academic programs and teacher support. Clear reporting lines ensure accountability, with the Superintendent setting strategic goals and the Director aligning educational initiatives to meet those objectives.
Impact on Educational Outcomes
Superintendents oversee district-wide policies and resource allocation, directly influencing curriculum implementation and teacher effectiveness, which are critical factors in improving student achievement. Directors of Education focus on program development and staff training, ensuring instructional quality and adherence to educational standards that drive academic success. Both roles significantly impact educational outcomes by shaping leadership strategies and operational frameworks within schools.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Superintendents excel in stakeholder engagement by facilitating transparent communication channels among school boards, administrators, and communities to ensure collaborative decision-making and shared educational goals. Directors of Education focus on strategic communication with teachers, staff, and external partners to implement policies effectively and promote continuous professional development. Both roles prioritize fostering trust, responsiveness, and active participation to drive student success and educational innovation.
Scope of Supervision and Team Management
A Superintendent typically oversees multiple schools within a district, managing broader educational policies, budget allocation, and compliance with state regulations, while a Director of Education often focuses on specific educational programs or departments, such as curriculum development or staff training. Superintendents lead large administrative teams and coordinate efforts across schools to ensure district-wide performance and strategic goals are met. Directors of Education manage specialized teams, driving targeted initiatives and professional development to enhance teaching quality and student outcomes.
Strategic Planning and Policy Development
Superintendents oversee district-wide strategic planning, ensuring alignment with long-term educational goals and community needs, while Directors of Education focus on developing and implementing policies that support curriculum standards and teacher effectiveness. Superintendents lead cross-functional teams to evaluate performance metrics and allocate resources efficiently, driving systemic improvements. Directors translate strategic directives into actionable policies, monitor compliance, and provide guidance to schools on regulatory changes and best practices.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Superintendents typically advance from roles such as principals or experienced educators, focusing on district-wide administration and policy development, while Directors of Education often transition from specialized academic or curriculum leadership positions, emphasizing instructional quality and program oversight. Career pathways for Superintendents include moving into higher executive roles like Chief Executive Officer or Education Consultant, whereas Directors of Education may advance to senior curriculum specialist roles or executive leadership within educational organizations. Both positions require strong leadership skills and offer opportunities for growth in educational administration and strategic planning.
Superintendent vs Director of Education Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com