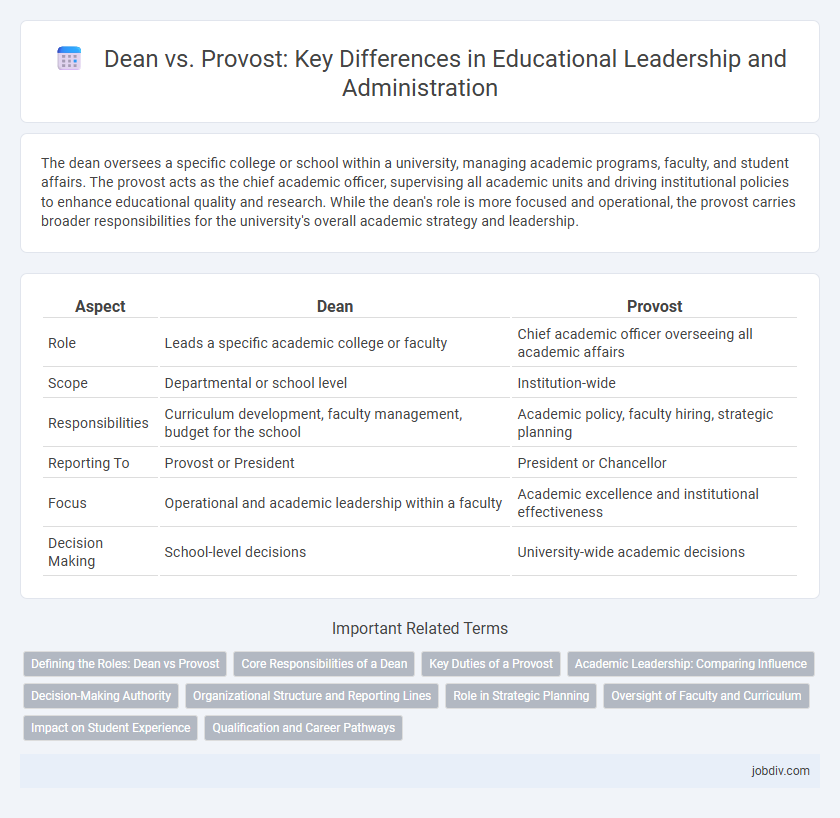
The dean oversees a specific college or school within a university, managing academic programs, faculty, and student affairs. The provost acts as the chief academic officer, supervising all academic units and driving institutional policies to enhance educational quality and research. While the dean's role is more focused and operational, the provost carries broader responsibilities for the university's overall academic strategy and leadership.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dean | Provost |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Leads a specific academic college or faculty | Chief academic officer overseeing all academic affairs |
| Scope | Departmental or school level | Institution-wide |
| Responsibilities | Curriculum development, faculty management, budget for the school | Academic policy, faculty hiring, strategic planning |
| Reporting To | Provost or President | President or Chancellor |
| Focus | Operational and academic leadership within a faculty | Academic excellence and institutional effectiveness |
| Decision Making | School-level decisions | University-wide academic decisions |
Defining the Roles: Dean vs Provost
A Dean typically manages a specific college or school within a university, overseeing academic programs, faculty affairs, and student services in that unit. The Provost serves as the chief academic officer for the entire institution, responsible for setting academic policies, resource allocation, and strategic planning across all colleges. Understanding the distinctions between these roles clarifies governance structures and clarifies responsibilities in higher education administration.
Core Responsibilities of a Dean
A Dean primarily oversees the academic and administrative functions of a specific college or faculty within a university, managing curriculum development, faculty recruitment, and student affairs. They play a critical role in shaping academic policies, budget allocation, and fostering faculty research and development. Unlike a Provost who handles broader institutional academic strategies, the Dean's core responsibilities are concentrated on the operational leadership and enhancement of their individual school or department.
Key Duties of a Provost
The Provost serves as the chief academic officer responsible for overseeing the institution's academic policies, curriculum development, and faculty affairs. Key duties include managing budget allocations for academic departments, fostering research initiatives, and ensuring compliance with accreditation standards. The Provost collaborates closely with deans to promote academic excellence and strategic planning across all colleges.
Academic Leadership: Comparing Influence
The Dean typically oversees a specific college or school within a university, managing faculty, curriculum, and student affairs to shape academic quality at a departmental level. The Provost holds broader authority, acting as the chief academic officer responsible for strategic planning, resource allocation, and institutional policies that impact all academic units. Their influence varies, with Deans focusing on targeted academic leadership while Provosts drive overarching academic vision and operational coherence across the university.
Decision-Making Authority
Deans typically oversee specific colleges or schools within a university, managing academic programs and faculty decisions at that level, which grants them authority over curriculum development and departmental policies. Provosts hold the chief academic officer role, possessing broader decision-making authority encompassing the entire institution's academic strategy, faculty appointments, and resource allocation. The provost's role includes final approval on major academic initiatives, while deans implement and manage those strategies within their divisions.
Organizational Structure and Reporting Lines
In academic institutions, the Dean typically oversees a specific college or faculty, managing departmental budgets, curriculum development, and faculty affairs. The Provost, positioned higher in the organizational hierarchy, serves as the chief academic officer responsible for the overall academic strategy, policy implementation, and coordination among deans. Reporting lines usually flow from department chairs to deans, who in turn report directly to the provost, establishing a clear chain of command within the university's governance structure.
Role in Strategic Planning
The Dean focuses on strategic planning within their specific college or school, aligning academic programs and resources to meet department goals and student needs. The Provost oversees university-wide strategic planning, integrating initiatives across all colleges to ensure cohesive academic standards and institutional priorities. Collaboration between the Dean and Provost is essential for effective implementation of the university's long-term educational objectives.
Oversight of Faculty and Curriculum
Deans typically oversee specific colleges or schools within a university, managing faculty affairs, curriculum development, and academic programs within their units. Provosts hold broader responsibility for the institution's overall academic administration, including supervising all deans, ensuring curriculum coherence across colleges, and setting university-wide academic policies. This hierarchical structure allows provosts to coordinate interdisciplinary initiatives while deans focus on specialized governance and faculty management.
Impact on Student Experience
A Dean directly influences the student experience by overseeing academic programs, faculty engagement, and student support services within a specific college or school, ensuring tailored educational quality and resources. The Provost shapes the broader student environment by setting institutional academic policies, allocating resources across departments, and fostering university-wide initiatives that enhance curriculum development and research opportunities. Both roles critically impact student success, with Deans providing hands-on leadership and the Provost guiding strategic academic priorities.
Qualification and Career Pathways
Deans typically require advanced degrees in their academic discipline, often holding a PhD, alongside extensive experience in faculty roles and departmental leadership. Provosts usually possess a robust academic background combined with significant administrative experience, frequently having served as deans or senior academic officers before advancing to the institution's chief academic officer position. Career pathways for deans often progress from faculty to department chair to dean, while provosts generally ascend through expanded leadership roles culminating in overseeing all academic affairs.
Dean vs Provost Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com