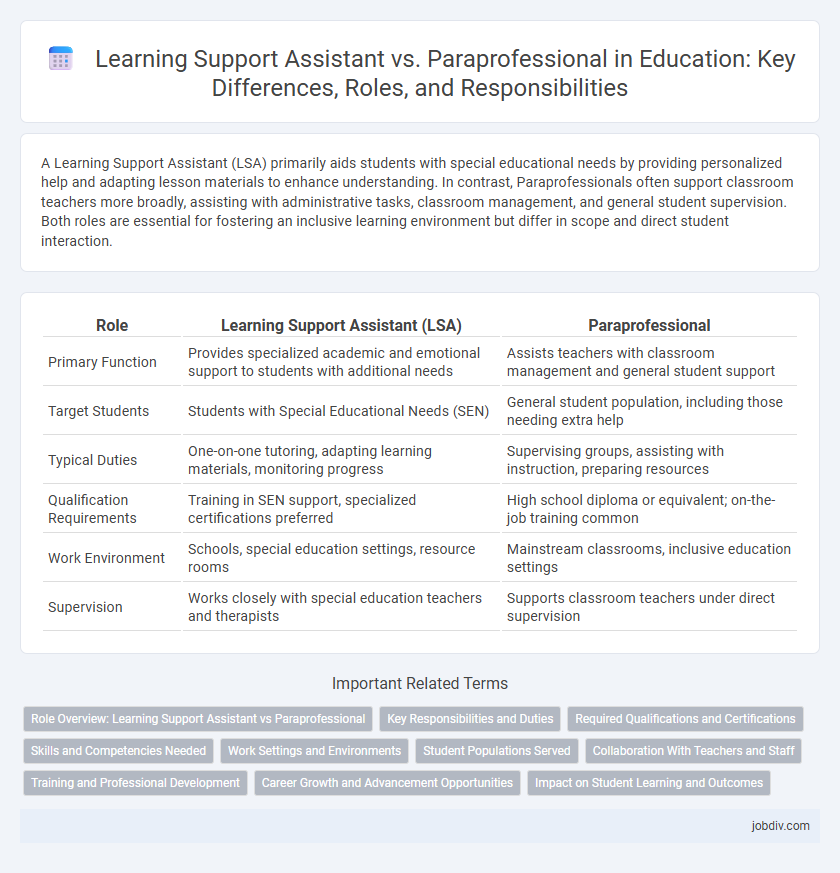
A Learning Support Assistant (LSA) primarily aids students with special educational needs by providing personalized help and adapting lesson materials to enhance understanding. In contrast, Paraprofessionals often support classroom teachers more broadly, assisting with administrative tasks, classroom management, and general student supervision. Both roles are essential for fostering an inclusive learning environment but differ in scope and direct student interaction.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Learning Support Assistant (LSA) | Paraprofessional |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides specialized academic and emotional support to students with additional needs | Assists teachers with classroom management and general student support |
| Target Students | Students with Special Educational Needs (SEN) | General student population, including those needing extra help |
| Typical Duties | One-on-one tutoring, adapting learning materials, monitoring progress | Supervising groups, assisting with instruction, preparing resources |
| Qualification Requirements | Training in SEN support, specialized certifications preferred | High school diploma or equivalent; on-the-job training common |
| Work Environment | Schools, special education settings, resource rooms | Mainstream classrooms, inclusive education settings |
| Supervision | Works closely with special education teachers and therapists | Supports classroom teachers under direct supervision |
Role Overview: Learning Support Assistant vs Paraprofessional
Learning Support Assistants primarily provide in-class assistance to students with special educational needs by supporting individualized learning plans and facilitating classroom engagement. Paraprofessionals offer a broader range of support, including one-on-one tutoring, behavioral interventions, and assisting teachers with instructional responsibilities across various settings. Both roles are essential for promoting inclusive education, but paraprofessionals typically hold additional qualifications and assume more specialized duties.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Learning Support Assistants primarily provide direct instructional support to students with special educational needs, assisting with individualized learning plans and facilitating classroom activities. Paraprofessionals often have broader responsibilities including behavioral support, administrative tasks, and collaborating with teachers to implement lesson plans. Both roles play crucial parts in enhancing student learning outcomes and ensuring inclusive education environments.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Learning Support Assistants typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, with some roles demanding specialized training or certifications in special education or behavior management. Paraprofessionals often need postsecondary education credentials, such as an associate degree or completion of a state-approved training program, alongside certification like the ParaPro Assessment or state-specific paraprofessional licenses. Both positions emphasize knowledge of student development and instructional support, but paraprofessionals tend to hold more formal qualifications reflecting their expanded instructional responsibilities.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Learning Support Assistants require strong interpersonal skills, patience, and the ability to implement individualized education plans effectively, emphasizing communication and behavioral support competencies. Paraprofessionals need advanced instructional abilities, including adapting curriculum materials, assisting with assessments, and supporting students with diverse learning needs across various subjects. Both roles demand collaboration skills, but paraprofessionals typically require more specialized training in educational strategies and classroom management techniques.
Work Settings and Environments
Learning Support Assistants primarily operate within inclusive classroom settings, collaborating closely with teachers to support students with diverse learning needs. Paraprofessionals work across various educational environments, including special education classrooms, resource rooms, and one-on-one support scenarios, addressing individualized student requirements. Both roles involve direct student interaction but differ in the scope and structure of their work environments.
Student Populations Served
Learning Support Assistants primarily serve students with special educational needs (SEN), supporting individualized learning plans and facilitating integration in mainstream classrooms. Paraprofessionals assist diverse student populations, including English language learners (ELLs), students with disabilities, and those requiring behavioral interventions. Both roles contribute to inclusive education by enhancing access and engagement for students with varying academic and developmental challenges.
Collaboration With Teachers and Staff
Learning Support Assistants collaborate closely with teachers by providing individualized support and facilitating differentiated instruction tailored to students' needs. Paraprofessionals work alongside educators to implement classroom management strategies and assist with administrative tasks, ensuring a cohesive learning environment. Both roles emphasize teamwork to enhance educational outcomes and address diverse student challenges effectively.
Training and Professional Development
Learning Support Assistants (LSAs) typically receive specialized training focused on individualized student support and behavior management techniques, often including certification in educational strategies and disability awareness. Paraprofessionals undergo broader professional development, emphasizing instructional assistance across diverse classroom settings, often requiring completion of state-mandated educational programs and ongoing workshops. Both roles benefit from continuous training in special education laws, communication strategies, and adaptive technology to enhance student engagement and academic outcomes.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Learning Support Assistants typically focus on providing direct academic and behavioral support within classrooms, developing specialized skills in student engagement and individualized instruction, which lays a strong foundation for advancement into roles such as Special Education Teacher or Educational Therapist. Paraprofessionals often gain broader experience by assisting with administrative tasks, adapting curriculum, and supporting diverse student needs, positioning themselves for career growth into positions like Instructional Coordinator or Educational Consultant. Both roles offer pathways to higher education and certification that enhance opportunities for leadership roles in educational settings.
Impact on Student Learning and Outcomes
Learning Support Assistants (LSAs) primarily provide individualized academic support, enhancing student engagement and improving learning outcomes through tailored interventions. Paraprofessionals often assist with behavioral management and inclusive classroom support, fostering a positive learning environment that contributes to overall student success. Both roles significantly impact student achievement by addressing diverse educational needs and promoting accessibility.
Learning Support Assistant vs Paraprofessional Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com