Paraprofessionals and teacher's aides both support classroom instruction but differ in responsibilities and certification requirements. Paraprofessionals often have specialized training and assist with instructional tasks, while teacher's aides primarily help with administrative or routine classroom duties. Understanding these distinctions helps schools allocate resources effectively and enhances student learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
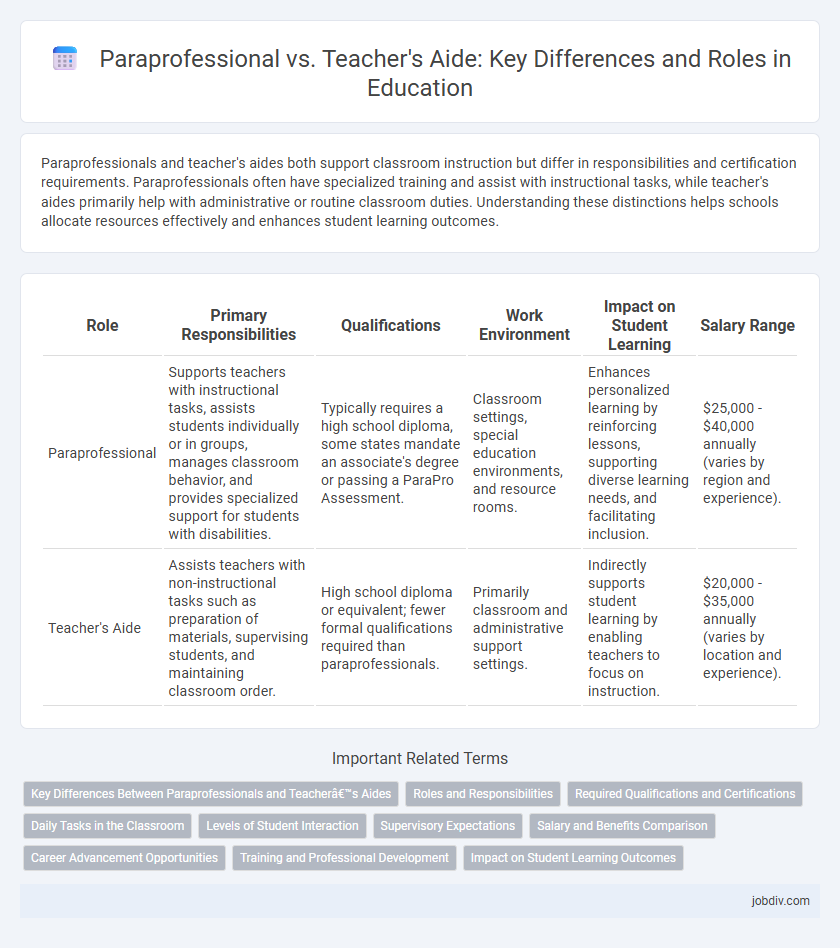
| Role | Primary Responsibilities | Qualifications | Work Environment | Impact on Student Learning | Salary Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paraprofessional | Supports teachers with instructional tasks, assists students individually or in groups, manages classroom behavior, and provides specialized support for students with disabilities. | Typically requires a high school diploma, some states mandate an associate's degree or passing a ParaPro Assessment. | Classroom settings, special education environments, and resource rooms. | Enhances personalized learning by reinforcing lessons, supporting diverse learning needs, and facilitating inclusion. | $25,000 - $40,000 annually (varies by region and experience). |
| Teacher's Aide | Assists teachers with non-instructional tasks such as preparation of materials, supervising students, and maintaining classroom order. | High school diploma or equivalent; fewer formal qualifications required than paraprofessionals. | Primarily classroom and administrative support settings. | Indirectly supports student learning by enabling teachers to focus on instruction. | $20,000 - $35,000 annually (varies by location and experience). |
Key Differences Between Paraprofessionals and Teacher’s Aides
Paraprofessionals typically hold specialized training or certifications and engage in more instructional responsibilities, including delivering individualized support to students with disabilities, while teacher's aides generally assist with classroom management and administrative tasks. Paraprofessionals often collaborate directly with certified teachers to implement lesson plans and assess student progress, whereas teacher's aides provide logistical help such as preparing materials and supervising students. Differences in job scope and required qualifications highlight the distinct roles each plays within the educational support team.
Roles and Responsibilities
Paraprofessionals primarily assist certified teachers by supporting classroom management, preparing instructional materials, and providing individualized attention to students with special needs. Teacher's aides often handle more routine tasks such as supervising students during non-instructional times, assisting with clerical duties, and reinforcing basic skills under direct teacher supervision. Both roles are essential for enhancing student learning but differ in scope, with paraprofessionals frequently taking on more specialized educational support responsibilities.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Paraprofessionals typically require a high school diploma and may need to complete a state-recognized training program or obtain a paraprofessional certification, such as the ParaPro Assessment. Teacher's aides often have similar educational requirements but might need additional specialized certifications depending on the school district or state, like CPR training or special education endorsements. Both roles demand background checks and adherence to state-specific guidelines to ensure student safety and support instructional quality.
Daily Tasks in the Classroom
Paraprofessionals provide direct instructional support by assisting with lesson delivery, managing student behavior, and adapting materials to meet individual learning needs. Teacher's aides primarily focus on clerical tasks such as preparing classroom materials, organizing resources, and supervising students during non-instructional times. Both roles enhance classroom efficiency but differ in the level of instructional involvement and student interaction.
Levels of Student Interaction
Paraprofessionals often engage in direct instructional support, working closely with small groups or individual students to reinforce lessons and assist with specialized learning needs. Teacher's aides typically provide more general assistance, such as classroom management, preparation of materials, and supervisory tasks, resulting in less frequent one-on-one student interaction. The level of student engagement by paraprofessionals is generally higher due to their role in targeted academic support and individualized attention.
Supervisory Expectations
Supervisory expectations for paraprofessionals typically include supporting classroom management and implementing instructional plans under direct teacher guidance, while teacher's aides often have more defined roles in assisting with student supervision and behavior monitoring. Paraprofessionals may lead small group instruction and provide specialized support for students with disabilities, requiring close collaboration with certified teachers. Teacher's aides are generally expected to follow detailed instructions and maintain student safety during non-instructional times such as recess or lunch periods.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Paraprofessionals typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $25,000 to $40,000, while teacher's aides often receive slightly lower compensation, averaging between $20,000 and $35,000 depending on the region and school district. Benefits for both roles may include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, but full-time paraprofessionals are more likely to receive comprehensive benefits packages compared to part-time or hourly-paid teacher's aides. Salary growth tends to be limited for both positions, with opportunities for advancement generally requiring additional certifications or transitioning into licensed teaching roles.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Paraprofessionals often pursue certification or higher education to transition into licensed teaching positions, while teacher's aides typically support classroom teachers without direct instructional responsibilities. Paraprofessionals have clearer career advancement pathways through roles such as lead paraprofessional, instructional specialist, or pursuing a teaching credential. Teacher's aides may advance to paraprofessional roles or specialize in areas like special education support but usually have limited upward mobility compared to paraprofessionals.
Training and Professional Development
Paraprofessionals typically receive targeted on-the-job training and may complete certification programs focused on classroom support techniques, whereas teachers' aides often have minimal formal training and learn primarily through direct supervision. Investment in professional development for paraprofessionals includes workshops on instructional strategies, behavior management, and special education, enhancing their effectiveness in diverse learning environments. Teachers' aides benefit from ongoing mentoring but generally lack access to comprehensive certification programs that advance pedagogical skills.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Paraprofessionals play a crucial role in enhancing student learning outcomes by providing targeted instructional support and personalized attention, which helps address diverse learning needs and fosters academic growth. Teacher's aides contribute to classroom management and assist with routine tasks, indirectly supporting student engagement and creating a conducive learning environment. Research indicates that paraprofessionals with specialized training in instructional strategies have a more significant positive impact on student achievement compared to general teacher's aides.
Paraprofessional vs Teacher’s Aide Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com