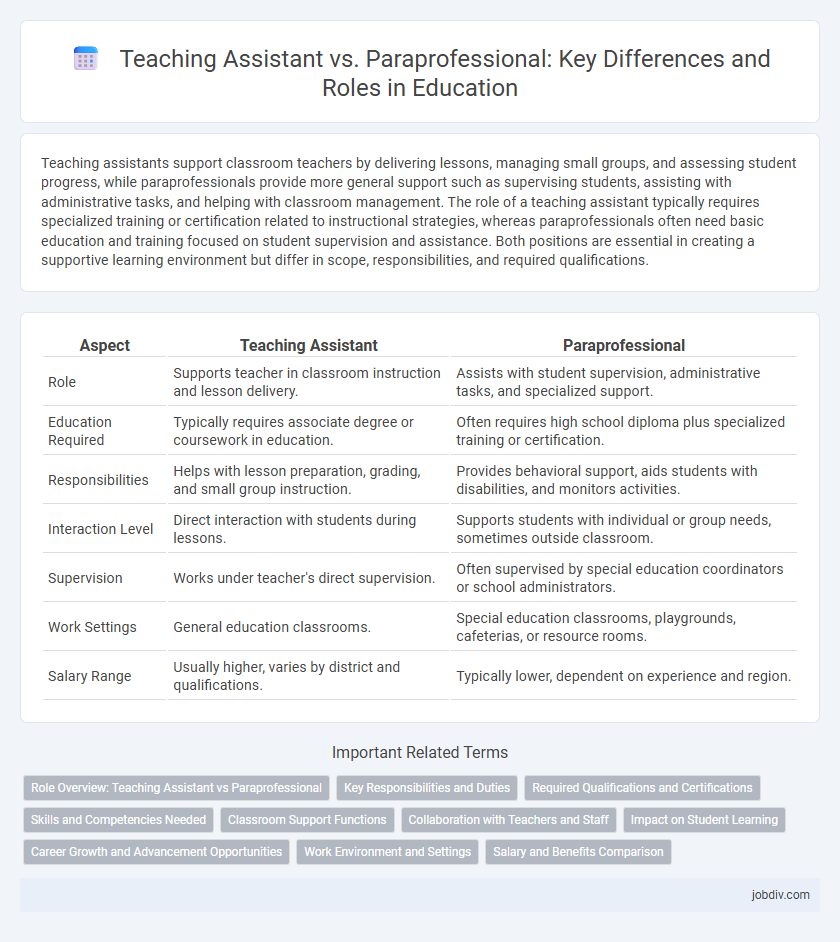
Teaching assistants support classroom teachers by delivering lessons, managing small groups, and assessing student progress, while paraprofessionals provide more general support such as supervising students, assisting with administrative tasks, and helping with classroom management. The role of a teaching assistant typically requires specialized training or certification related to instructional strategies, whereas paraprofessionals often need basic education and training focused on student supervision and assistance. Both positions are essential in creating a supportive learning environment but differ in scope, responsibilities, and required qualifications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Teaching Assistant | Paraprofessional |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Supports teacher in classroom instruction and lesson delivery. | Assists with student supervision, administrative tasks, and specialized support. |
| Education Required | Typically requires associate degree or coursework in education. | Often requires high school diploma plus specialized training or certification. |
| Responsibilities | Helps with lesson preparation, grading, and small group instruction. | Provides behavioral support, aids students with disabilities, and monitors activities. |
| Interaction Level | Direct interaction with students during lessons. | Supports students with individual or group needs, sometimes outside classroom. |
| Supervision | Works under teacher's direct supervision. | Often supervised by special education coordinators or school administrators. |
| Work Settings | General education classrooms. | Special education classrooms, playgrounds, cafeterias, or resource rooms. |
| Salary Range | Usually higher, varies by district and qualifications. | Typically lower, dependent on experience and region. |
Role Overview: Teaching Assistant vs Paraprofessional
Teaching assistants support classroom teachers by helping with lesson implementation, student supervision, and individualized instruction. Paraprofessionals often provide specialized support for students with disabilities, assisting with behavior management and adapting materials. Both roles enhance educational delivery but differ in scope and focus based on student needs and instructional goals.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Teaching Assistants support classroom teachers by delivering instructional assistance, managing student behavior, and preparing educational materials to enhance learning outcomes. Paraprofessionals perform specialized roles such as providing individualized student support, aiding in behavioral interventions, and facilitating communication between students with disabilities and educators. Both positions contribute to fostering an inclusive learning environment, with Teaching Assistants focusing on broad instructional duties and Paraprofessionals emphasizing targeted support for diverse learner needs.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Teaching assistants typically require at least a high school diploma, with many positions favoring candidates who hold an associate's or bachelor's degree in education or a related field, while paraprofessionals often need specialized certifications such as the ParaPro Assessment or state-specific paraprofessional licenses. Both roles may require background checks and ongoing professional development, but teaching assistants frequently undergo more extensive training in instructional strategies to support classroom teachers. Certification requirements vary by state and institution, emphasizing practical skills for paraprofessionals and educational theory for teaching assistants.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Teaching assistants require strong instructional skills, classroom management abilities, and knowledge of educational technology to support lesson delivery effectively. Paraprofessionals must demonstrate competencies in student supervision, basic academic support, and adapting materials to meet diverse learning needs. Both roles benefit from strong communication skills, patience, and collaboration with teachers and students to foster a productive learning environment.
Classroom Support Functions
Teaching assistants primarily focus on supporting classroom instruction by aiding teachers with lesson preparation, managing student behavior, and providing one-on-one or small group tutoring to enhance learning outcomes. Paraprofessionals often undertake similar classroom support tasks but may also handle administrative duties, assist with special education services, and facilitate communication between teachers, students, and parents. Both roles are essential for creating an effective learning environment, yet teaching assistants generally have more direct involvement in instructional activities compared to paraprofessionals.
Collaboration with Teachers and Staff
Teaching assistants work closely with teachers to support instructional delivery and classroom management, often participating directly in lesson planning and student assessments. Paraprofessionals collaborate with teachers and school staff by providing targeted support to students, especially those with special needs, facilitating communication between educators and families. Both roles enhance the educational environment through teamwork, but teaching assistants typically have more direct involvement in academic instruction.
Impact on Student Learning
Teaching assistants provide direct instructional support by reinforcing lessons and offering personalized help, which enhances student comprehension and engagement. Paraprofessionals focus on non-instructional support such as classroom management and assisting students with special needs, creating a conducive learning environment. Both roles contribute to improved academic outcomes by addressing diverse student needs and fostering inclusive educational settings.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Teaching assistants often have more direct instructional roles, enabling them to develop specialized skills that support advancement into lead teaching positions or educational coordination roles. Paraprofessionals typically focus on providing classroom support and may pursue career growth by obtaining additional certifications or degrees to transition into teaching or specialized support roles. Both positions offer pathways for professional development, but teaching assistants generally experience faster career progression due to their closer involvement in instructional delivery and curriculum implementation.
Work Environment and Settings
Teaching assistants typically work in traditional classroom settings alongside licensed teachers, providing direct instructional support to students. Paraprofessionals often have more diverse work environments, including special education classrooms, resource rooms, and student support centers, where they assist with individualized instruction and behavioral interventions. Both roles require collaboration with educators but differ in their scope of responsibilities and specialized settings.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Teaching assistants typically earn higher salaries than paraprofessionals, with averages ranging from $25,000 to $40,000 annually depending on location and experience. Benefits for teaching assistants often include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, whereas paraprofessionals may receive limited or no benefits based on district policies. Salary differences reflect the varying responsibilities and qualifications required for each role in educational settings.
Teaching Assistant vs Paraprofessional Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com