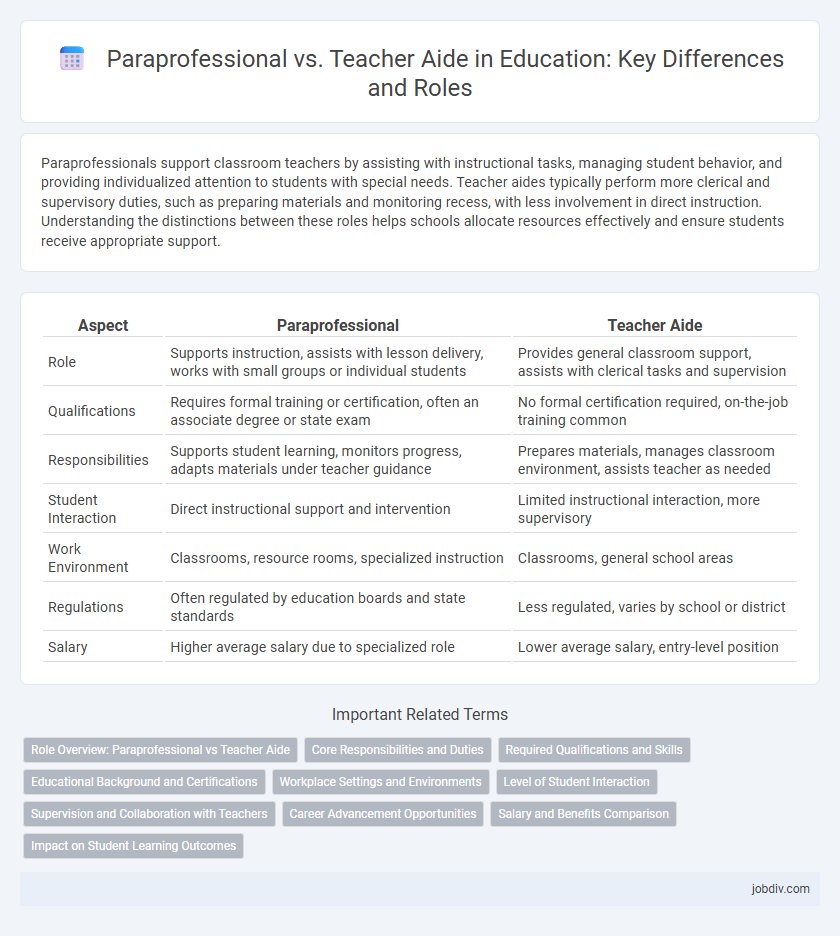
Paraprofessionals support classroom teachers by assisting with instructional tasks, managing student behavior, and providing individualized attention to students with special needs. Teacher aides typically perform more clerical and supervisory duties, such as preparing materials and monitoring recess, with less involvement in direct instruction. Understanding the distinctions between these roles helps schools allocate resources effectively and ensure students receive appropriate support.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Paraprofessional | Teacher Aide |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Supports instruction, assists with lesson delivery, works with small groups or individual students | Provides general classroom support, assists with clerical tasks and supervision |
| Qualifications | Requires formal training or certification, often an associate degree or state exam | No formal certification required, on-the-job training common |
| Responsibilities | Supports student learning, monitors progress, adapts materials under teacher guidance | Prepares materials, manages classroom environment, assists teacher as needed |
| Student Interaction | Direct instructional support and intervention | Limited instructional interaction, more supervisory |
| Work Environment | Classrooms, resource rooms, specialized instruction | Classrooms, general school areas |
| Regulations | Often regulated by education boards and state standards | Less regulated, varies by school or district |
| Salary | Higher average salary due to specialized role | Lower average salary, entry-level position |
Role Overview: Paraprofessional vs Teacher Aide
Paraprofessionals typically possess specialized training and may assist with instructional duties, individual student support, and implementation of educational plans, whereas teacher aides often provide general classroom assistance such as clerical tasks and supervision. Paraprofessionals work closely with certified teachers to deliver targeted educational interventions, especially for students with special needs. Teacher aides focus on maintaining classroom order and supporting the teacher with non-instructional responsibilities that facilitate daily operations.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Paraprofessionals assist certified teachers by providing targeted instructional support, managing classroom activities, and delivering specialized interventions to students with diverse learning needs. Teacher aides primarily handle non-instructional tasks such as supervising students, preparing materials, and maintaining classroom organization to support an effective learning environment. Both roles are essential in enhancing student engagement, but paraprofessionals hold more direct instructional responsibilities aligned with educational objectives.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Paraprofessionals generally require a minimum of an associate degree or a certain number of college credits, along with specialized training in assisting with instructional delivery and student support, while teacher aides often need a high school diploma and some on-the-job training focused on basic classroom assistance. Essential skills for paraprofessionals include knowledge of educational strategies, communication with students and staff, and the ability to implement individualized education plans (IEPs), whereas teacher aides typically focus on routine classroom tasks, student supervision, and basic clerical duties. Both roles demand patience, strong interpersonal skills, and a commitment to supporting student learning in diverse educational environments.
Educational Background and Certifications
Paraprofessionals typically hold at least an associate degree or have completed specialized training programs, while teacher aides may only require a high school diploma or equivalent. Paraprofessionals often possess certification such as a paraeducator license or state-approved credential, enhancing their capability to support instruction. Teacher aides usually receive on-the-job training without formal certification, limiting their instructional responsibilities compared to paraprofessionals.
Workplace Settings and Environments
Paraprofessionals typically work in diverse classroom settings, supporting special education or general education teachers by delivering individualized instruction and assisting with classroom management. Teacher aides often serve in more general support roles within elementary, middle, or high school environments, handling tasks such as preparing materials and supervising students during non-instructional times. Both roles require collaboration with certified teachers but differ in responsibilities based on the specific educational setting and student needs.
Level of Student Interaction
Paraprofessionals engage directly with students by providing individualized instructional support and assisting with classroom activities, enhancing learning outcomes through personalized attention. Teacher aides typically perform supportive roles such as preparing materials and monitoring behavior, with less frequent direct academic interaction. The distinction in student interaction levels impacts the scope of responsibilities and instructional influence each role holds within the educational environment.
Supervision and Collaboration with Teachers
Paraprofessionals often work under the direct supervision of certified teachers, supporting instruction by reinforcing lessons and managing classroom behavior, whereas teacher aides typically provide more general assistance without specialized instructional responsibilities. Collaboration between paraprofessionals and teachers involves active participation in lesson planning and adapting teaching methods to meet diverse student needs. Teacher aides collaborate primarily by helping with clerical tasks and supervising students during non-instructional times, ensuring a smooth classroom environment.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Paraprofessionals often have more defined pathways for career advancement through specialized certifications and additional training in educational strategies, positioning them for roles such as lead paraprofessionals or instructional coordinators. Teacher aides typically have more limited advancement prospects, primarily assisting teachers without formal avenues for professional development or increased responsibilities. Understanding these distinctions helps education professionals plan career growth aligned with their qualifications and goals.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Paraprofessionals typically earn higher salaries than teacher aides, with average annual wages ranging from $30,000 to $45,000 compared to aides' $20,000 to $35,000, reflecting their specialized training and responsibilities. Benefits for paraprofessionals often include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, whereas teacher aides may receive limited or no such employer-sponsored benefits. This salary and benefits gap underscores the greater institutional investment in paraprofessionals due to their role in supporting instructional and classroom management tasks.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Paraprofessionals provide targeted instructional support by reinforcing lessons and assisting with individualized education plans, directly enhancing student comprehension and engagement. Teacher aides perform essential classroom management tasks that create an organized learning environment, indirectly supporting academic achievement by allowing teachers to focus more on instruction. The combined roles of paraprofessionals and teacher aides contribute to improved student learning outcomes through both direct educational support and the facilitation of productive classroom dynamics.
Paraprofessional vs Teacher Aide Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com