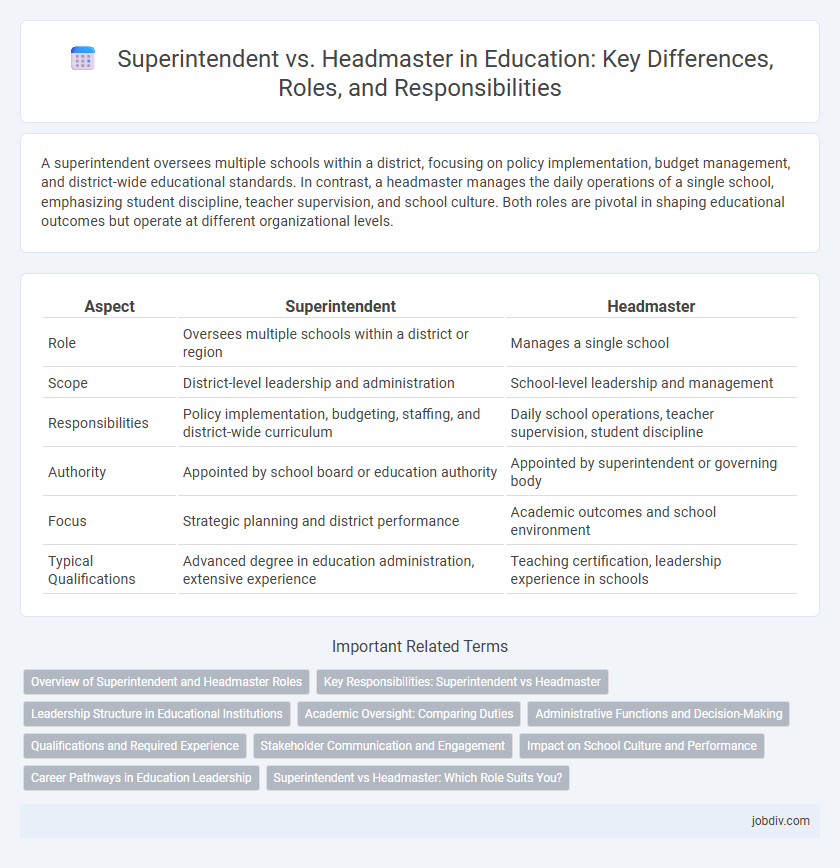
A superintendent oversees multiple schools within a district, focusing on policy implementation, budget management, and district-wide educational standards. In contrast, a headmaster manages the daily operations of a single school, emphasizing student discipline, teacher supervision, and school culture. Both roles are pivotal in shaping educational outcomes but operate at different organizational levels.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Superintendent | Headmaster |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Oversees multiple schools within a district or region | Manages a single school |
| Scope | District-level leadership and administration | School-level leadership and management |
| Responsibilities | Policy implementation, budgeting, staffing, and district-wide curriculum | Daily school operations, teacher supervision, student discipline |
| Authority | Appointed by school board or education authority | Appointed by superintendent or governing body |
| Focus | Strategic planning and district performance | Academic outcomes and school environment |
| Typical Qualifications | Advanced degree in education administration, extensive experience | Teaching certification, leadership experience in schools |
Overview of Superintendent and Headmaster Roles
Superintendents oversee entire school districts, managing multiple schools, budgets, and district-wide policies to ensure educational standards and compliance. Headmasters focus on the daily administration of individual schools, handling student discipline, staff supervision, and school-specific programs. Both roles are critical for educational leadership but operate at different organizational levels within the education system.
Key Responsibilities: Superintendent vs Headmaster
Superintendents oversee entire school districts, managing budgets, curriculum standards, and district-wide policies to ensure cohesive educational quality across multiple schools. Headmasters primarily focus on the day-to-day operations, discipline, staff management, and student performance within a single school. The superintendent's role involves strategic planning and external stakeholder communication, while the headmaster ensures implementation of these strategies at the school level.
Leadership Structure in Educational Institutions
Superintendents oversee multiple schools within a district, providing strategic leadership, policy implementation, and resource allocation to ensure consistent educational quality across all institutions. Headmasters, or principals, manage individual schools, focusing on day-to-day operations, staff supervision, and student discipline to foster a positive learning environment. This hierarchical leadership structure enables efficient governance by aligning district-level objectives with school-level execution and community engagement.
Academic Oversight: Comparing Duties
Superintendents oversee multiple schools within a district, focusing on broad policy implementation, budget management, and district-wide academic standards to ensure consistent educational quality. Headmasters manage the daily academic and administrative operations of a single school, directly supervising teachers, student performance, and school-specific curriculum development. Both roles prioritize academic oversight, yet superintendents operate at a strategic, systemic level while headmasters engage in tactical, school-level leadership.
Administrative Functions and Decision-Making
Superintendents oversee multiple schools within a district, managing budgets, curriculum standards, and district-wide policies, while headmasters focus on day-to-day operations and discipline within a single school. Decision-making authority for superintendents includes strategic planning, resource allocation, and compliance with educational regulations, whereas headmasters handle staff supervision, student affairs, and immediate administrative concerns. Both roles require leadership but differ significantly in scope and impact on educational administration.
Qualifications and Required Experience
Superintendents typically hold advanced degrees such as a Master's or Doctorate in Education Administration and require extensive experience, often 7-10 years in school leadership roles including as principals or headmasters. Headmasters generally need a Bachelor's or Master's degree in Education or related fields, accompanied by 3-5 years of direct classroom teaching and some administrative experience. The superintendent's role demands broader oversight skills in district-wide management, while headmasters focus on school-level leadership and day-to-day operations.
Stakeholder Communication and Engagement
Superintendents manage district-wide stakeholder communication, coordinating with school boards, parents, and community leaders to align educational goals and policies. Headmasters focus on direct engagement with teachers, students, and parents within a single school, fostering day-to-day collaboration and addressing immediate concerns. Effective stakeholder communication by both roles is critical to creating cohesive educational environments and ensuring transparency across all levels.
Impact on School Culture and Performance
Superintendents influence school culture and performance by shaping district-wide policies and resource allocation, fostering consistent standards and strategic goals across multiple schools. Headmasters directly impact individual school environments through daily leadership, teacher motivation, and student engagement, creating a unique and localized school culture. Both roles are essential for driving academic success and nurturing positive, inclusive learning atmospheres within their respective scopes.
Career Pathways in Education Leadership
Career pathways in education leadership often diverge between superintendent and headmaster roles, with superintendents typically overseeing entire school districts and requiring experience in administration, policy development, and community relations. Headmasters usually manage individual schools, focusing on daily operations, staff supervision, and student outcomes, often transitioning from teaching or assistant principal positions. Both positions demand advanced degrees in educational leadership or administration and strong skills in communication, strategic planning, and team management.
Superintendent vs Headmaster: Which Role Suits You?
Superintendents oversee multiple schools within a district, managing budgets, policies, and district-wide initiatives, making strategic decisions that impact diverse educational environments. Headmasters focus on leading a single school, directly managing staff, student discipline, and day-to-day operations to foster a positive learning atmosphere. Choosing between superintendent and headmaster roles depends on your leadership style, preference for broad organizational impact versus hands-on school management, and career ambitions in educational administration.
Superintendent vs Headmaster Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com