A tutor provides personalized instruction tailored to a student's strengths and interests, aiming to enhance overall academic performance and deepen understanding. A remedial educator focuses specifically on addressing learning gaps and skill deficiencies to help students meet grade-level standards. Both roles are crucial in supporting student success but differ in approach and objective.
Table of Comparison
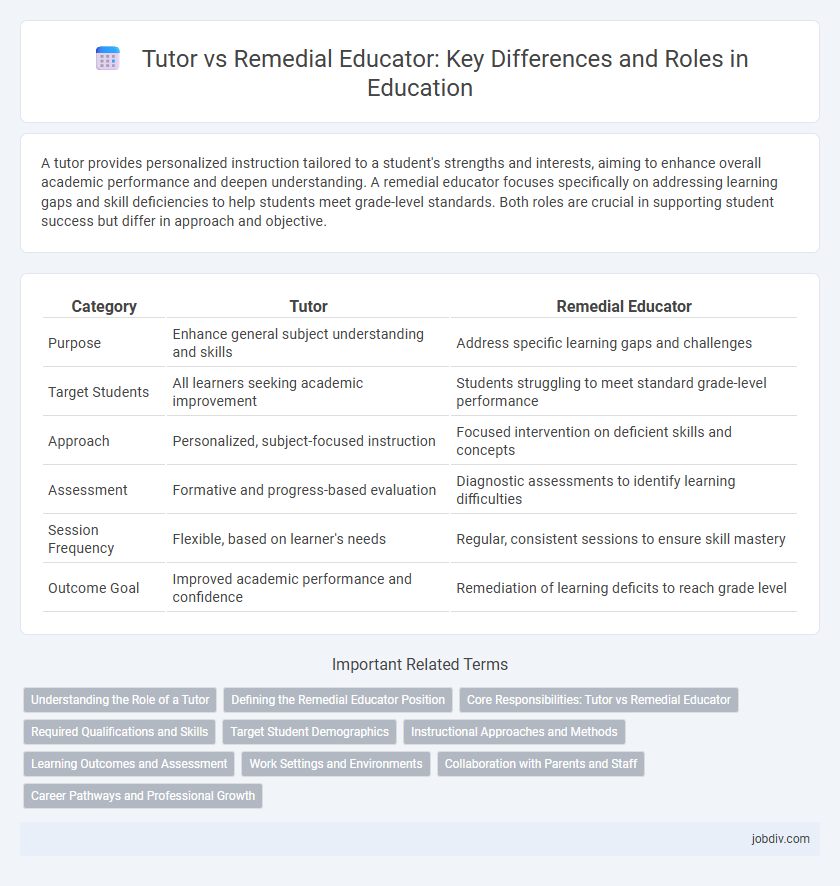
| Category | Tutor | Remedial Educator |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance general subject understanding and skills | Address specific learning gaps and challenges |
| Target Students | All learners seeking academic improvement | Students struggling to meet standard grade-level performance |
| Approach | Personalized, subject-focused instruction | Focused intervention on deficient skills and concepts |
| Assessment | Formative and progress-based evaluation | Diagnostic assessments to identify learning difficulties |
| Session Frequency | Flexible, based on learner's needs | Regular, consistent sessions to ensure skill mastery |
| Outcome Goal | Improved academic performance and confidence | Remediation of learning deficits to reach grade level |
Understanding the Role of a Tutor
A tutor provides personalized academic support by addressing specific subject challenges and enhancing students' overall learning skills, often working outside of standard classroom instruction. Unlike remedial educators who focus primarily on helping students catch up to grade-level competencies through targeted interventions, tutors tailor their approach to individual learning styles and goals. The role of a tutor emphasizes fostering independent study habits and boosting confidence to achieve academic success.
Defining the Remedial Educator Position
A remedial educator specializes in identifying and addressing learning gaps that hinder student progress, employing targeted strategies tailored to individual needs. Unlike tutors who often reinforce existing knowledge, remedial educators focus on foundational skills in subjects like reading, math, and language arts to ensure students achieve grade-level competency. This role requires expertise in diagnostic assessment and customized intervention plans to support diverse learners effectively.
Core Responsibilities: Tutor vs Remedial Educator
Tutors primarily focus on reinforcing subject knowledge, enhancing study skills, and providing personalized academic support to improve overall student performance. Remedial educators target specific learning deficits by implementing tailored interventions designed to address gaps in foundational skills such as reading, writing, and mathematics. Both roles aim to improve student outcomes, but tutors emphasize enrichment while remedial educators concentrate on skill recovery and remediation.
Required Qualifications and Skills
A tutor typically requires subject-specific expertise, strong communication skills, and often a high school diploma or a bachelor's degree in the relevant field. A remedial educator must have specialized training in learning disabilities, educational psychology, or special education, often holding certifications or degrees such as a master's in special education. Both roles demand patience, adaptability, and the ability to assess individual learner needs to tailor instruction effectively.
Target Student Demographics
Tutors primarily serve students seeking to enhance understanding in specific subjects or accelerate learning, often targeting middle to high school students and college undergraduates. Remedial educators focus on learners who struggle with foundational skills, commonly working with students in elementary or secondary education who require intervention to meet grade-level standards. Both roles address diverse student needs but differ in their approach based on academic proficiency and learning challenges.
Instructional Approaches and Methods
Tutors typically employ personalized, student-centered instructional approaches, adapting lessons to individual learning styles and pacing to enhance understanding and retention. Remedial educators focus on diagnostic assessment to identify learning gaps, then apply targeted interventions and scaffolded instruction to build foundational skills and bring students up to grade level. Both prioritize active engagement but differ in scope, with tutors enhancing overall learning while remedial educators concentrate on addressing specific deficits.
Learning Outcomes and Assessment
Tutors provide personalized instruction targeting specific academic skills, improving learning outcomes through tailored support and ongoing formative assessments that identify student strengths and weaknesses. Remedial educators focus on addressing foundational gaps by using diagnostic assessments to develop intervention strategies, ensuring students meet grade-level competencies. Both roles emphasize continuous evaluation, but tutors often adapt teaching methods to accelerate progress, while remedial educators prioritize mastery of core concepts to prevent further learning delays.
Work Settings and Environments
Tutors typically work in diverse settings such as private homes, online platforms, and educational centers, offering personalized academic support tailored to individual student needs. Remedial educators are often employed within school systems, learning centers, or specialized programs, focusing on addressing learning gaps and helping students achieve grade-level competencies. Both roles require adaptable environments, but remedial educators frequently collaborate with teachers and use structured curricula aligned with school standards.
Collaboration with Parents and Staff
Effective collaboration between tutors and remedial educators with parents and school staff enhances student learning outcomes by ensuring consistent communication and tailored support strategies. Tutors focus on reinforcing curriculum content alongside classroom instruction, while remedial educators address specific learning difficulties through specialized interventions. Regular meetings and shared progress reports between educators and families foster a holistic approach to student development and academic success.
Career Pathways and Professional Growth
Tutors typically follow a flexible career path focused on personalized academic support, often working independently or within tutoring centers, allowing for specialization in subjects or test preparation. Remedial educators usually pursue formal teaching credentials, advancing within school systems to roles such as intervention specialists or special education teachers, emphasizing skill-building for students with learning gaps. Professional growth for tutors involves certifications and niche expertise, while remedial educators benefit from ongoing teacher training and education degree advancements.
Tutor vs Remedial Educator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com