A Learning Specialist provides personalized instruction tailored to students with unique learning needs, focusing on skill development and academic strategies. In contrast, a Resource Teacher supports students by offering supplementary assistance within general education settings, often collaborating with classroom teachers. Both roles are essential for fostering inclusive education and enhancing student achievement.
Table of Comparison
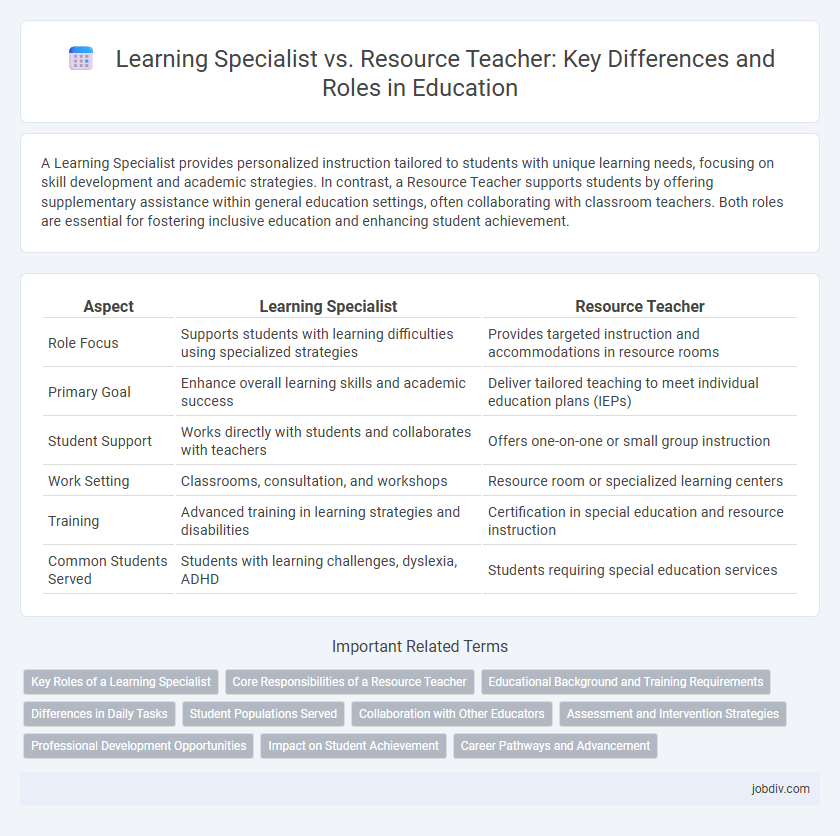
| Aspect | Learning Specialist | Resource Teacher |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Supports students with learning difficulties using specialized strategies | Provides targeted instruction and accommodations in resource rooms |
| Primary Goal | Enhance overall learning skills and academic success | Deliver tailored teaching to meet individual education plans (IEPs) |
| Student Support | Works directly with students and collaborates with teachers | Offers one-on-one or small group instruction |
| Work Setting | Classrooms, consultation, and workshops | Resource room or specialized learning centers |
| Training | Advanced training in learning strategies and disabilities | Certification in special education and resource instruction |
| Common Students Served | Students with learning challenges, dyslexia, ADHD | Students requiring special education services |
Key Roles of a Learning Specialist
A Learning Specialist focuses on personalized instructional strategies to support students with diverse learning needs, utilizing assessments to develop tailored learning plans. Their key roles include collaborating with teachers, parents, and students to enhance academic achievement and social-emotional development. Resource Teachers primarily provide targeted interventions and classroom support, but Learning Specialists emphasize holistic student growth through specialized expertise in learning differences.
Core Responsibilities of a Resource Teacher
Resource Teachers primarily focus on providing targeted academic support and interventions to students with learning difficulties, ensuring they meet grade-level standards. They collaborate with classroom teachers to modify curricula, develop individualized education plans (IEPs), and implement specialized teaching strategies. Their core responsibilities include assessing student progress, facilitating inclusive classroom environments, and coordinating with parents and educational staff to promote student success.
Educational Background and Training Requirements
Learning specialists typically hold advanced degrees in education, special education, or a related field, often requiring certifications such as a Reading Specialist or Learning Disabilities Specialist credential. Resource teachers usually possess a teaching license with specialized training in special education, focusing on individualized instruction for students with diverse learning needs. Both roles demand ongoing professional development to stay current with educational strategies and interventions.
Differences in Daily Tasks
Learning Specialists primarily assess student needs, design individualized learning plans, and provide targeted academic interventions, while Resource Teachers focus on delivering specialized instructional support within the classroom. Learning Specialists spend significant time conducting evaluations and collaborating with psychologists or therapists to tailor strategies. Resource Teachers manage small groups or one-on-one sessions, implement accommodations, and monitor progress on specific subjects or skills.
Student Populations Served
Learning Specialists primarily support students with identified learning disabilities, providing tailored interventions and individualized education plans (IEPs) to address specific academic challenges. Resource Teachers serve a broader range of students, including those with mild to moderate disabilities, offering targeted instruction within general education settings to promote inclusion. Both professionals collaborate closely with teachers and families to adapt curriculum and maximize student success across diverse learning populations.
Collaboration with Other Educators
Learning specialists collaborate closely with classroom teachers to design personalized instructional strategies that address diverse student needs. Resource teachers work alongside general educators by providing targeted support and adapting curricula for students requiring specialized interventions. Both roles emphasize teamwork to enhance student outcomes through shared expertise and coordinated efforts.
Assessment and Intervention Strategies
Learning specialists employ comprehensive assessment techniques such as formative, summative, and diagnostic evaluations to tailor individualized intervention strategies that address diverse learner needs and promote academic growth. Resource teachers utilize standardized assessments and curriculum-based measurements to identify students requiring targeted support, implementing specific interventions aligned with individualized education programs (IEPs). Collaboration between learning specialists and resource teachers ensures continuous monitoring and adaptation of interventions based on student performance data, maximizing educational outcomes.
Professional Development Opportunities
Learning specialists have access to extensive professional development opportunities focused on specialized instructional strategies, assessment techniques, and intervention programs tailored to diverse learner needs. Resource teachers engage in targeted training to enhance curriculum adaptation, collaboration with classroom teachers, and support for individualized education plans (IEPs). Both roles benefit from workshops and certifications that deepen expertise in student-centered instruction and inclusive education practices.
Impact on Student Achievement
Learning Specialists develop tailored interventions and strategies to address specific learning disabilities, significantly improving personalized student outcomes. Resource Teachers provide targeted support within general education settings, enhancing academic progress through direct instruction and collaboration with classroom teachers. Both roles contribute to boosting student achievement by addressing diverse learning needs and promoting inclusive educational environments.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Learning Specialists typically focus on individualized student support, specializing in areas such as special education, literacy intervention, and cognitive development, which offers career advancement opportunities in educational psychology or program coordination. Resource Teachers provide targeted classroom support by collaborating with general education teachers to implement specialized instructional strategies, creating pathways toward roles in curriculum development or instructional leadership. Both career trajectories emphasize professional development and certification, with Learning Specialists often pursuing advanced degrees in educational diagnostics and Resource Teachers enhancing skills in differentiated instruction and inclusive education.
Learning Specialist vs Resource Teacher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com