Educators inspire critical thinking and foster holistic development by engaging students in meaningful learning experiences, while instructors primarily focus on delivering specific content and skills. The role of an educator extends beyond teaching; it emphasizes mentoring, motivating, and adapting methods to diverse learning needs. Instructors ensure foundational knowledge is acquired efficiently, forming the essential groundwork for deeper exploration led by educators.
Table of Comparison
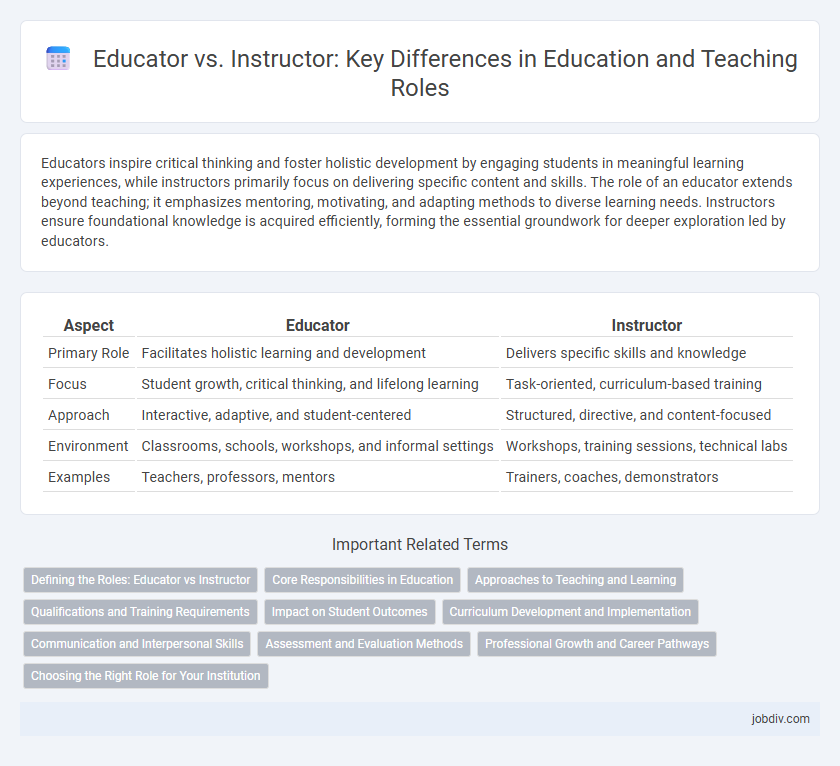
| Aspect | Educator | Instructor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Facilitates holistic learning and development | Delivers specific skills and knowledge |
| Focus | Student growth, critical thinking, and lifelong learning | Task-oriented, curriculum-based training |
| Approach | Interactive, adaptive, and student-centered | Structured, directive, and content-focused |
| Environment | Classrooms, schools, workshops, and informal settings | Workshops, training sessions, technical labs |
| Examples | Teachers, professors, mentors | Trainers, coaches, demonstrators |
Defining the Roles: Educator vs Instructor
An educator designs and facilitates comprehensive learning experiences that foster critical thinking and personal development, emphasizing holistic growth beyond the curriculum. An instructor primarily delivers specific knowledge or skills, focusing on structured content and measurable outcomes within a defined subject area. Understanding the distinction clarifies expectations in teaching effectiveness and learner engagement strategies.
Core Responsibilities in Education
Educators focus on holistic student development by creating inclusive learning environments, designing curricula, and fostering critical thinking skills, while instructors primarily deliver subject-specific knowledge through lectures and assessments. Educators often engage in mentorship and adapt teaching strategies to individual learning needs, whereas instructors emphasize mastery of content and skills within a structured timeframe. Both play crucial roles, but educators typically adopt a broader approach to student growth beyond academic instruction.
Approaches to Teaching and Learning
Educators emphasize holistic development by fostering critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence through student-centered learning approaches, while instructors often focus on delivering specific skills and knowledge using structured, curriculum-based methods. Educators employ collaborative and experiential techniques that encourage active participation, whereas instructors prioritize clear objectives and assessment-driven instruction to ensure mastery of content. The difference in approaches influences how learners engage with material, with educators promoting lifelong learning and instructors ensuring competency in targeted areas.
Qualifications and Training Requirements
Educators typically hold advanced degrees such as a master's or doctorate in education, emphasizing comprehensive pedagogical theory and curriculum development. Instructors often require specific certifications or professional licenses relevant to their subject matter, with training focused on skill proficiency and practical application. The qualifications for educators tend to be broader and more research-oriented, while instructors prioritize hands-on experience and targeted expertise.
Impact on Student Outcomes
Educators foster critical thinking and lifelong learning by creating student-centered environments, which significantly improve academic achievement and personal development. Instructors primarily deliver content and focus on skill acquisition, often resulting in immediate knowledge gains but less emphasis on long-term cognitive growth. Studies show that educator-led approaches correlate with higher student motivation and retention rates, positively impacting overall student outcomes.
Curriculum Development and Implementation
Educators play a crucial role in curriculum development by designing comprehensive learning frameworks that align with educational standards and address diverse student needs. Instructors primarily focus on the implementation of these curricula, delivering content and facilitating classroom activities to ensure effective knowledge transfer. Collaboration between educators and instructors enhances the adaptation and continuous improvement of curriculum for optimal student outcomes.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Educators excel in communication by fostering open dialogue and adapting their messaging to diverse learning styles, enhancing overall student engagement. Instructors focus on clear, concise delivery of specific content, ensuring comprehension through structured explanations and feedback. Strong interpersonal skills enable both roles to build trust and motivate learners, but educators typically emphasize mentorship and emotional support more deeply.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Educators employ diverse assessment and evaluation methods to measure student learning, emphasizing formative assessments, reflective practices, and continuous feedback to foster critical thinking and comprehension. In contrast, instructors often utilize standardized tests, quizzes, and summative evaluations aimed at measuring knowledge retention and performance against specific academic standards. Both roles contribute to a comprehensive understanding of student progress, though educators integrate a broader range of qualitative and quantitative tools to support holistic development.
Professional Growth and Career Pathways
Educators often engage in continuous professional development to broaden their pedagogical skills and advance in leadership roles within academic institutions. Instructors typically focus on subject-specific expertise and practical teaching methods, which can lead to specialized certifications or positions in vocational training. Both career pathways emphasize lifelong learning, but educators tend to pursue broader educational theory and administration, while instructors prioritize applied skill development and direct student engagement.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Institution
Selecting the right role between educator and instructor depends on your institution's goals and student needs. Educators typically focus on holistic development, critical thinking, and fostering a lifelong love for learning, making them ideal for institutions prioritizing comprehensive education. Instructors emphasize skill acquisition and subject mastery, suited for vocational training or specialized courses requiring targeted expertise.
Educator vs Instructor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com