School psychologists specialize in assessing and addressing students' cognitive, emotional, and behavioral issues through psychological testing and interventions. School social workers concentrate on connecting students and families with resources, addressing social and environmental barriers impacting learning and promoting mental health support. Both professionals collaborate to create supportive educational environments, but their approaches and focus areas differ significantly.
Table of Comparison
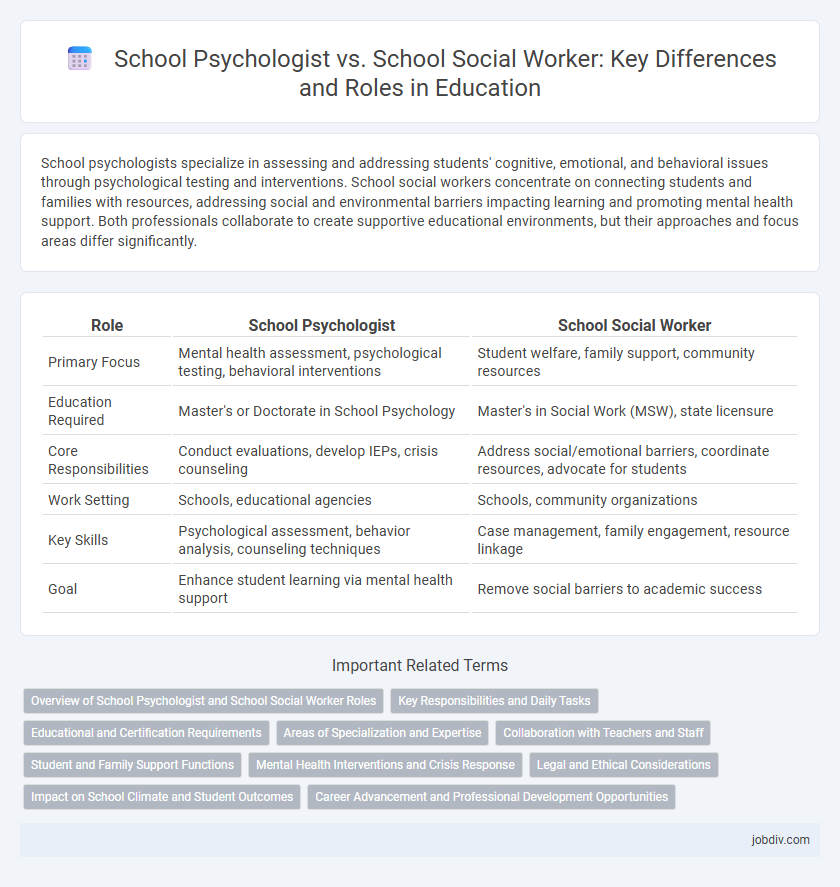
| Role | School Psychologist | School Social Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Mental health assessment, psychological testing, behavioral interventions | Student welfare, family support, community resources |
| Education Required | Master's or Doctorate in School Psychology | Master's in Social Work (MSW), state licensure |
| Core Responsibilities | Conduct evaluations, develop IEPs, crisis counseling | Address social/emotional barriers, coordinate resources, advocate for students |
| Work Setting | Schools, educational agencies | Schools, community organizations |
| Key Skills | Psychological assessment, behavior analysis, counseling techniques | Case management, family engagement, resource linkage |
| Goal | Enhance student learning via mental health support | Remove social barriers to academic success |
Overview of School Psychologist and School Social Worker Roles
School psychologists specialize in assessing and supporting students' cognitive, emotional, and behavioral needs through psychological testing, counseling, and intervention strategies. School social workers focus on connecting students and families with community resources, addressing social and environmental factors affecting academic performance, and providing crisis intervention. Both roles collaborate with educators to create supportive learning environments but differ in their primary methods and areas of expertise.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
School psychologists specialize in assessing student cognitive, emotional, and behavioral needs through psychological testing and intervention planning to support academic success and mental health. School social workers focus on addressing social and environmental barriers, connecting families with resources, and providing counseling to improve student well-being and school attendance. Both roles collaborate with educators and parents but maintain distinct responsibilities: psychologists emphasize evaluation and individualized education programs, while social workers handle crisis intervention and community outreach.
Educational and Certification Requirements
School psychologists typically require a specialist-level degree such as an Educational Specialist (Ed.S.) or a doctoral degree (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) in school psychology, along with state certification or licensure, which often includes a supervised internship. School social workers generally need a master's degree in social work (MSW) with a focus on school or clinical social work, followed by state licensure as a social worker, which may include supervised practice hours and passing a licensing exam. Both professions demand specialized training in child development and educational systems, but school psychologists emphasize psychological assessment and intervention, whereas school social workers concentrate on addressing social and emotional barriers to learning.
Areas of Specialization and Expertise
School psychologists specialize in assessing cognitive, emotional, and social development to support student learning and mental health through psychological testing, behavioral interventions, and crisis management. School social workers focus on addressing environmental and social factors affecting students by connecting families with resources, providing counseling, and coordinating community services. Both professions collaborate to enhance student well-being but differ in their primary approaches, with psychologists emphasizing assessment and intervention and social workers targeting social support and advocacy.
Collaboration with Teachers and Staff
School psychologists collaborate closely with teachers and staff to assess student behavior, develop intervention strategies, and support mental health, ensuring tailored educational plans. School social workers engage with educators to address social, emotional, and family-related challenges affecting student performance and attendance. Both professionals work together to create a holistic support system, enhancing student well-being and academic success through coordinated efforts.
Student and Family Support Functions
School psychologists specialize in assessing student learning and behavioral challenges, providing tailored interventions and counseling to enhance academic performance and emotional well-being. School social workers focus on connecting families with community resources, addressing socio-economic barriers, and advocating for students' social and emotional needs within the school environment. Both professionals collaborate to create supportive, inclusive educational settings that promote student success and family engagement.
Mental Health Interventions and Crisis Response
School psychologists specialize in assessing and addressing students' cognitive, emotional, and behavioral needs through evidence-based mental health interventions and individualized counseling. School social workers focus on connecting students and families with community resources, providing crisis intervention, and supporting socio-emotional development within the educational environment. Both professionals collaborate to enhance mental health services and crisis response strategies, ensuring comprehensive support for student well-being.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
School psychologists operate under strict confidentiality laws such as FERPA and IDEA, ensuring student assessments and interventions comply with federal regulations. School social workers navigate ethical mandates from NASW standards, emphasizing client advocacy, mandated reporting, and collaborative care within legal frameworks. Both professionals must balance confidentiality with mandatory reporting requirements to protect student welfare and uphold legal responsibilities.
Impact on School Climate and Student Outcomes
School psychologists play a critical role in enhancing school climate by conducting assessments, providing mental health interventions, and developing behavior plans that promote a positive learning environment. School social workers address systemic issues affecting students, such as family challenges and social barriers, by connecting them with community resources and fostering supportive relationships. Both professionals contribute significantly to improved student outcomes through collaboration, though school psychologists emphasize individual psychological support while social workers focus on social and environmental factors.
Career Advancement and Professional Development Opportunities
School psychologists often advance through specialized certifications in areas like neuropsychology or forensic psychology, boosting their expertise and earning potential within educational or clinical settings. School social workers can pursue advanced degrees such as MSW or LICSW licenses, enabling roles in administration, policy-making, or clinical supervision. Both professions benefit from ongoing professional development via workshops, conferences, and specialized training in trauma-informed care, behavioral interventions, and mental health assessment tools.
School Psychologist vs School Social Worker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com