The Chancellor oversees the overall administration and strategic direction of a university, acting as the chief executive officer. The Provost serves as the chief academic officer, responsible for managing academic policies, faculty affairs, and curriculum development. Clear distinctions in their roles ensure effective governance and academic excellence within higher education institutions.
Table of Comparison
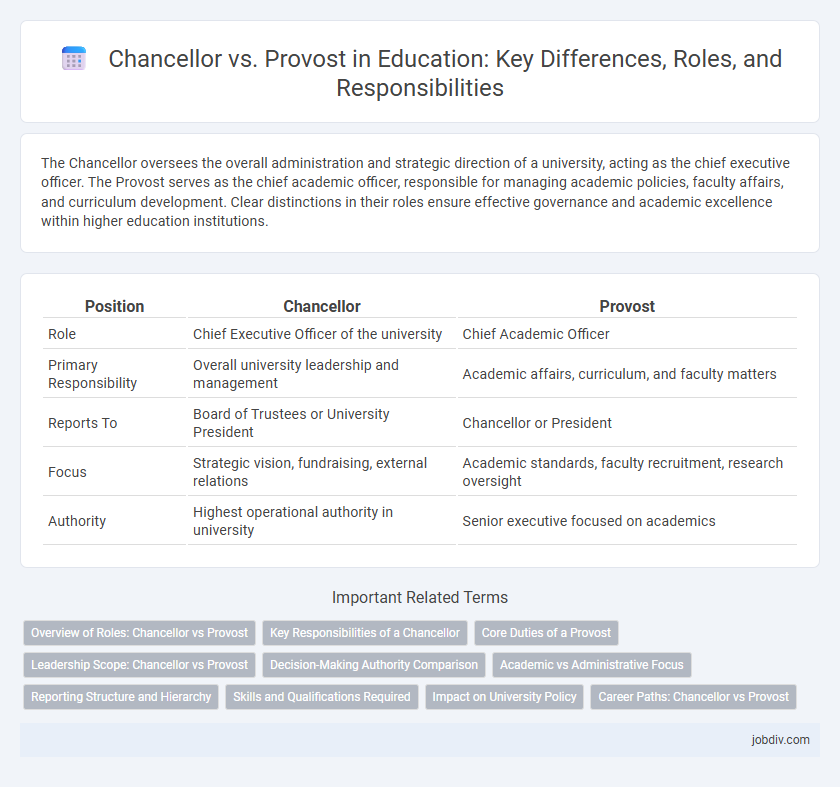
| Position | Chancellor | Provost |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Chief Executive Officer of the university | Chief Academic Officer |
| Primary Responsibility | Overall university leadership and management | Academic affairs, curriculum, and faculty matters |
| Reports To | Board of Trustees or University President | Chancellor or President |
| Focus | Strategic vision, fundraising, external relations | Academic standards, faculty recruitment, research oversight |
| Authority | Highest operational authority in university | Senior executive focused on academics |
Overview of Roles: Chancellor vs Provost
The Chancellor serves as the chief executive officer of a university, overseeing all administrative, academic, and financial operations to set strategic direction and ensure institutional growth. The Provost acts as the chief academic officer, responsible for academic policies, faculty affairs, curriculum development, and research initiatives, directly supporting the university's educational mission. While the Chancellor manages broader institutional goals and external relations, the Provost focuses on maintaining academic excellence and fostering an environment conducive to learning and scholarship.
Key Responsibilities of a Chancellor
The Chancellor serves as the chief executive officer of a university, overseeing all academic and administrative functions to ensure institutional goals are met. Key responsibilities include strategic planning, budget management, external relations, and representing the university at official events. The Chancellor also plays a critical role in fundraising and maintaining partnerships with government agencies and the community.
Core Duties of a Provost
The Provost serves as the chief academic officer responsible for overseeing curriculum development, faculty appointments, and research initiatives within an educational institution. This role ensures academic policies align with the university's mission, promoting quality teaching and scholarship. Unlike the Chancellor who often handles overall institutional strategy and external relations, the Provost focuses primarily on maintaining academic standards and enhancing educational programs.
Leadership Scope: Chancellor vs Provost
The Chancellor oversees the entire university system, including multiple campuses and major administrative functions, embodying broad institutional leadership. The Provost specifically manages academic affairs, shaping curriculum, faculty, and research priorities within the university. This distinction positions the Chancellor as the chief executive officer and the Provost as the chief academic officer in higher education leadership.
Decision-Making Authority Comparison
Chancellors hold the highest decision-making authority in university governance, overseeing strategic direction, resource allocation, and external relations. Provosts typically serve as chief academic officers, making decisions related to curriculum development, faculty affairs, and academic policies. While chancellors focus on broader institutional goals, provosts ensure academic quality and operational efficiency within the educational programs.
Academic vs Administrative Focus
The chancellor typically holds a broader administrative role overseeing the entire university system, including financial and strategic planning aspects. The provost concentrates on academic affairs, managing curriculum development, faculty appointments, and research initiatives to enhance educational quality. This distinction highlights the chancellor's focus on institutional leadership versus the provost's dedication to academic excellence.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchy
The Chancellor typically serves as the chief executive officer of a university system, overseeing multiple campuses and reporting directly to the board of trustees, while the Provost acts as the chief academic officer responsible for academic affairs and reports to the Chancellor. In the organizational hierarchy, the Provost ranks below the Chancellor, managing deans and academic departments to implement educational policies set by the Chancellor. This reporting structure ensures clear governance where strategic decisions flow from the Chancellor to the Provost for execution across the institution's academic units.
Skills and Qualifications Required
Chancellors require strategic leadership skills, extensive experience in higher education administration, and a deep understanding of university governance to effectively oversee multiple campuses or the entire institution. Provosts need strong academic credentials, such as a doctoral degree, combined with expertise in curriculum development, faculty management, and research oversight to guide the institution's academic mission. Both roles demand excellent communication, decision-making abilities, and a commitment to advancing educational excellence.
Impact on University Policy
Chancellors hold the ultimate authority in university governance, shaping broad strategic policies and representing the institution externally to influence funding and legislative decisions. Provosts directly impact academic policy by overseeing curriculum development, faculty appointments, and research priorities, ensuring alignment with institutional goals. Collaborative efforts between Chancellor and Provost ensure coherent policy implementation that drives academic excellence and operational efficiency.
Career Paths: Chancellor vs Provost
Chancellors typically advance through senior administrative roles such as vice chancellor or dean, often possessing extensive experience in academic leadership and strategic institutional management. Provosts usually progress from faculty positions to department chair or dean roles, emphasizing academic affairs, curriculum development, and faculty oversight. Career paths for chancellors emphasize broad university governance and external relations, whereas provosts focus on academic policy and internal academic operations.
Chancellor vs Provost Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com