Curriculum designers develop educational programs and materials tailored to meet learning objectives, ensuring content aligns with academic standards. Instructional coordinators focus on implementing these curricula, training teachers, and evaluating teaching methods to enhance student outcomes. Both roles collaborate closely to create effective learning environments and improve educational quality.
Table of Comparison
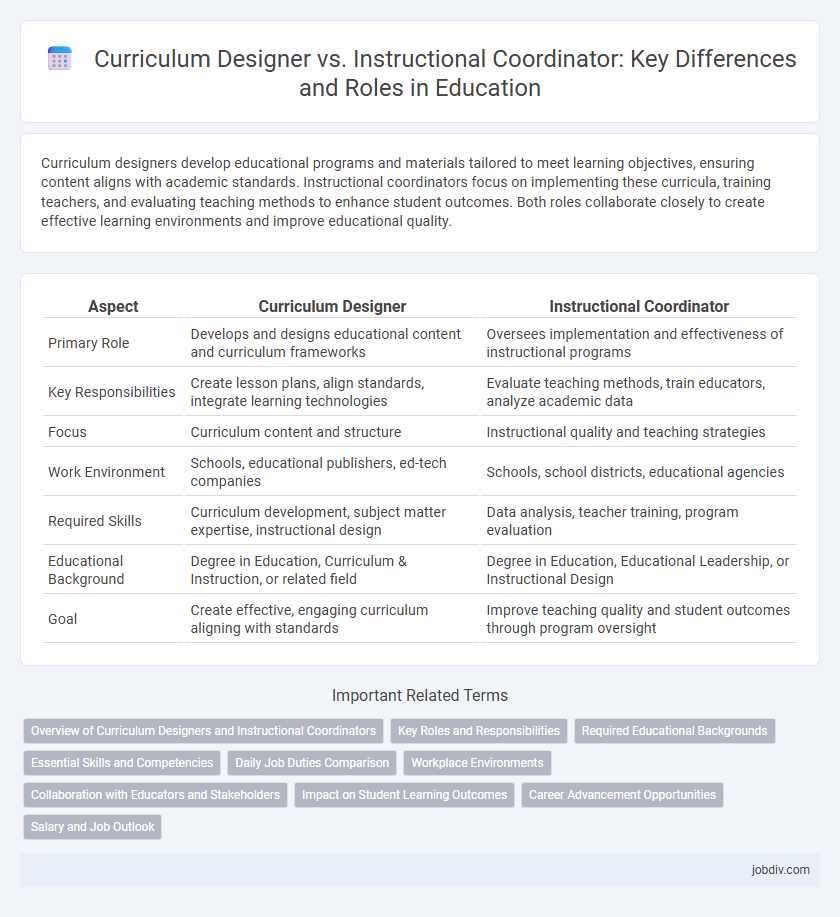
| Aspect | Curriculum Designer | Instructional Coordinator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Develops and designs educational content and curriculum frameworks | Oversees implementation and effectiveness of instructional programs |
| Key Responsibilities | Create lesson plans, align standards, integrate learning technologies | Evaluate teaching methods, train educators, analyze academic data |
| Focus | Curriculum content and structure | Instructional quality and teaching strategies |
| Work Environment | Schools, educational publishers, ed-tech companies | Schools, school districts, educational agencies |
| Required Skills | Curriculum development, subject matter expertise, instructional design | Data analysis, teacher training, program evaluation |
| Educational Background | Degree in Education, Curriculum & Instruction, or related field | Degree in Education, Educational Leadership, or Instructional Design |
| Goal | Create effective, engaging curriculum aligning with standards | Improve teaching quality and student outcomes through program oversight |
Overview of Curriculum Designers and Instructional Coordinators
Curriculum designers develop educational content and materials aligned with learning standards to enhance student outcomes across various grade levels and subjects. Instructional coordinators oversee implementation of curriculum, evaluate teaching methods, and provide professional development to ensure effective instruction and compliance with educational policies. Both roles require collaboration with educators and administrators to optimize instructional strategies and improve academic achievement.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Curriculum Designers develop comprehensive educational frameworks, aligning content with learning standards and integrating innovative teaching strategies to enhance student engagement. Instructional Coordinators evaluate and refine existing curricula through data analysis and teacher feedback, ensuring instructional methods meet academic goals and comply with regulatory requirements. Both roles collaborate closely with educators to implement effective training and improve overall educational quality.
Required Educational Backgrounds
Curriculum designers typically require a bachelor's degree in education, curriculum development, or a related field, often complemented by a master's degree in education or instructional design to enhance their expertise. Instructional coordinators generally need at least a master's degree in education, curriculum and instruction, or educational leadership, reflecting their role in overseeing educational standards and teacher training. Both roles benefit from certifications in curriculum design or educational technology to stay current with evolving instructional strategies.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Curriculum designers excel in creative content development, aligning educational materials with academic standards, while instructional coordinators focus on evaluating teaching methods and implementing effective instructional strategies. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, collaboration, and deep knowledge of educational theories, yet curriculum designers prioritize innovation in lesson planning, whereas instructional coordinators emphasize assessment and teacher training expertise. Mastery of curriculum standards, data-driven decision-making, and technology integration are critical for success in these education roles.
Daily Job Duties Comparison
Curriculum Designers develop and organize educational content, create lesson plans, and align materials with academic standards to enhance learning outcomes. Instructional Coordinators analyze teaching methods, evaluate curriculum effectiveness, and provide professional development to educators for improved instructional practices. Both roles require collaboration with teachers and administrators, but Curriculum Designers focus more on content creation while Instructional Coordinators emphasize implementation and assessment.
Workplace Environments
Curriculum Designers typically work in schools, educational consultancies, and publishing companies where they create instructional materials and plan course content. Instructional Coordinators are often employed by school districts, government agencies, or higher education institutions, focusing on implementing educational standards and teacher training programs. Both roles require collaboration with educators, but Curriculum Designers emphasize content development while Instructional Coordinators prioritize instructional quality and policy execution.
Collaboration with Educators and Stakeholders
Curriculum Designers collaborate closely with educators to develop cohesive learning materials that align with educational standards and student needs, ensuring curriculum relevance and effectiveness. Instructional Coordinators engage with teachers, school administrators, and stakeholders to implement and evaluate instructional programs, fostering continuous improvement through data-driven feedback. Both roles emphasize partnership with educational teams to promote innovative teaching strategies and enhance student achievement.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Curriculum designers develop comprehensive educational programs that align with academic standards and address diverse learning needs, directly influencing student engagement and achievement. Instructional coordinators implement these curricula and provide teacher training, ensuring effective instructional strategies that enhance classroom performance. Together, their roles synergize to improve student learning outcomes by fostering coherent, standards-based, and research-driven instruction.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Curriculum designers and instructional coordinators both play critical roles in shaping educational programs, with curriculum designers focusing on developing content and instructional coordinators overseeing implementation and training. Career advancement for curriculum designers often leads to senior design positions, educational consultancy, or roles in academic publishing, while instructional coordinators may progress to district-level administration, director of curriculum roles, or education policy advising. Both paths offer opportunities for specialization, leadership, and influence on educational standards and teacher development.
Salary and Job Outlook
Curriculum Designers earn an average annual salary of $68,000, with a projected job growth rate of 6% through 2030, reflecting steady demand in education sectors. Instructional Coordinators typically make around $66,000 per year, but their employment is expected to grow faster at 7%, driven by increasing emphasis on educational standards and teacher training. Both roles require expertise in curriculum development and instructional strategies, yet the slight salary difference is offset by the stronger job outlook favoring Instructional Coordinators.
Curriculum Designer vs Instructional Coordinator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com