A Pedagogy Coordinator oversees curriculum development and teaching strategies tailored to children and adolescents, emphasizing structured guidance and foundational skill-building. An Andragogy Coordinator specializes in adult education, focusing on self-directed learning, practical application, and leveraging learners' experiences to enhance engagement. Both roles require adapting instructional methods to suit the distinct learning needs and motivations of their respective audiences.
Table of Comparison
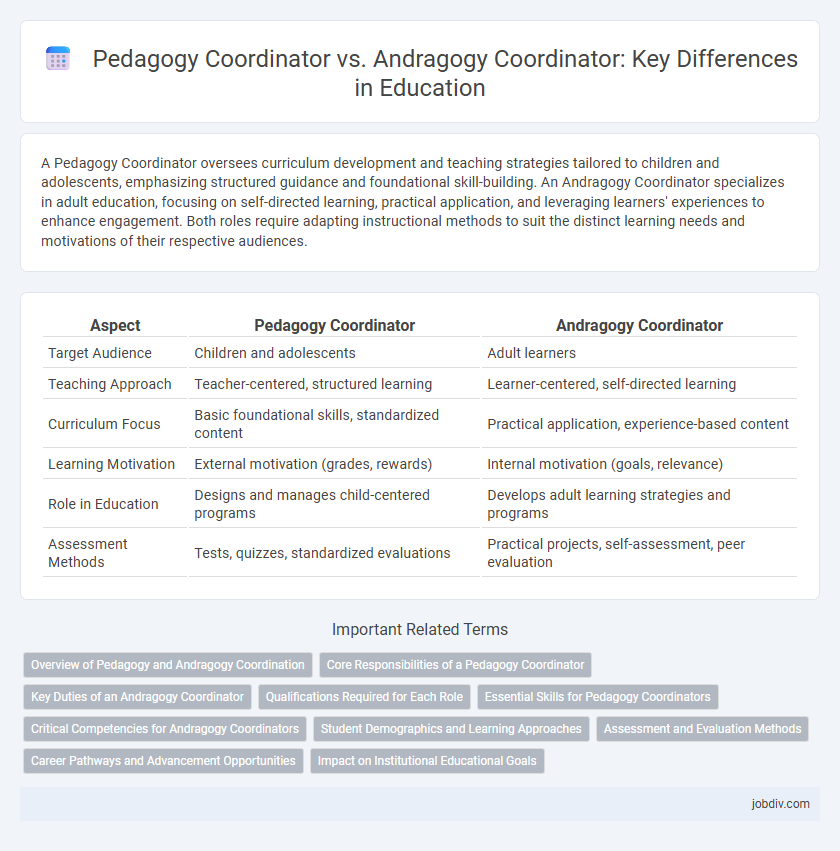
| Aspect | Pedagogy Coordinator | Andragogy Coordinator |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Children and adolescents | Adult learners |
| Teaching Approach | Teacher-centered, structured learning | Learner-centered, self-directed learning |
| Curriculum Focus | Basic foundational skills, standardized content | Practical application, experience-based content |
| Learning Motivation | External motivation (grades, rewards) | Internal motivation (goals, relevance) |
| Role in Education | Designs and manages child-centered programs | Develops adult learning strategies and programs |
| Assessment Methods | Tests, quizzes, standardized evaluations | Practical projects, self-assessment, peer evaluation |
Overview of Pedagogy and Andragogy Coordination
Pedagogy Coordination emphasizes structured curriculum development, learner assessment, and teaching strategies tailored for children's cognitive and social development stages. Andragogy Coordination focuses on adult learning principles, promoting self-directed learning, practical applications, and leveraging learners' experiences to enhance engagement and retention. Both roles require expertise in educational theory, curriculum design, and learner motivation, but they address distinct developmental needs and learning environments.
Core Responsibilities of a Pedagogy Coordinator
A Pedagogy Coordinator primarily oversees curriculum development, instructional strategies, and teacher training tailored to children and adolescents, ensuring age-appropriate learning environments and methodologies. They implement educational standards, assess student progress, and support educators in enhancing classroom engagement and effectiveness. Their role contrasts with Andragogy Coordinators, who focus on adult education principles and learner autonomy in training programs.
Key Duties of an Andragogy Coordinator
An Andragogy Coordinator specializes in adult learning methodologies, designing curricula that emphasize self-directed and experiential learning tailored for adult learners. Key duties include facilitating professional development workshops, assessing adult learners' needs through targeted evaluations, and integrating technology to enhance interactive learning experiences. This role also involves collaborating with instructors to implement effective teaching strategies that promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills among adult students.
Qualifications Required for Each Role
Pedagogy Coordinators typically require a background in early childhood or K-12 education, including a bachelor's or master's degree in education, along with certifications in curriculum development and classroom management. Andragogy Coordinators often hold advanced degrees in adult education, instructional design, or workforce training, complemented by experience with adult learning theories and professional development programs. Both roles demand strong organizational skills, but the specific qualifications align closely with the learner demographics they serve--children and adolescents for pedagogy, adults for andragogy.
Essential Skills for Pedagogy Coordinators
Pedagogy Coordinators require expertise in curriculum design tailored to child development theories, strong classroom management skills, and proficiency in formative assessment techniques to enhance student learning outcomes. Mastery of differentiated instruction and collaboration with teachers for early learner engagement are crucial for effective program implementation. These coordinators also excel in fostering environments that support cognitive and social growth aligned with educational standards for children and adolescents.
Critical Competencies for Andragogy Coordinators
Andragogy Coordinators must demonstrate critical competencies such as facilitation of adult learning theories, integrating experiential learning techniques, and fostering self-directed learning environments tailored to adult learners. These coordinators emphasize collaborative approaches, recognizing learners' prior experiences and promoting practical application to enhance workforce readiness. Unlike Pedagogy Coordinators who focus on traditional child-centered education models, Andragogy Coordinators prioritize adaptability, motivation, and continuous professional development for mature students.
Student Demographics and Learning Approaches
Pedagogy Coordinators primarily design curricula for children and adolescents, emphasizing structured, teacher-led instruction to accommodate younger students' developmental stages. Andragogy Coordinators focus on adult learners, implementing self-directed, experience-based learning strategies tailored to mature students with diverse backgrounds. Understanding the distinct student demographics enables each coordinator to optimize learning approaches that enhance educational outcomes.
Assessment and Evaluation Methods
Pedagogy Coordinators emphasize formative and summative assessments tailored to children's cognitive and developmental stages, incorporating standardized tests, quizzes, and performance tasks to monitor and enhance learning outcomes. Andragogy Coordinators prioritize self-assessment, peer evaluation, and practical project-based assessments that leverage adult learners' life experiences and foster critical reflection and autonomous learning. Both roles utilize data-driven evaluation methods, but Pedagogy focuses on structured measurement of skill acquisition, while Andragogy centers on applying knowledge in real-world contexts and improving professional competencies.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Pedagogy Coordinators typically oversee curriculum development and instructional strategies for K-12 education, positioning themselves for advancement into school administration or educational consultancy roles. Andragogy Coordinators focus on adult learning programs, often progressing toward leadership positions within corporate training, higher education administration, or workforce development organizations. Both career pathways offer opportunities to influence educational policy, program design, and professional development, with specialization guiding the sector and advancement trajectory.
Impact on Institutional Educational Goals
A Pedagogy Coordinator designs curriculum and instructional strategies primarily for children and adolescents, directly influencing foundational academic achievement and standardized testing outcomes, which align with institutional goals for student proficiency and retention rates. An Andragogy Coordinator develops adult learning programs emphasizing self-directed and experiential learning, thereby enhancing workforce readiness, professional development, and lifelong learning initiatives that support institutional goals for continuing education and community engagement. Both roles are integral to achieving comprehensive educational objectives by addressing diverse learner needs and optimizing teaching methodologies across age groups.
Pedagogy Coordinator vs Andragogy Coordinator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com