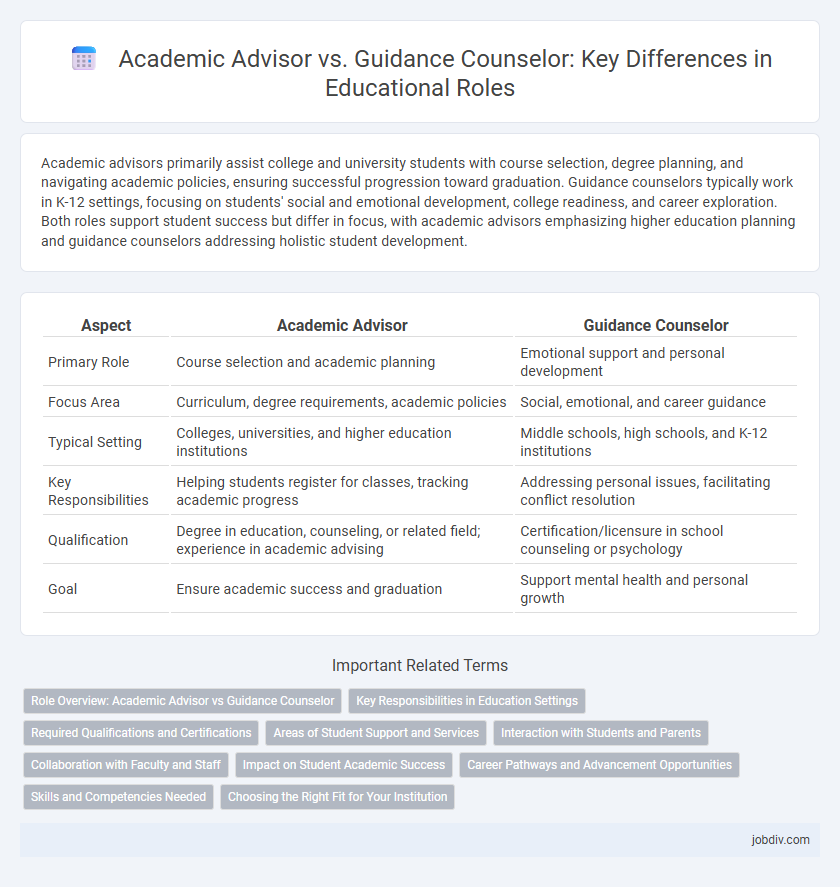
Academic advisors primarily assist college and university students with course selection, degree planning, and navigating academic policies, ensuring successful progression toward graduation. Guidance counselors typically work in K-12 settings, focusing on students' social and emotional development, college readiness, and career exploration. Both roles support student success but differ in focus, with academic advisors emphasizing higher education planning and guidance counselors addressing holistic student development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Academic Advisor | Guidance Counselor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Course selection and academic planning | Emotional support and personal development |
| Focus Area | Curriculum, degree requirements, academic policies | Social, emotional, and career guidance |
| Typical Setting | Colleges, universities, and higher education institutions | Middle schools, high schools, and K-12 institutions |
| Key Responsibilities | Helping students register for classes, tracking academic progress | Addressing personal issues, facilitating conflict resolution |
| Qualification | Degree in education, counseling, or related field; experience in academic advising | Certification/licensure in school counseling or psychology |
| Goal | Ensure academic success and graduation | Support mental health and personal growth |
Role Overview: Academic Advisor vs Guidance Counselor
Academic advisors primarily focus on course selection, degree requirements, and academic progress monitoring to help students achieve their educational goals efficiently. Guidance counselors provide broader support encompassing personal development, social-emotional well-being, and career planning alongside academic guidance. Both roles collaborate to enhance student success, but academic advisors emphasize curriculum navigation while guidance counselors address holistic student needs.
Key Responsibilities in Education Settings
Academic advisors primarily focus on course selection, degree planning, and academic progress to ensure students meet graduation requirements. Guidance counselors address broader aspects including social-emotional support, career development, and personal issues affecting student well-being. Both roles collaborate to provide comprehensive support, but academic advisors emphasize educational pathways while guidance counselors prioritize holistic student development.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Academic advisors typically need a master's degree in higher education, counseling, or a related field, along with certification such as the National Academic Advising Association's Certificate in Academic Advising. Guidance counselors require a master's degree in school counseling or counseling psychology, plus state licensure and certifications like the National Certified Counselor (NCC) credential. Both roles emphasize expertise in student development theories, but guidance counselors must meet stricter licensure standards due to their broader mental health responsibilities.
Areas of Student Support and Services
Academic advisors focus on course selection, academic planning, and degree requirements to ensure students meet graduation criteria efficiently. Guidance counselors provide comprehensive support, including personal, social, and emotional counseling, helping students navigate challenges beyond academics. Both roles collaborate to enhance student success through tailored advising and addressing diverse student needs.
Interaction with Students and Parents
Academic advisors primarily engage with students to develop course plans, monitor academic progress, and provide career-related guidance, fostering a personalized educational experience. Guidance counselors interact with both students and parents to address emotional, social, and behavioral issues, facilitating comprehensive support and communication. This collaborative interaction ensures alignment between academic goals and personal development, enhancing overall student success.
Collaboration with Faculty and Staff
Academic advisors collaborate closely with faculty and staff to create personalized student success plans by integrating course requirements with individual academic goals. Guidance counselors work alongside teachers and administrators to address students' social, emotional, and behavioral needs, ensuring a supportive learning environment. Both roles are essential in fostering interdisciplinary communication that enhances student development and retention rates.
Impact on Student Academic Success
Academic advisors play a crucial role in student academic success by helping students select appropriate courses, create degree plans, and monitor academic progress to ensure timely graduation. Guidance counselors support students' overall well-being by addressing social, emotional, and career-related challenges that can affect academic performance. Both roles collaboratively enhance student outcomes through tailored support and resource referrals, improving retention and completion rates.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Academic advisors specialize in aligning students' course selections with their chosen degree programs, ensuring a clear academic pathway toward graduation and subsequent career opportunities. Guidance counselors provide holistic support, including emotional and social development, while also offering career assessments to help students explore and prepare for diverse career pathways. Both roles contribute to student success, but academic advisors focus more on educational progression whereas guidance counselors emphasize broader personal and career development.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Academic advisors require strong organizational skills, proficiency in academic planning, and the ability to interpret curriculum requirements to guide students effectively. Guidance counselors must excel in interpersonal communication, emotional intelligence, and crisis intervention to support students' mental health and personal development. Both roles demand problem-solving abilities and a deep understanding of educational policies to foster student success.
Choosing the Right Fit for Your Institution
Academic advisors specialize in course planning, degree requirements, and academic progress tracking, making them essential for institutions prioritizing student academic success. Guidance counselors provide broader support, including emotional well-being, career counseling, and personal development, aligning with schools focused on holistic student growth. Selecting the right fit depends on your institution's primary goals--academic achievement or comprehensive student support.
Academic Advisor vs Guidance Counselor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com