Instructional coordinators focus on developing and implementing effective teaching strategies and training programs to enhance classroom instruction. Curriculum specialists design, evaluate, and refine educational content to ensure alignment with academic standards and student learning goals. Both roles collaborate to improve educational outcomes but emphasize different aspects of the teaching and learning process.
Table of Comparison
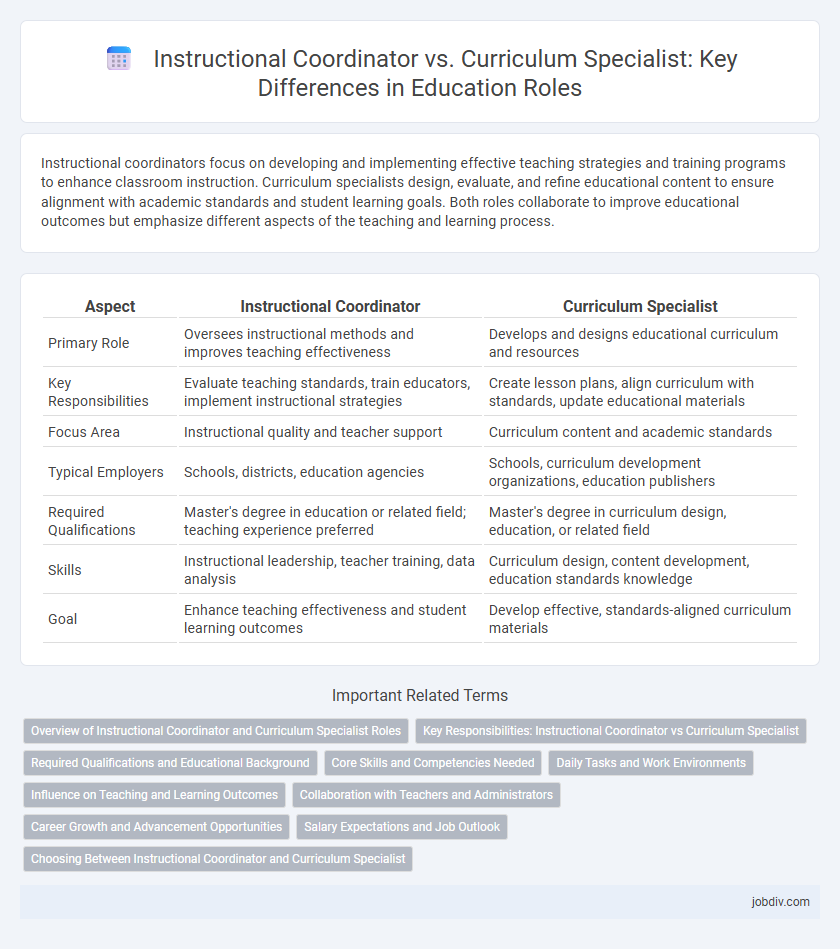
| Aspect | Instructional Coordinator | Curriculum Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees instructional methods and improves teaching effectiveness | Develops and designs educational curriculum and resources |
| Key Responsibilities | Evaluate teaching standards, train educators, implement instructional strategies | Create lesson plans, align curriculum with standards, update educational materials |
| Focus Area | Instructional quality and teacher support | Curriculum content and academic standards |
| Typical Employers | Schools, districts, education agencies | Schools, curriculum development organizations, education publishers |
| Required Qualifications | Master's degree in education or related field; teaching experience preferred | Master's degree in curriculum design, education, or related field |
| Skills | Instructional leadership, teacher training, data analysis | Curriculum design, content development, education standards knowledge |
| Goal | Enhance teaching effectiveness and student learning outcomes | Develop effective, standards-aligned curriculum materials |
Overview of Instructional Coordinator and Curriculum Specialist Roles
Instructional Coordinators analyze and develop academic programs, ensuring alignment with educational standards and teacher training needs. Curriculum Specialists focus on designing, evaluating, and improving instructional materials to support specific subject areas and learning objectives. Both roles collaborate to enhance educational effectiveness but emphasize different aspects of curriculum implementation and teacher support.
Key Responsibilities: Instructional Coordinator vs Curriculum Specialist
Instructional Coordinators analyze teaching standards and evaluate instructional materials to improve educational outcomes, focusing on staff training and implementing instructional strategies. Curriculum Specialists design, develop, and revise educational content and assessment tools aligned with academic standards to ensure cohesive curriculum delivery. Both roles collaborate with educators to enhance student learning but emphasize different aspects: coordinators on instructional practices and specialists on curriculum development.
Required Qualifications and Educational Background
Instructional Coordinators typically require a master's degree in education, curriculum and instruction, or educational leadership, along with experience in teaching or administrative roles. Curriculum Specialists often hold a bachelor's or master's degree in education, curriculum design, or a related field and possess strong knowledge of instructional strategies and learning standards. Both roles benefit from certifications in curriculum development or instructional design to ensure effective educational program implementation.
Core Skills and Competencies Needed
Instructional Coordinators require expertise in educational assessment, data analysis, and professional development to effectively implement and evaluate teaching strategies. Curriculum Specialists must possess strong skills in curriculum design, knowledge of state standards, and the ability to align learning objectives with instructional materials. Both roles demand proficiency in collaboration, communication, and technology integration to enhance student learning outcomes.
Daily Tasks and Work Environments
Instructional Coordinators primarily analyze and implement educational programs by training teachers and evaluating curriculum effectiveness within schools or district offices. Curriculum Specialists focus on designing, refining, and aligning instructional materials with academic standards, often collaborating with educators and administrators in school settings or education agencies. Both roles require data-driven decision-making, but Instructional Coordinators emphasize professional development while Curriculum Specialists concentrate on content development and alignment.
Influence on Teaching and Learning Outcomes
Instructional Coordinators analyze teaching methods and curriculum effectiveness to improve student achievement and align instructional materials with state standards. Curriculum Specialists design and evaluate curricula, ensuring content relevance and coherence to foster deeper understanding and skills development among learners. Both roles directly impact teaching quality and learning outcomes through strategic planning and targeted professional development for educators.
Collaboration with Teachers and Administrators
Instructional Coordinators work closely with teachers and administrators to design and implement effective teaching strategies, ensuring alignment with educational standards and school goals. Curriculum Specialists collaborate with educators to develop, evaluate, and refine curriculum materials, fostering a cohesive learning experience across grade levels and subjects. Both roles emphasize partnership and communication to enhance instructional quality and student achievement.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Instructional Coordinators typically experience career growth by advancing into roles such as Director of Curriculum or Education Program Manager, leveraging their skills in teacher training and instructional design. Curriculum Specialists can progress by specializing further in subject matter expertise or moving into academic consultant positions, which allows for influence over educational standards and policy development. Both career paths offer advancement opportunities in educational leadership, with Instructional Coordinators often taking broader administrative roles and Curriculum Specialists focusing on curriculum innovation and alignment with state or national standards.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Instructional Coordinators typically earn an average salary of $66,000 per year, with a projected job growth rate of 7% through 2031, reflecting steady demand in educational institutions. Curriculum Specialists often command salaries ranging from $55,000 to $75,000 annually, depending on experience and location, and benefit from a positive employment outlook driven by ongoing curriculum development needs. Both roles require expertise in educational strategies, yet Instructional Coordinators may have broader responsibilities overseeing staff training, which can influence salary variations and career advancement opportunities.
Choosing Between Instructional Coordinator and Curriculum Specialist
Choosing between an Instructional Coordinator and a Curriculum Specialist depends on the specific educational goals and institutional needs. Instructional Coordinators typically focus on implementing teaching standards, analyzing student performance data, and training educators, while Curriculum Specialists develop and refine curriculum content aligned with academic standards and learning objectives. Evaluating whether the priority is on professional development and instructional improvement or curriculum design and alignment will guide the decision effectively.
Instructional Coordinator vs Curriculum Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com