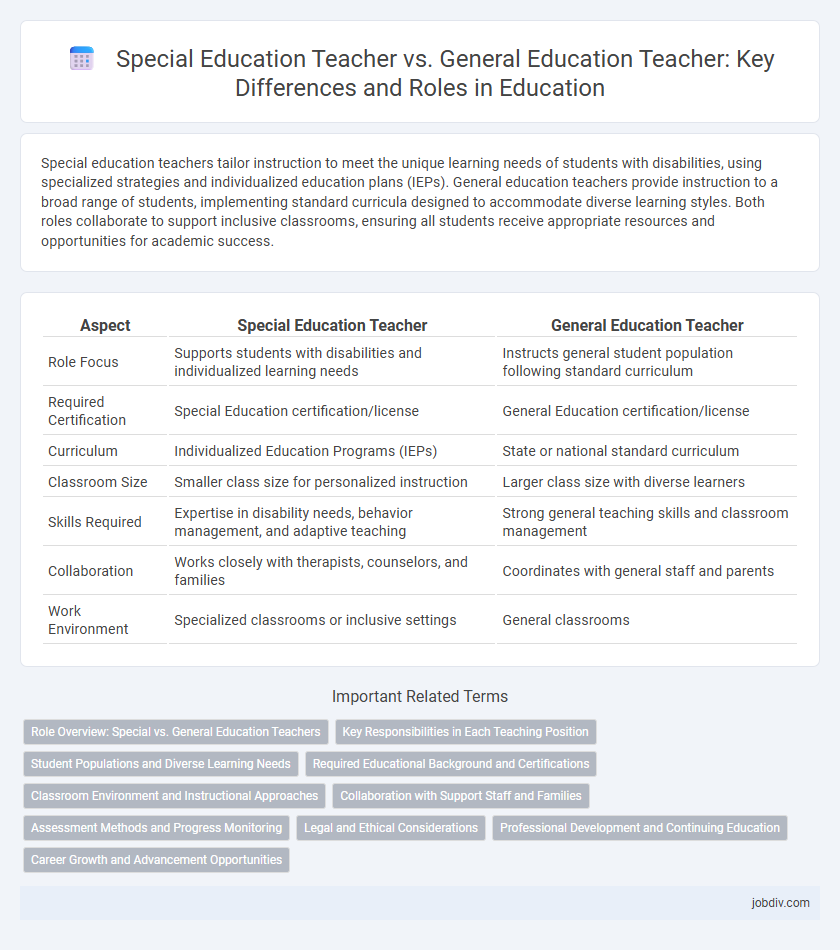
Special education teachers tailor instruction to meet the unique learning needs of students with disabilities, using specialized strategies and individualized education plans (IEPs). General education teachers provide instruction to a broad range of students, implementing standard curricula designed to accommodate diverse learning styles. Both roles collaborate to support inclusive classrooms, ensuring all students receive appropriate resources and opportunities for academic success.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Special Education Teacher | General Education Teacher |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Supports students with disabilities and individualized learning needs | Instructs general student population following standard curriculum |
| Required Certification | Special Education certification/license | General Education certification/license |
| Curriculum | Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) | State or national standard curriculum |
| Classroom Size | Smaller class size for personalized instruction | Larger class size with diverse learners |
| Skills Required | Expertise in disability needs, behavior management, and adaptive teaching | Strong general teaching skills and classroom management |
| Collaboration | Works closely with therapists, counselors, and families | Coordinates with general staff and parents |
| Work Environment | Specialized classrooms or inclusive settings | General classrooms |
Role Overview: Special vs. General Education Teachers
Special education teachers design individualized learning plans and adapt instructional methods to support students with disabilities, ensuring compliance with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and legal mandates. General education teachers deliver standardized curriculum to diverse classrooms, focusing on grade-level academic standards and facilitating inclusive learning environments. Both roles require collaboration with parents, specialists, and school administrators to promote student success, but special education teachers typically engage in more specialized assessments and behavioral interventions.
Key Responsibilities in Each Teaching Position
Special Education Teachers develop individualized education programs (IEPs) tailored to students with disabilities, employing specialized instructional strategies and collaborating with support staff to address unique learning needs. General Education Teachers design and implement grade-level curriculum, manage classroom behavior, and assess student progress across diverse subjects to support standardized academic goals. Both roles require effective communication with parents and professionals to enhance student development and educational outcomes.
Student Populations and Diverse Learning Needs
Special education teachers specialize in instructing students with disabilities, providing tailored support to address individualized education plans (IEPs) and diverse learning challenges, while general education teachers typically serve the broader student population without specific disabilities. Students in special education programs often require modifications and accommodations to curricula, fostering inclusive learning environments that accommodate varying cognitive, emotional, and physical needs. General education teachers focus on standard curriculum delivery but collaborate with special educators to support students requiring additional assistance within mainstream classrooms.
Required Educational Background and Certifications
Special education teachers typically require a bachelor's degree in special education or a related field, along with state-specific special education certification that often includes training in individualized education program (IEP) development and behavior management. General education teachers usually need a bachelor's degree in education with a focus on a subject area, plus state certification in general education, emphasizing classroom management and instructional strategies for diverse learners. Both roles may require ongoing professional development and licensure renewal to maintain certification and stay current with educational best practices.
Classroom Environment and Instructional Approaches
Special education teachers create highly individualized classroom environments tailored to diverse learning needs, utilizing adaptive instructional strategies and specialized resources that promote accessibility and engagement. General education teachers typically manage larger, more standardized classroom settings, employing broader instructional approaches focused on grade-level curriculum and differentiated instruction for varied student abilities. Both roles require collaboration and flexibility, but special education emphasizes personalized teaching methods to support students with disabilities and ensure inclusive learning experiences.
Collaboration with Support Staff and Families
Special education teachers collaborate extensively with support staff such as speech therapists, occupational therapists, and counselors to develop and implement individualized education plans (IEPs) that address diverse learning needs. General education teachers work with support staff to accommodate differentiated instruction within the general curriculum, ensuring all students have access to learning opportunities. Both roles require strong partnerships with families to communicate progress, address concerns, and foster a supportive learning environment tailored to each student's success.
Assessment Methods and Progress Monitoring
Special education teachers utilize individualized assessment methods such as functional behavior assessments, adaptive skill evaluations, and progress monitoring tools tailored to students' specific learning disabilities. General education teachers primarily rely on standardized tests, quizzes, and classroom-based formative assessments to evaluate student progress within the broader curriculum. Both teachers employ data-driven progress monitoring, but special educators emphasize continuous, personalized tracking to adjust interventions and support individualized education programs (IEPs).
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Special Education Teachers must adhere to the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), ensuring Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are properly implemented to meet legal requirements. General Education Teachers share responsibility for accommodating students with disabilities under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, maintaining inclusive classroom environments. Both educators must uphold confidentiality under the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) while practicing ethical standards in student assessment and intervention.
Professional Development and Continuing Education
Special education teachers require specialized professional development focused on individualized instruction techniques, behavioral management, and legal compliance under IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act). General education teachers pursue continuing education centered on curriculum standards, instructional strategies, and classroom management applicable to diverse student populations. Both roles benefit from ongoing training to stay current with educational technology, differentiated instruction, and state certification requirements.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Special education teachers often experience diverse career growth opportunities through specialized certifications, leadership roles in Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), and positions in advocacy or administration. General education teachers can advance by pursuing roles such as department heads, curriculum specialists, or school administrators, leveraging broad subject expertise and instructional experience. Both career paths offer unique advancement avenues, with special education emphasizing specialized skills and general education focusing on wide-ranging instructional leadership.
Special Education Teacher vs General Education Teacher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com