The dean typically oversees academic policies and faculty affairs at a college or university, while the principal manages daily operations and student discipline in a primary or secondary school. Deans focus on higher education administration, curriculum development, and faculty support. Principals concentrate on creating a safe learning environment, implementing school policies, and engaging with parents and teachers.
Table of Comparison
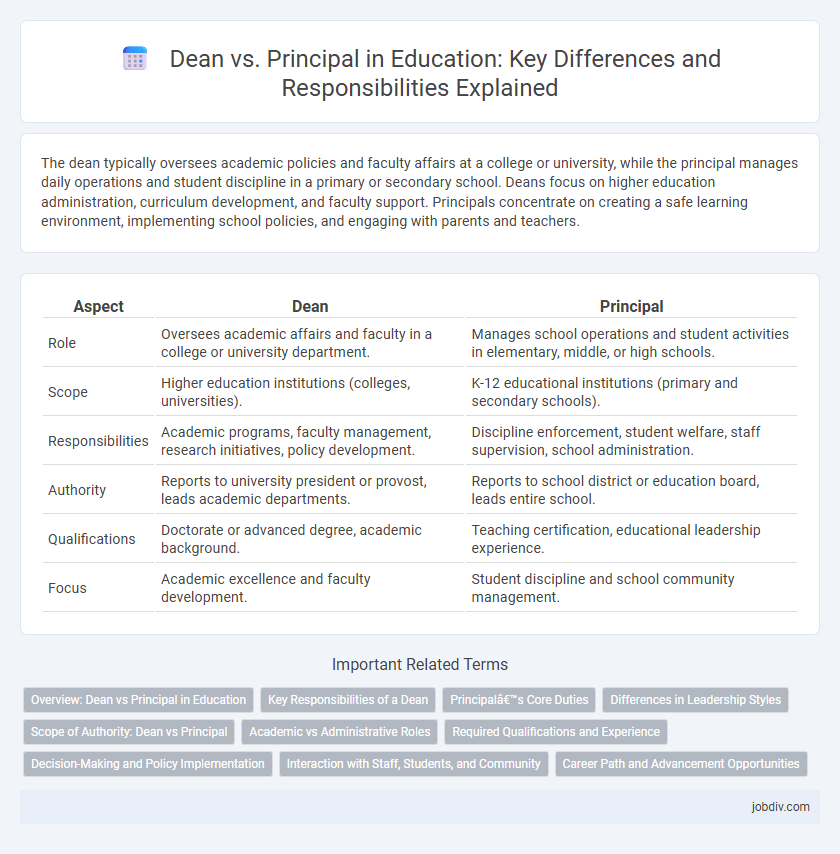
| Aspect | Dean | Principal |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Oversees academic affairs and faculty in a college or university department. | Manages school operations and student activities in elementary, middle, or high schools. |
| Scope | Higher education institutions (colleges, universities). | K-12 educational institutions (primary and secondary schools). |
| Responsibilities | Academic programs, faculty management, research initiatives, policy development. | Discipline enforcement, student welfare, staff supervision, school administration. |
| Authority | Reports to university president or provost, leads academic departments. | Reports to school district or education board, leads entire school. |
| Qualifications | Doctorate or advanced degree, academic background. | Teaching certification, educational leadership experience. |
| Focus | Academic excellence and faculty development. | Student discipline and school community management. |
Overview: Dean vs Principal in Education
A Dean typically oversees academic policies, faculty coordination, and student affairs within specific departments or colleges, while a Principal manages the overall daily operations, administration, and discipline of a school. Deans are often found in higher education institutions such as universities, whereas Principals are common in primary and secondary schools. Both roles require leadership skills but focus on different levels and scopes of educational management.
Key Responsibilities of a Dean
A Dean primarily oversees academic programs, faculty development, and strategic planning within a specific college or faculty, ensuring alignment with institutional goals. They manage budget allocations, spearhead research initiatives, and uphold academic standards, often collaborating with department heads and committees. Unlike principals, whose roles center on overall school management and student discipline, deans focus on higher education administration and curriculum advancement.
Principal’s Core Duties
The principal oversees daily school operations, implements educational policies, and ensures a safe learning environment while managing staff performance and student discipline. They coordinate curriculum development, engage with parents and community stakeholders, and maintain compliance with district regulations. Unlike deans who often focus on student behavior and specific departments, principals hold comprehensive leadership responsibilities crucial for school success.
Differences in Leadership Styles
Deans typically adopt a strategic leadership style, focusing on academic policies, faculty development, and long-term institutional goals, while principals emphasize operational leadership by managing daily school functions, student discipline, and community engagement. The dean's role involves guiding faculty through curriculum development and research initiatives, whereas the principal directly oversees teachers and student activities to maintain a productive learning environment. This distinction in leadership styles highlights the dean's focus on higher education administration versus the principal's emphasis on K-12 school management.
Scope of Authority: Dean vs Principal
A Dean typically oversees academic policies, faculty affairs, and departmental management within a college or university, focusing on broader educational strategies and curriculum standards. A Principal manages the daily operations of a school, including student discipline, teacher supervision, and school administration, ensuring compliance with district and state regulations. The Dean's authority is generally academic and institutional, while the Principal's scope is operational and school-specific.
Academic vs Administrative Roles
Deans primarily oversee academic programs, faculty development, and curriculum standards, ensuring educational quality and scholarly research within their departments or faculties. Principals focus on the administrative management of schools, including student discipline, staff coordination, and operational decisions to maintain a safe and efficient learning environment. Both roles are essential in education but differ significantly in scope, with deans concentrating on academic leadership and principals on school administration.
Required Qualifications and Experience
Deans typically require advanced degrees such as a master's or doctoral degree in education or a related field, along with extensive experience in academic administration and faculty leadership. Principals usually need a master's degree in educational leadership or administration and must possess certified teaching experience coupled with school-level management skills. Both positions demand strong leadership capabilities, but deans often have a broader scope in higher education settings, while principals focus on K-12 school leadership.
Decision-Making and Policy Implementation
The dean typically focuses on strategic decision-making and long-term policy implementation at the college or university level, overseeing academic programs and faculty governance. The principal manages day-to-day operations and enforces school policies, directly impacting student discipline, staff coordination, and routine administrative decisions in primary or secondary education institutions. Both roles require collaboration but differ in scope, with deans influencing institutional direction and principals ensuring effective execution of policies on the ground.
Interaction with Staff, Students, and Community
Deans typically focus on academic leadership, coordinating faculty and curriculum development, while principals manage overall school operations and daily interactions with teachers and students. Deans often engage with faculty on academic policies and research initiatives, whereas principals maintain close relationships with students, parents, and the broader community to foster a supportive school environment. Both roles require effective communication skills, but principals have more direct involvement in student discipline and extracurricular activities.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Deans typically advance through academic ranks by earning advanced degrees and demonstrating leadership in research, teaching, and administrative roles within universities, making their career path more focused on higher education institutions. Principals usually progress from teaching positions by gaining experience in school leadership, often starting as assistant principals or department heads in K-12 settings, with advancement opportunities centered around improving school performance and district administration roles. Understanding these career trajectories highlights that deans have pathways oriented toward academia and specialized fields, whereas principals move within school systems emphasizing operational management and community engagement.
Dean vs Principal Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com