Energy Storage Engineers design and optimize systems that store excess energy efficiently for later use, focusing on batteries, flywheels, and thermal storage technologies. Transmission Engineers specialize in the high-voltage power grid, ensuring reliable and safe delivery of electricity from generation sites to distribution networks. Both roles are critical for modern energy infrastructure, with storage engineers addressing demand fluctuations and transmission engineers maintaining grid stability and capacity.
Table of Comparison
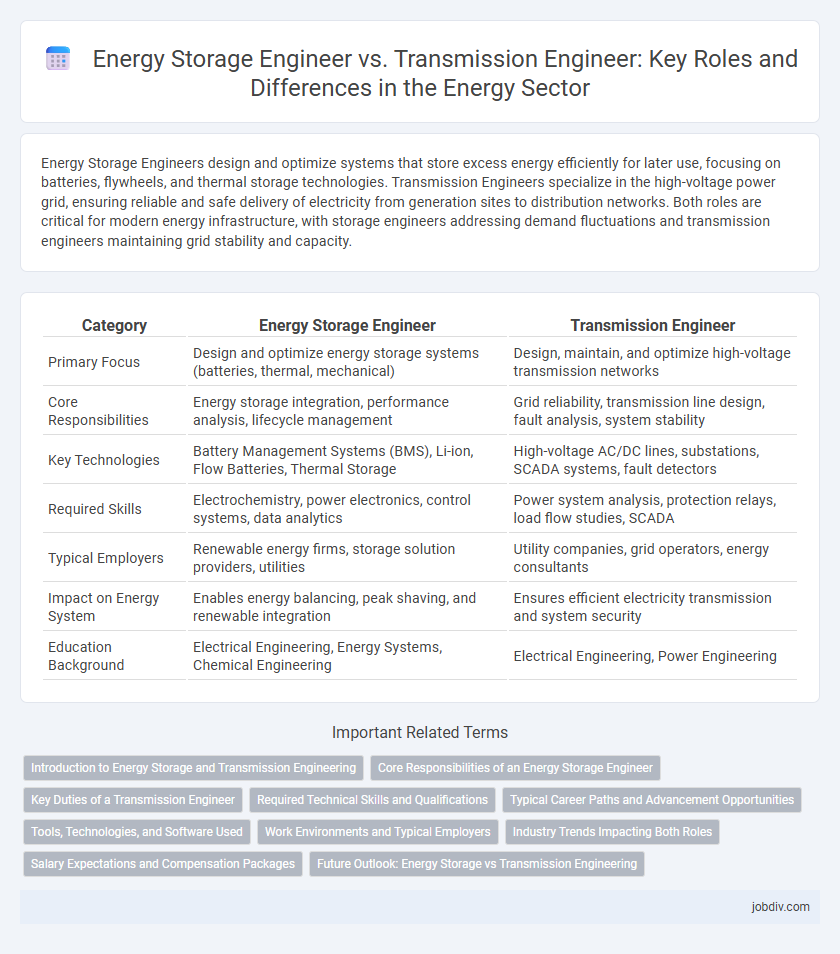
| Category | Energy Storage Engineer | Transmission Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and optimize energy storage systems (batteries, thermal, mechanical) | Design, maintain, and optimize high-voltage transmission networks |
| Core Responsibilities | Energy storage integration, performance analysis, lifecycle management | Grid reliability, transmission line design, fault analysis, system stability |
| Key Technologies | Battery Management Systems (BMS), Li-ion, Flow Batteries, Thermal Storage | High-voltage AC/DC lines, substations, SCADA systems, fault detectors |
| Required Skills | Electrochemistry, power electronics, control systems, data analytics | Power system analysis, protection relays, load flow studies, SCADA |
| Typical Employers | Renewable energy firms, storage solution providers, utilities | Utility companies, grid operators, energy consultants |
| Impact on Energy System | Enables energy balancing, peak shaving, and renewable integration | Ensures efficient electricity transmission and system security |
| Education Background | Electrical Engineering, Energy Systems, Chemical Engineering | Electrical Engineering, Power Engineering |
Introduction to Energy Storage and Transmission Engineering
Energy Storage Engineers specialize in the design and implementation of systems that store electrical energy for later use, focusing on technologies like batteries, flywheels, and pumped hydro storage, which enhance grid reliability and support renewable integration. Transmission Engineers concentrate on the high-voltage infrastructure that transports electricity from power plants to distribution networks, ensuring efficient, stable, and secure power delivery across vast distances. The intersection of these disciplines is critical for optimizing grid performance, managing energy flow, and advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Core Responsibilities of an Energy Storage Engineer
Energy Storage Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and optimizing battery systems, capacitors, and other technologies to store electrical energy efficiently. They conduct performance analysis, manage thermal systems, and ensure the integration of storage units with renewable energy sources and grid infrastructure. Their role prioritizes enhancing storage capacity, improving energy density, and enabling grid stability through advanced energy management systems.
Key Duties of a Transmission Engineer
Transmission Engineers focus on designing, maintaining, and optimizing high-voltage power lines and substations to ensure efficient electricity transmission from generation sites to distribution networks. They conduct load flow analysis, manage grid stability, and implement upgrades to minimize energy losses and prevent outages. Their role involves coordinating with grid operators and regulatory bodies to comply with safety standards and support reliable energy delivery.
Required Technical Skills and Qualifications
Energy Storage Engineers require expertise in battery technologies, power electronics, and thermal management, along with proficiency in simulation software and grid integration techniques. Transmission Engineers must master high-voltage transmission systems, grid stability analysis, and protective relaying, with strong skills in SCADA systems and electromagnetic transients simulation. Both roles typically demand a degree in electrical engineering or related fields, with specialized certifications enhancing career prospects.
Typical Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Energy Storage Engineers typically advance by gaining expertise in battery technologies, grid-scale energy storage systems, and renewable integration, often progressing to senior design or project management roles within utility or energy technology firms. Transmission Engineers usually follow a path centered on high-voltage power system design, grid reliability, and infrastructure expansion, moving towards positions such as lead transmission planner or regional grid operations manager. Both career trajectories offer opportunities to specialize further in regulatory compliance, system optimization, and emerging smart grid technologies.
Tools, Technologies, and Software Used
Energy Storage Engineers primarily utilize battery management systems (BMS), advanced modeling tools like MATLAB/Simulink, and software for state-of-charge estimation and lifecycle analysis to optimize storage performance and integration. Transmission Engineers focus on power system analysis software such as PSS(r)E and PowerWorld, SCADA systems for real-time grid monitoring, and high-voltage equipment design tools to ensure efficient and reliable electricity transmission. Both roles increasingly leverage IoT devices and data analytics platforms to enhance grid stability and energy efficiency.
Work Environments and Typical Employers
Energy Storage Engineers typically work in research facilities, utility companies, and renewable energy firms specializing in battery technologies, grid-scale storage, and energy management systems. Transmission Engineers are often employed by electric utilities, government agencies, and large infrastructure corporations focused on power grid design, high-voltage transmission lines, and system reliability. Both roles require collaboration with cross-functional teams, but Energy Storage Engineers tend to have more laboratory and project-based environments, while Transmission Engineers primarily operate in field settings and control centers.
Industry Trends Impacting Both Roles
Energy storage engineers and transmission engineers increasingly collaborate to address grid modernization challenges driven by the integration of renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies. Industry trends such as the rise of distributed energy resources and advances in battery storage systems are reshaping both roles by demanding expertise in grid stability, energy efficiency, and real-time data analytics. Evolving regulatory frameworks and decarbonization goals further intensify the need for innovative solutions in energy storage capacity and transmission infrastructure resilience.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Packages
Energy Storage Engineers typically command higher salary expectations due to specialized skills in battery technology, grid integration, and renewable energy systems, with average compensation ranging from $90,000 to $140,000 annually. Transmission Engineers, focused on power grid infrastructure and high-voltage systems, earn between $80,000 and $130,000, often complemented by benefits such as performance bonuses, health insurance, and retirement plans. Compensation packages for both roles frequently include stock options or project-based incentives, reflecting the critical importance of their expertise in modern energy networks.
Future Outlook: Energy Storage vs Transmission Engineering
Energy Storage Engineers will see increasing demand as renewable energy adoption accelerates, requiring advanced solutions for grid stability and decentralized power management. Transmission Engineers remain critical for expanding high-voltage networks to support long-distance electricity transport and integrating large-scale renewable projects. Future energy systems will rely on a synergistic approach where energy storage innovations complement transmission infrastructure upgrades to optimize grid efficiency and resilience.
Energy Storage Engineer vs Transmission Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com