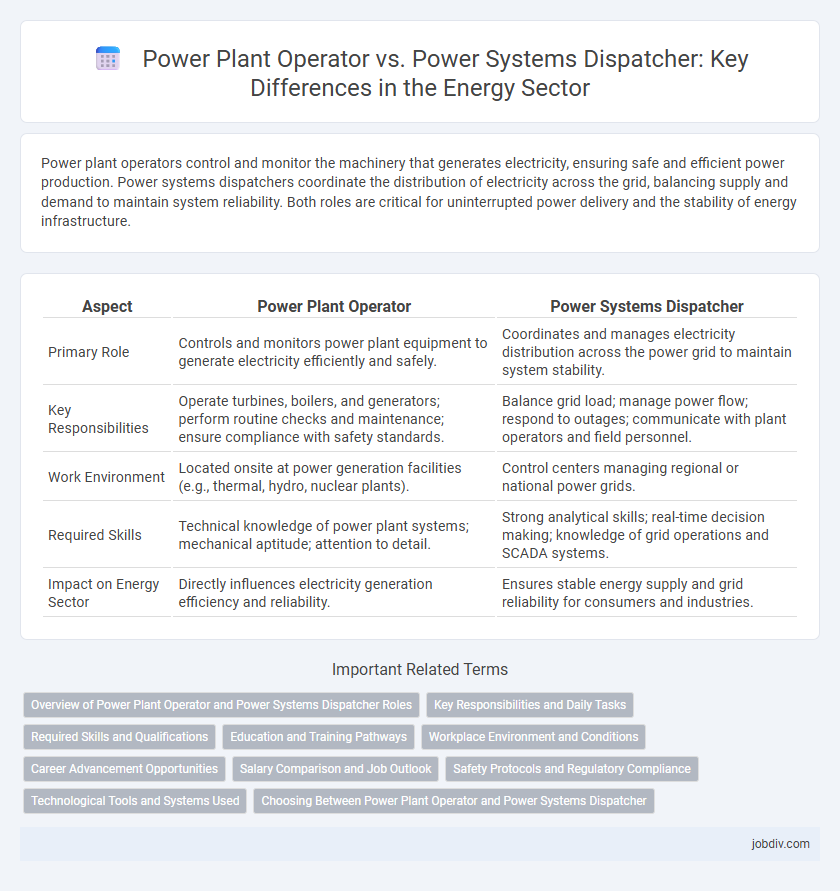
Power plant operators control and monitor the machinery that generates electricity, ensuring safe and efficient power production. Power systems dispatchers coordinate the distribution of electricity across the grid, balancing supply and demand to maintain system reliability. Both roles are critical for uninterrupted power delivery and the stability of energy infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Power Plant Operator | Power Systems Dispatcher |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Controls and monitors power plant equipment to generate electricity efficiently and safely. | Coordinates and manages electricity distribution across the power grid to maintain system stability. |
| Key Responsibilities | Operate turbines, boilers, and generators; perform routine checks and maintenance; ensure compliance with safety standards. | Balance grid load; manage power flow; respond to outages; communicate with plant operators and field personnel. |
| Work Environment | Located onsite at power generation facilities (e.g., thermal, hydro, nuclear plants). | Control centers managing regional or national power grids. |
| Required Skills | Technical knowledge of power plant systems; mechanical aptitude; attention to detail. | Strong analytical skills; real-time decision making; knowledge of grid operations and SCADA systems. |
| Impact on Energy Sector | Directly influences electricity generation efficiency and reliability. | Ensures stable energy supply and grid reliability for consumers and industries. |
Overview of Power Plant Operator and Power Systems Dispatcher Roles
Power Plant Operators control and maintain equipment that generates electric power, ensuring efficient energy production and safety compliance. Power Systems Dispatchers manage electricity distribution by monitoring grid performance and coordinating the flow of electricity to meet demand and prevent outages. Both roles require real-time decision-making to maintain stability and reliability within the power grid infrastructure.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Power Plant Operators monitor and control machinery to generate electricity, ensuring optimal performance and safety standards within energy production facilities. Power Systems Dispatchers oversee the distribution of electricity across transmission networks, managing load balancing and responding to outages to maintain grid stability. Both roles demand real-time decision-making and adherence to regulatory protocols to support continuous power supply.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Power Plant Operators require technical knowledge of machinery operation, monitoring control systems, and safety protocols, often holding certifications like NERC or a heavy equipment license. Power Systems Dispatchers need expertise in grid management, real-time system analysis, and communication skills to coordinate power distribution efficiently, typically requiring a background in electrical engineering or specialized dispatcher training. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and adherence to regulatory standards to ensure continuous and safe energy supply.
Education and Training Pathways
Power Plant Operators typically require specialized technical training or an associate degree in power plant technology, supplemented by extensive on-the-job training to manage equipment and monitor systems effectively. Power Systems Dispatchers often hold degrees in electrical engineering or a related field and undergo rigorous certification programs focused on grid management, system reliability, and emergency response protocols. Both roles demand continuous professional development to keep pace with evolving energy technologies and regulatory standards.
Workplace Environment and Conditions
Power Plant Operators typically work inside industrial control rooms within power plants, managing equipment under controlled temperature and noise conditions but may face exposure to hazardous materials and shift work. Power Systems Dispatchers operate in centralized control centers, monitoring and directing electricity distribution in real-time with high responsibility for grid stability, often enduring stress and long hours in sedentary office environments. Both roles require alertness and quick decision-making, yet Power Plant Operators encounter more hands-on technical tasks while Dispatchers focus on system-wide coordination and emergency response.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Power Plant Operators typically advance by gaining specialized technical certifications and moving into senior operational roles or plant management, emphasizing hands-on expertise in energy production. Power Systems Dispatchers progress through enhanced training in grid management technology and real-time system coordination, often transitioning into supervisory or control center management positions. Career advancement in both paths depends heavily on acquiring advanced knowledge in energy systems, regulatory compliance, and emergency response protocols.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Power Plant Operators typically earn a median annual salary of around $85,000, while Power Systems Dispatchers earn slightly higher, averaging about $90,000 per year due to the critical decision-making responsibilities they hold. The job outlook for Power Systems Dispatchers is projected to grow by 5% over the next decade, driven by increasing grid complexity and the integration of renewable energy sources, whereas Power Plant Operator employment is expected to remain relatively stable with modest growth. Both roles require technical expertise, but dispatchers often have more dynamic workloads and higher stress levels given their role in real-time grid management.
Safety Protocols and Regulatory Compliance
Power Plant Operators manage on-site equipment operations, ensuring adherence to safety protocols such as lockout/tagout procedures and emergency shutdown systems to prevent accidents and maintain regulatory compliance with OSHA and EPA standards. Power Systems Dispatchers coordinate the power grid, monitoring and controlling electrical loads while following strict NERC CIP reliability standards to secure grid stability and prevent blackouts. Both roles prioritize risk mitigation by implementing industry-specific regulations and continuous safety training to uphold operational integrity in the energy sector.
Technological Tools and Systems Used
Power Plant Operators utilize control systems like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and DCS (Distributed Control Systems) to monitor and manage equipment performance in real-time, ensuring efficient energy generation. Power Systems Dispatchers rely heavily on advanced Energy Management Systems (EMS) and Wide Area Measurement Systems (WAMS) to balance grid demand, manage load distribution, and respond to outages across large electrical networks. Both roles integrate digital interfaces and automation technologies but emphasize different aspects of grid stability and power generation control.
Choosing Between Power Plant Operator and Power Systems Dispatcher
Choosing between a Power Plant Operator and a Power Systems Dispatcher depends on preferred work environments and responsibilities. Power Plant Operators focus on controlling and maintaining equipment within power generation facilities to ensure optimal energy production, while Power Systems Dispatchers manage the distribution and flow of electricity across the grid to balance supply and demand. Career decisions should weigh preferences for hands-on technical work versus real-time system monitoring and coordination in energy management.
Power Plant Operator vs Power Systems Dispatcher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com