Battery storage specialists excel in optimizing lithium-ion and solid-state battery technologies for efficient energy retention and rapid discharge cycles, making them ideal for grid stabilization and renewable energy integration. Hydrogen storage specialists focus on advanced methods for storing hydrogen safely and compactly, enabling long-term energy storage and facilitating fuel cell applications in transportation and power generation. Both roles are crucial for advancing sustainable energy systems, with battery experts addressing short-term storage needs and hydrogen experts supporting large-scale, long-duration energy demands.
Table of Comparison
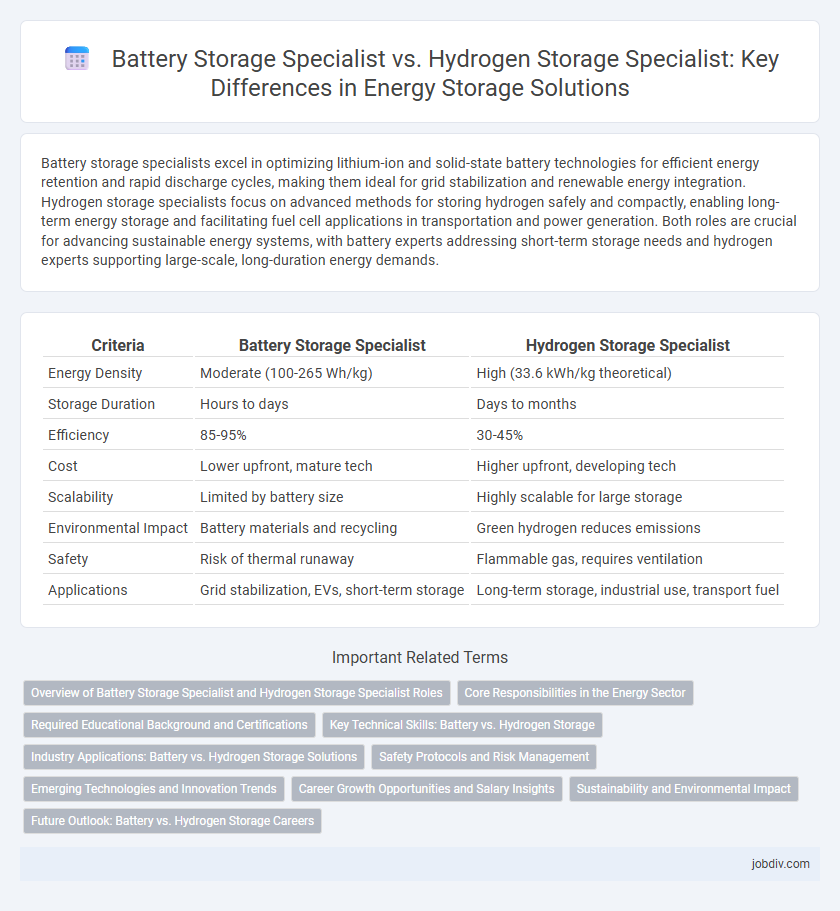
| Criteria | Battery Storage Specialist | Hydrogen Storage Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Moderate (100-265 Wh/kg) | High (33.6 kWh/kg theoretical) |
| Storage Duration | Hours to days | Days to months |
| Efficiency | 85-95% | 30-45% |
| Cost | Lower upfront, mature tech | Higher upfront, developing tech |
| Scalability | Limited by battery size | Highly scalable for large storage |
| Environmental Impact | Battery materials and recycling | Green hydrogen reduces emissions |
| Safety | Risk of thermal runaway | Flammable gas, requires ventilation |
| Applications | Grid stabilization, EVs, short-term storage | Long-term storage, industrial use, transport fuel |
Overview of Battery Storage Specialist and Hydrogen Storage Specialist Roles
Battery Storage Specialists focus on the design, implementation, and maintenance of energy storage systems primarily using lithium-ion or flow batteries, ensuring efficient energy management and grid stability. Hydrogen Storage Specialists develop and optimize storage solutions for hydrogen fuel, emphasizing safety protocols and integration with fuel cell technologies for renewable energy applications. Both roles require expertise in energy conversion, storage capacity, and system scalability but differ in the type of medium and storage technology they specialize in.
Core Responsibilities in the Energy Sector
Battery Storage Specialists manage the design, implementation, and maintenance of electrochemical energy storage systems, focusing on optimizing battery performance, lifecycle, and safety in grid applications. Hydrogen Storage Specialists concentrate on developing and overseeing technologies for storing hydrogen safely and efficiently, including compression, liquefaction, and material-based storage methods. Both roles require expertise in energy storage optimization but diverge in technical approaches and applications within renewable energy integration and grid stability.
Required Educational Background and Certifications
Battery Storage Specialists typically require a degree in electrical engineering, chemical engineering, or renewable energy, with certifications such as Certified Energy Manager (CEM) or battery system-specific credentials like NABCEP. Hydrogen Storage Specialists often hold advanced degrees in chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, or materials science, with certifications including Hydrogen Safety Training and International Association for Hydrogen Safety (IAHySafe) credentials. Both roles demand strong knowledge of energy storage technologies, safety protocols, and regulatory compliance to manage respective storage solutions effectively.
Key Technical Skills: Battery vs. Hydrogen Storage
Battery Storage Specialists excel in electrochemical system design, battery management systems (BMS), and Lithium-ion cell optimization, enabling efficient energy storage and discharge cycles. Hydrogen Storage Specialists focus on gas compression, cryogenic technologies, and materials engineering for safe hydrogen containment and fuel cell integration. Both roles require expertise in energy density, thermal management, and system scalability, but distinct knowledge in electrochemistry versus hydrogen production and storage infrastructure is critical.
Industry Applications: Battery vs. Hydrogen Storage Solutions
Battery storage specialists focus on applications such as grid stabilization, renewable energy integration, and electric vehicle power systems, where fast charge-discharge cycles and energy density are critical. Hydrogen storage specialists target industries requiring long-duration energy storage and high energy capacity, including heavy transportation, industrial processes, and backup power for remote locations. The choice between battery and hydrogen storage solutions depends on application-specific factors like energy density, discharge duration, and scalability in sectors like utilities, manufacturing, and mobility.
Safety Protocols and Risk Management
Battery Storage Specialists implement rigorous safety protocols including thermal runaway prevention, electrical insulation standards, and regular system diagnostics to mitigate fire and explosion risks in lithium-ion setups. Hydrogen Storage Specialists focus on leak detection, flammable gas management, and high-pressure containment integrity to prevent ignition and ensure safe handling of highly combustible hydrogen. Both roles require advanced risk management strategies tailored to the unique hazards presented by electrochemical versus gaseous storage technologies.
Emerging Technologies and Innovation Trends
Battery Storage Specialists drive innovation in lithium-ion and solid-state technologies, enhancing energy density and lifecycle for grid-scale and renewable energy integration. Hydrogen Storage Specialists focus on developing advanced materials and compression techniques to improve hydrogen's storage efficiency and safety for fuel cell applications and seasonal energy storage. Emerging trends highlight cross-disciplinary approaches combining electrochemical and molecular storage solutions to address scalability and sustainability challenges in clean energy systems.
Career Growth Opportunities and Salary Insights
Battery Storage Specialists have seen rapid career growth due to increasing demand for lithium-ion technology in renewable energy integration, with average salaries ranging from $80,000 to $120,000 annually. Hydrogen Storage Specialists are emerging in a niche market fueled by green hydrogen investments, commanding salaries between $90,000 and $130,000, reflecting the specialized technical expertise required. Opportunities for advancement in battery storage are robust due to established industries, while hydrogen storage offers high potential growth as infrastructure and production scale up globally.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Battery storage specialists drive advances in energy density and recyclability, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing hazardous waste through efficient lithium-ion or solid-state battery solutions. Hydrogen storage specialists focus on sustainable production methods, such as green hydrogen via electrolysis, offering zero-emission energy storage with water as the only byproduct upon use. Both roles are pivotal in transitioning to renewable energy systems, with battery technologies excelling in grid-scale applications and hydrogen providing long-term, large-capacity storage critical for decarbonizing heavy industry and transport sectors.
Future Outlook: Battery vs. Hydrogen Storage Careers
Battery Storage Specialists are increasingly in demand due to rapid growth in electric vehicle adoption and grid-scale renewable integration, with market projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% through 2030. Hydrogen Storage Specialists are positioned for exponential growth as green hydrogen becomes a key component in decarbonizing hard-to-electrify sectors like heavy industry and aviation, with investments expected to surpass $100 billion by 2035. Career opportunities in battery storage emphasize advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state technologies, while hydrogen storage careers focus on innovations in fuel cell development and safe, efficient large-scale hydrogen containment.
Battery Storage Specialist vs Hydrogen Storage Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com