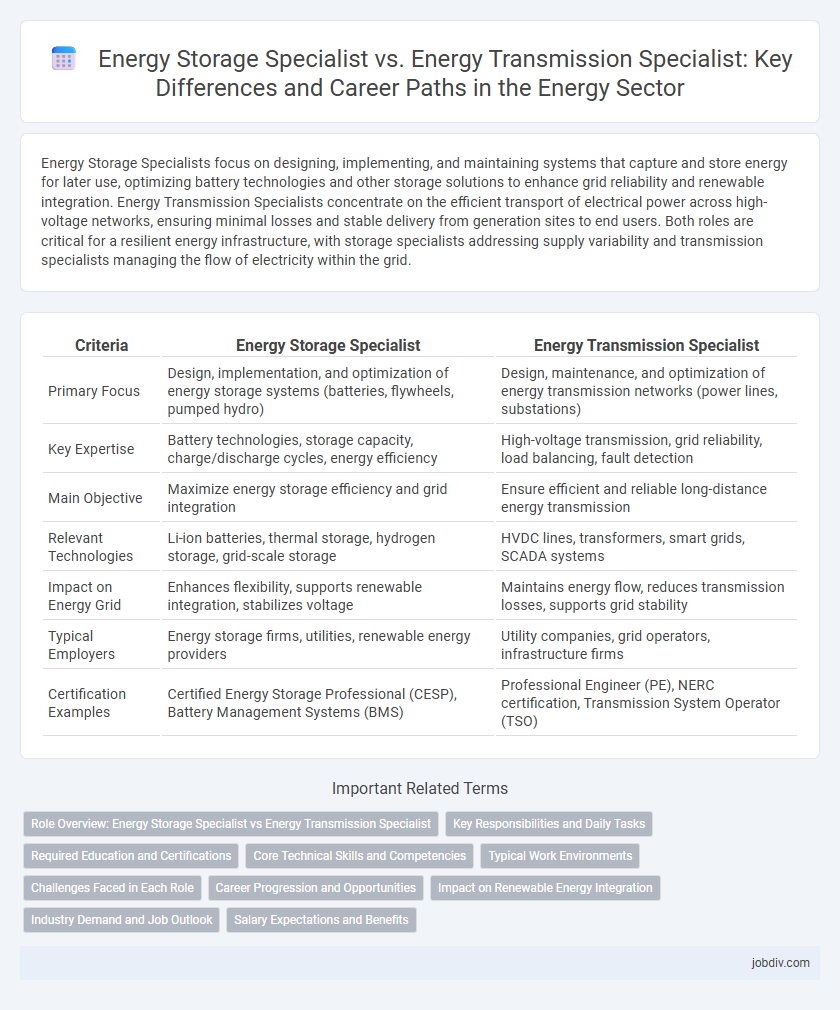
Energy Storage Specialists focus on designing, implementing, and maintaining systems that capture and store energy for later use, optimizing battery technologies and other storage solutions to enhance grid reliability and renewable integration. Energy Transmission Specialists concentrate on the efficient transport of electrical power across high-voltage networks, ensuring minimal losses and stable delivery from generation sites to end users. Both roles are critical for a resilient energy infrastructure, with storage specialists addressing supply variability and transmission specialists managing the flow of electricity within the grid.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Energy Storage Specialist | Energy Transmission Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design, implementation, and optimization of energy storage systems (batteries, flywheels, pumped hydro) | Design, maintenance, and optimization of energy transmission networks (power lines, substations) |
| Key Expertise | Battery technologies, storage capacity, charge/discharge cycles, energy efficiency | High-voltage transmission, grid reliability, load balancing, fault detection |
| Main Objective | Maximize energy storage efficiency and grid integration | Ensure efficient and reliable long-distance energy transmission |
| Relevant Technologies | Li-ion batteries, thermal storage, hydrogen storage, grid-scale storage | HVDC lines, transformers, smart grids, SCADA systems |
| Impact on Energy Grid | Enhances flexibility, supports renewable integration, stabilizes voltage | Maintains energy flow, reduces transmission losses, supports grid stability |
| Typical Employers | Energy storage firms, utilities, renewable energy providers | Utility companies, grid operators, infrastructure firms |
| Certification Examples | Certified Energy Storage Professional (CESP), Battery Management Systems (BMS) | Professional Engineer (PE), NERC certification, Transmission System Operator (TSO) |
Role Overview: Energy Storage Specialist vs Energy Transmission Specialist
Energy Storage Specialists focus on designing, implementing, and managing systems that store energy efficiently, such as batteries, pumped hydro, or thermal storage, optimizing grid stability and renewable energy integration. Energy Transmission Specialists prioritize the planning, operation, and maintenance of power lines and substations, ensuring the reliable and safe delivery of electricity over long distances. Both roles require deep knowledge of electrical systems, but storage specialists emphasize energy retention technologies while transmission specialists specialize in grid infrastructure and energy flow management.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Energy Storage Specialists manage battery systems, optimize energy retention, and ensure seamless integration of storage solutions with renewable sources. Energy Transmission Specialists focus on maintaining grid infrastructure, monitoring power flow, and coordinating the efficient delivery of electricity across networks. Both roles demand expertise in system analysis, safety protocols, and real-time problem solving to enhance energy reliability and efficiency.
Required Education and Certifications
Energy Storage Specialists typically require a background in electrical or mechanical engineering, often holding a bachelor's degree with certifications like Certified Energy Manager (CEM) or Energy Storage Professional (ESP). Energy Transmission Specialists generally possess degrees in electrical engineering or power systems engineering, along with certifications such as NERC System Operator or Professional Engineer (PE) license focused on transmission. Both roles demand specialized knowledge in energy infrastructure, but their certifications emphasize distinct aspects of energy systems management and safety compliance.
Core Technical Skills and Competencies
Energy Storage Specialists excel in battery management systems, thermal regulation, and energy density optimization, ensuring efficient and reliable energy retention. Energy Transmission Specialists focus on high-voltage power systems, grid infrastructure design, and real-time load balancing to maintain seamless energy flow. Both roles require proficiency in electrical engineering principles, but storage experts prioritize electrochemical technologies, while transmission experts emphasize power system stability and network integration.
Typical Work Environments
Energy Storage Specialists typically work in environments such as battery manufacturing plants, renewable energy facilities, and research laboratories focused on advancing storage technologies like lithium-ion and flow batteries. Energy Transmission Specialists are usually employed by utility companies, grid operators, and infrastructure firms, working in control centers, substations, and field locations to manage high-voltage transmission lines and ensure grid reliability. Both roles require collaboration with engineers and technicians but differ significantly in their operational settings and day-to-day activities related to energy handling.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Energy Storage Specialists contend with challenges such as optimizing battery lifespan, managing thermal stability, and integrating diverse storage technologies into existing grids. Energy Transmission Specialists face obstacles including maintaining grid reliability, mitigating power losses over long distances, and upgrading infrastructure to accommodate renewable energy sources. Both roles require addressing regulatory compliance and ensuring system resilience amid evolving energy demands.
Career Progression and Opportunities
Energy Storage Specialists advance by mastering battery technologies, grid-scale storage solutions, and energy management systems, opening roles in renewable integration and smart grid innovation. Energy Transmission Specialists focus on high-voltage infrastructure, grid reliability, and power flow optimization, leading to opportunities in grid modernization and utility management. Career progression in storage often involves R&D and project management, while transmission specialists move toward regulatory compliance and system planning leadership.
Impact on Renewable Energy Integration
Energy Storage Specialists enhance renewable energy integration by optimizing battery systems and managing energy during supply-demand fluctuations, ensuring grid stability and continuous power availability. Energy Transmission Specialists focus on upgrading and maintaining transmission infrastructure to efficiently transport renewable energy from generation sites to consumption areas, reducing losses and enabling large-scale deployment. Both roles are critical for maximizing renewable energy utilization and supporting a resilient, low-carbon energy grid.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Energy Storage Specialists are seeing rising demand due to the growing adoption of renewable energy systems and the need for efficient battery technologies, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 15% job growth in energy storage fields over the next decade. Energy Transmission Specialists remain essential for maintaining and upgrading electrical grids, supported by increased investments in smart grid technologies and infrastructure modernization, resulting in a steady 10% employment growth forecast. Industry trends emphasize energy storage for grid stability and load balancing, while transmission focuses on reliable energy distribution, both critical to achieving national clean energy goals.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Energy Storage Specialists typically command salaries ranging from $80,000 to $120,000 annually, reflecting expertise in battery technologies and grid integration, while Energy Transmission Specialists earn between $75,000 and $110,000, focusing on high-voltage system management and network reliability. Benefits for both roles often include performance bonuses, health insurance, retirement plans, and opportunities for continuing education in renewable energy advancements. Companies value these specialists for their critical roles in enhancing energy efficiency, grid stability, and supporting sustainable energy transitions.
Energy Storage Specialist vs Energy Transmission Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com