Electricity market analysts specialize in forecasting prices, demand, and supply dynamics within power markets, utilizing data on renewable integration, grid constraints, and regulatory policies. Gas market analysts focus on natural gas supply chains, price trends, and geopolitical factors that influence gas markets and storage capacities. Both roles require strong analytical skills but differ in their energy commodity expertise and market drivers.
Table of Comparison
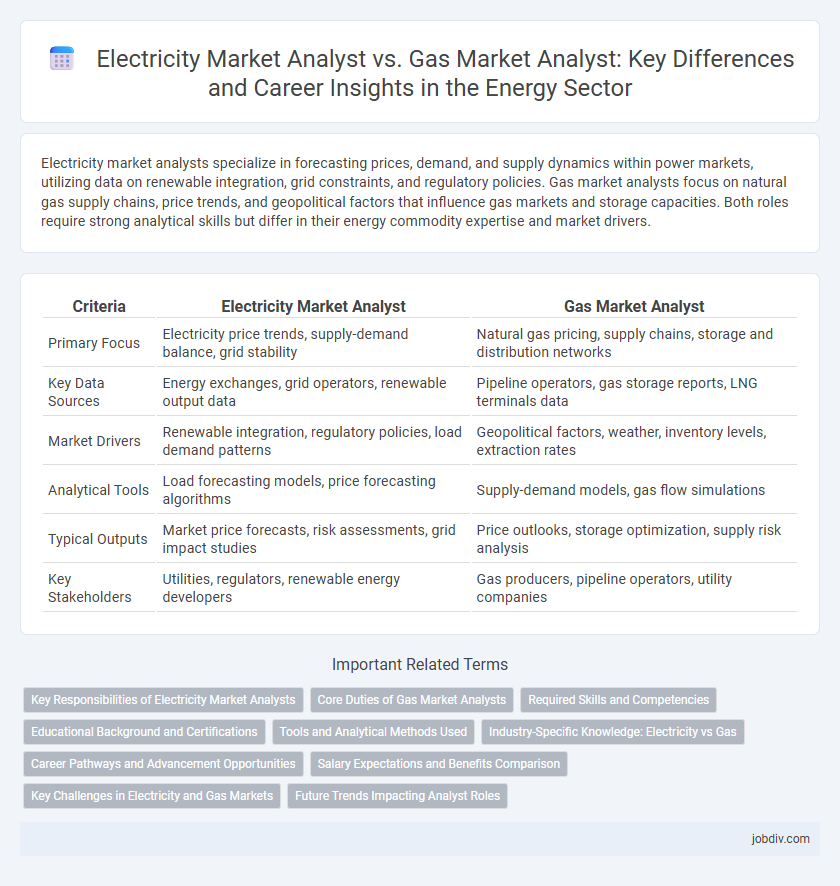
| Criteria | Electricity Market Analyst | Gas Market Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Electricity price trends, supply-demand balance, grid stability | Natural gas pricing, supply chains, storage and distribution networks |
| Key Data Sources | Energy exchanges, grid operators, renewable output data | Pipeline operators, gas storage reports, LNG terminals data |
| Market Drivers | Renewable integration, regulatory policies, load demand patterns | Geopolitical factors, weather, inventory levels, extraction rates |
| Analytical Tools | Load forecasting models, price forecasting algorithms | Supply-demand models, gas flow simulations |
| Typical Outputs | Market price forecasts, risk assessments, grid impact studies | Price outlooks, storage optimization, supply risk analysis |
| Key Stakeholders | Utilities, regulators, renewable energy developers | Gas producers, pipeline operators, utility companies |
Key Responsibilities of Electricity Market Analysts
Electricity Market Analysts specialize in analyzing grid dynamics, forecasting energy prices, and evaluating regulatory impacts on electricity supply and demand. They assess market trends, monitor generation dispatch, and optimize trading strategies to maximize profits in competitive electricity markets. Their role requires expertise in renewable integration, capacity planning, and real-time market operations to ensure reliable and cost-effective electricity delivery.
Core Duties of Gas Market Analysts
Gas Market Analysts specialize in evaluating supply, demand, and price trends in natural gas markets, providing crucial forecasts that influence trading and investment decisions. They analyze pipeline capacities, storage levels, and regulatory impacts to assess market fluctuations and risks specific to gas commodities. These analysts support energy companies and policymakers by delivering insights on gas market dynamics, contract negotiations, and infrastructure developments.
Required Skills and Competencies
Electricity Market Analysts require strong skills in power systems modeling, load forecasting, and renewable energy integration, with proficiency in tools like MATLAB and PLEXOS. Gas Market Analysts focus on natural gas supply-demand dynamics, pipeline infrastructure, and pricing mechanisms, often utilizing software such as GAMS and EViews. Both roles demand analytical expertise, knowledge of market regulations, and the ability to interpret complex data to forecast market trends.
Educational Background and Certifications
Electricity Market Analysts typically hold degrees in electrical engineering, energy economics, or finance, with certifications such as the Certified Energy Analyst (CEA) or Energy Risk Professional (ERP) enhancing their market acumen. Gas Market Analysts often possess educational backgrounds in petroleum engineering, geology, or natural resource economics, complemented by credentials like the Certified Natural Gas Professional (CNGP) or Energy Risk Professional (ERP) to deepen their expertise in gas markets. Both roles require strong analytical skills and knowledge of regulatory frameworks, but their specialized training and certifications reflect the distinct characteristics of electricity and gas markets.
Tools and Analytical Methods Used
Electricity Market Analysts primarily use load forecasting models, price elasticity analysis, and demand-response simulations to evaluate grid dynamics and market prices, leveraging tools such as SCADA systems and energy management software. Gas Market Analysts focus on pipeline flow modeling, supply-demand balancing, and storage optimization using tools like Gas Control Systems and reservoir simulation software. Both roles employ statistical analysis, forecasting algorithms, and risk assessment models but differ in sector-specific software tailored to electrical versus gas market complexities.
Industry-Specific Knowledge: Electricity vs Gas
Electricity Market Analysts specialize in grid operations, renewable integration, and regulatory policies specific to power generation and distribution, emphasizing demand forecasting and market pricing signals. Gas Market Analysts focus on natural gas supply chains, pipeline capacity, storage dynamics, and contract structures, prioritizing commodity trading and transportation constraints. Both roles require deep expertise in their respective commodity markets but differ markedly in technical frameworks and regulatory environments governing electricity versus gas sectors.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Electricity Market Analysts specialize in forecasting power demand, pricing trends, and grid stability, often advancing to roles in energy trading, regulatory compliance, or senior market strategy positions within utility companies. Gas Market Analysts focus on natural gas supply, price fluctuations, and pipeline logistics, with career paths leading to risk management, procurement strategy, or executive roles in energy firms. Both roles require strong analytical skills and industry knowledge, but opportunities for advancement differ based on market specialization and sector dynamics.
Salary Expectations and Benefits Comparison
Electricity Market Analysts typically command higher salaries due to the complex regulatory environment and increasing demand for renewable energy integration, with average annual earnings ranging from $70,000 to $110,000. Gas Market Analysts often earn between $65,000 and $100,000, reflecting the volatility in natural gas prices and shifting energy policies. Benefits for both roles frequently include health insurance, performance bonuses, and opportunities for professional development, but Electricity Market Analysts may receive additional incentives tied to sustainability goals and energy transition projects.
Key Challenges in Electricity and Gas Markets
Electricity Market Analysts face key challenges such as price volatility driven by intermittent renewable energy sources and grid stability concerns due to increasing demand and decentralization. Gas Market Analysts contend with geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating demand influenced by seasonal weather patterns and shifting global trade dynamics. Both roles require deep understanding of regulatory frameworks, market dynamics, and forecasting models to navigate the complexities within their respective energy sectors.
Future Trends Impacting Analyst Roles
Electricity Market Analysts increasingly leverage advanced forecasting models integrating renewable energy trends and smart grid data to predict price volatility and demand shifts. Gas Market Analysts focus on the impact of geopolitical developments and LNG market expansions, adapting to evolving regulatory frameworks and decarbonization policies affecting supply chains. Both roles require expertise in data analytics, but electricity analysts prioritize grid integration challenges while gas analysts emphasize market liquidity and contract dynamics influenced by future energy transition scenarios.
Electricity Market Analyst vs Gas Market Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com