Biofuel Process Engineers specialize in converting organic materials into sustainable fuels, optimizing biochemical reactions and refining techniques to enhance energy yield and reduce emissions. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on the design, development, and integration of hydrogen production and storage technologies, enabling efficient clean energy solutions for transportation and power generation. Both roles drive innovation in renewable energy but differ in feedstock handling, process complexity, and application scale.
Table of Comparison
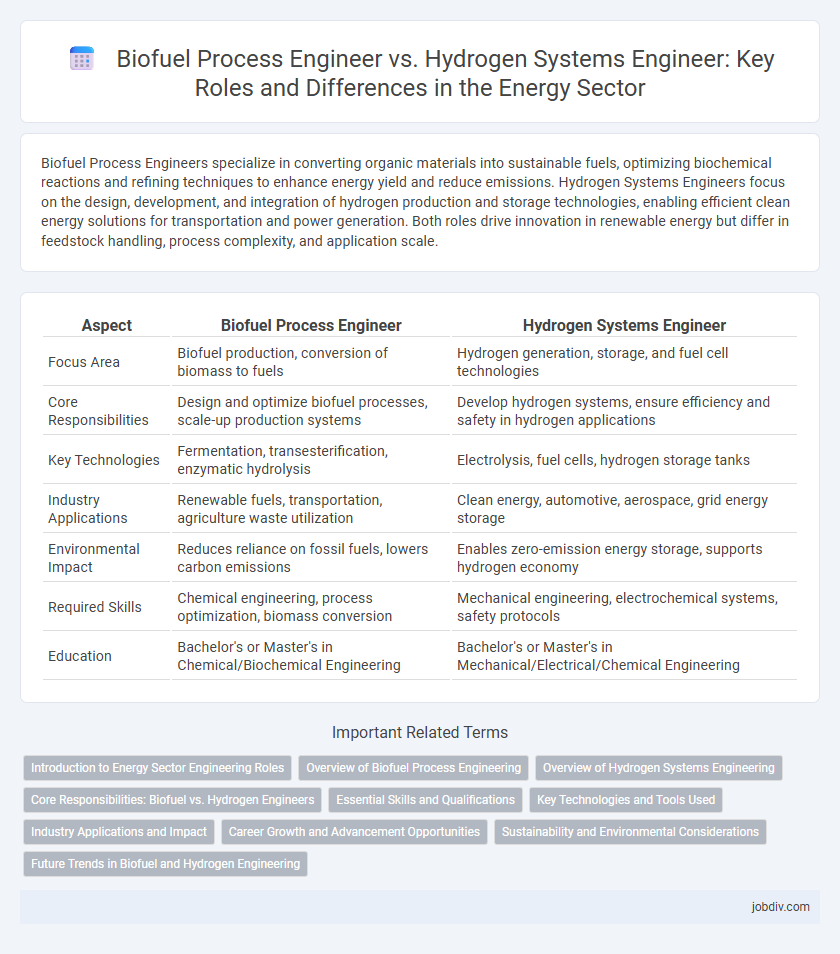
| Aspect | Biofuel Process Engineer | Hydrogen Systems Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Biofuel production, conversion of biomass to fuels | Hydrogen generation, storage, and fuel cell technologies |
| Core Responsibilities | Design and optimize biofuel processes, scale-up production systems | Develop hydrogen systems, ensure efficiency and safety in hydrogen applications |
| Key Technologies | Fermentation, transesterification, enzymatic hydrolysis | Electrolysis, fuel cells, hydrogen storage tanks |
| Industry Applications | Renewable fuels, transportation, agriculture waste utilization | Clean energy, automotive, aerospace, grid energy storage |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowers carbon emissions | Enables zero-emission energy storage, supports hydrogen economy |
| Required Skills | Chemical engineering, process optimization, biomass conversion | Mechanical engineering, electrochemical systems, safety protocols |
| Education | Bachelor's or Master's in Chemical/Biochemical Engineering | Bachelor's or Master's in Mechanical/Electrical/Chemical Engineering |
Introduction to Energy Sector Engineering Roles
Biofuel Process Engineers specialize in designing and optimizing biochemical and thermochemical processes to convert biomass into sustainable fuels, focusing on feedstock selection, fermentation, and conversion efficiency. Hydrogen Systems Engineers develop and manage technologies related to hydrogen production, storage, and distribution, emphasizing electrolysis, fuel cell integration, and infrastructure development. Both roles are critical in advancing renewable energy solutions and require expertise in chemical engineering, energy systems, and environmental impact assessment.
Overview of Biofuel Process Engineering
Biofuel Process Engineers focus on designing and optimizing processes that convert biomass into renewable fuels such as ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas, emphasizing sustainable energy production and carbon reduction. Their expertise includes reaction engineering, fermentation technology, and feedstock pretreatment to maximize fuel yield and efficiency. This role involves scaling lab-based bioconversion methods to industrial levels, integrating process control, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Overview of Hydrogen Systems Engineering
Hydrogen Systems Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and optimizing hydrogen production, storage, and distribution systems, emphasizing fuel cell integration and renewable energy sources. Their expertise includes electrolysis technologies, hydrogen safety protocols, and infrastructure for large-scale hydrogen deployment. Unlike Biofuel Process Engineers who focus on biomass conversion, Hydrogen Systems Engineers drive advancements in clean energy solutions critical for decarbonizing transportation and industry sectors.
Core Responsibilities: Biofuel vs. Hydrogen Engineers
Biofuel Process Engineers specialize in developing and optimizing biochemical conversion methods to transform organic materials into sustainable fuels, overseeing fermentation, enzymatic hydrolysis, and distillation processes. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on designing and managing hydrogen production, storage, and distribution systems, including electrolysis technology, fuel cell integration, and pipeline infrastructure. Both roles require expertise in process optimization and safety compliance but differ fundamentally in feedstock handling and energy conversion pathways.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Biofuel Process Engineers require expertise in biochemical engineering, fermentation technology, and chemical process optimization to convert biomass into sustainable fuels. Hydrogen Systems Engineers must possess skills in electrochemical systems, hydrogen production methods such as electrolysis, and fuel cell technology, emphasizing safety and storage standards. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, proficiency in process simulation software, and a solid foundation in environmental regulations related to renewable energy.
Key Technologies and Tools Used
Biofuel Process Engineers specialize in technologies like anaerobic digestion, transesterification, and gasification, utilizing tools such as bioreactors, chromatography, and process simulators to optimize biomass conversion into fuels. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on electrolysis, fuel cells, and hydrogen storage solutions, employing tools including electrolyzers, PEM fuel cells, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software to enhance hydrogen production and distribution. Both roles require expertise in process optimization software and material characterization techniques tailored to their specific fuel types.
Industry Applications and Impact
Biofuel Process Engineers specialize in developing and optimizing biochemical conversion processes to produce renewable fuels from organic materials, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions in transportation and power sectors. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on designing and integrating hydrogen production, storage, and distribution systems to support clean energy infrastructures, enabling large-scale adoption of hydrogen fuel cells in industries such as automotive and manufacturing. Both roles drive sustainable energy solutions, with biofuels addressing liquid fuel markets and hydrogen systems promoting zero-emission energy carriers for diverse industrial applications.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Biofuel Process Engineers experience career growth by developing expertise in sustainable energy production, scaling biofuel technologies, and optimizing conversion processes, often advancing into roles such as project managers or sustainability directors. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on cutting-edge hydrogen production, storage, and fuel cell integration technologies, with career advancement opportunities in research leadership, system design, and renewable energy consultancy. Both fields offer robust career trajectories driven by expanding clean energy demand, with hydrogen professionals positioned advantageously due to rapid hydrogen economy growth projections.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Biofuel Process Engineers optimize biomass conversion to renewable fuels, reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles through sustainable feedstock utilization. Hydrogen Systems Engineers design and implement hydrogen production, storage, and fuel cell integration, emphasizing zero-emission energy solutions and lifecycle environmental impact reduction. Both roles crucially advance decarbonization, prioritizing sustainable energy systems and environmental compliance.
Future Trends in Biofuel and Hydrogen Engineering
Biofuel Process Engineers are advancing the integration of sustainable feedstocks and enzyme optimization to enhance biofuel yield and reduce carbon emissions, aligning with global decarbonization goals. Hydrogen Systems Engineers focus on developing efficient electrolysis methods and scalable hydrogen storage solutions, crucial for the growing hydrogen economy and green energy transition. Synergistic innovations in biofuel and hydrogen technologies drive the future of renewable energy, emphasizing carbon-neutral fuels and energy system resilience.
Biofuel Process Engineer vs Hydrogen Systems Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com