Power Engineers specialize in the operation, maintenance, and optimization of traditional energy systems such as thermal, hydroelectric, and nuclear power plants, ensuring reliable electricity generation. Renewable Energy Engineers focus on designing and implementing sustainable energy solutions like solar, wind, and geothermal systems to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmental stewardship. Both roles require expertise in energy technologies but differ in their approach to energy production and sustainability goals.
Table of Comparison
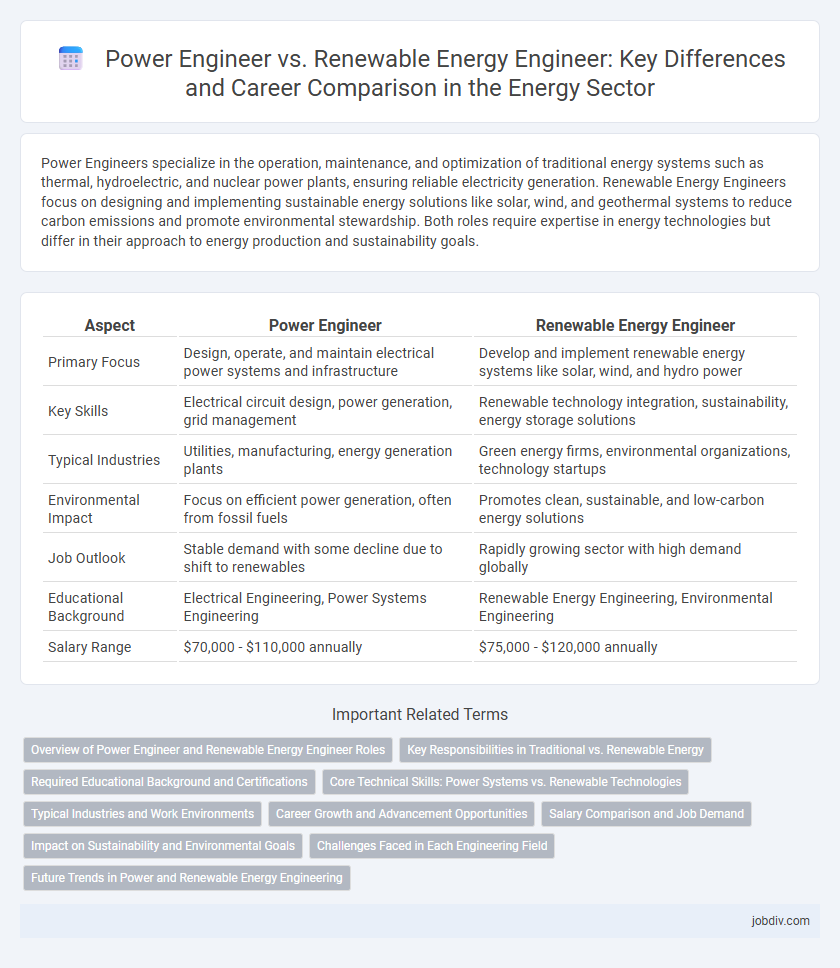
| Aspect | Power Engineer | Renewable Energy Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design, operate, and maintain electrical power systems and infrastructure | Develop and implement renewable energy systems like solar, wind, and hydro power |
| Key Skills | Electrical circuit design, power generation, grid management | Renewable technology integration, sustainability, energy storage solutions |
| Typical Industries | Utilities, manufacturing, energy generation plants | Green energy firms, environmental organizations, technology startups |
| Environmental Impact | Focus on efficient power generation, often from fossil fuels | Promotes clean, sustainable, and low-carbon energy solutions |
| Job Outlook | Stable demand with some decline due to shift to renewables | Rapidly growing sector with high demand globally |
| Educational Background | Electrical Engineering, Power Systems Engineering | Renewable Energy Engineering, Environmental Engineering |
| Salary Range | $70,000 - $110,000 annually | $75,000 - $120,000 annually |
Overview of Power Engineer and Renewable Energy Engineer Roles
Power Engineers specialize in designing, operating, and maintaining electrical power systems, including generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure primarily based on traditional energy sources such as coal, natural gas, and nuclear power. Renewable Energy Engineers focus on developing and implementing sustainable energy solutions, working with technologies like solar panels, wind turbines, and bioenergy systems to reduce environmental impact. Both roles require strong skills in electrical engineering, but Renewable Energy Engineers emphasize innovation in clean energy technology and energy efficiency.
Key Responsibilities in Traditional vs. Renewable Energy
Power Engineers primarily manage the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity using traditional energy sources like coal, natural gas, and nuclear power, ensuring system reliability and compliance with safety standards. Renewable Energy Engineers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining sustainable energy systems such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal, emphasizing efficiency and environmental impact reduction. Both roles require expertise in energy systems, but Renewable Energy Engineers prioritize innovation in clean technologies and integration of intermittent energy sources into the grid.
Required Educational Background and Certifications
Power engineers typically require a bachelor's degree in electrical or mechanical engineering, along with certifications such as the Professional Engineer (PE) license and Power Engineer certification specific to their region. Renewable energy engineers often hold degrees in renewable energy engineering, environmental engineering, or sustainable energy, complemented by certifications like LEED Accredited Professional (LEED AP) and Certified Energy Manager (CEM). Both fields demand strong foundations in energy systems, but renewable energy engineers focus more on sustainable technologies and certifications aligned with green energy standards.
Core Technical Skills: Power Systems vs. Renewable Technologies
Power engineers specialize in power systems, including generation, transmission, distribution, and grid stability, leveraging skills in electrical machines, power electronics, and high-voltage engineering. Renewable energy engineers focus on renewable technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind turbines, energy storage, and smart grid integration, emphasizing expertise in sustainable energy systems and environmental impact analysis. Both roles require proficiency in electrical circuit design and system optimization but diverge in the specific technologies and sustainability goals they prioritize.
Typical Industries and Work Environments
Power engineers typically work in industries such as utility companies, manufacturing plants, and construction firms, focusing on electrical power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. Renewable energy engineers are primarily employed in sectors including solar, wind, and bioenergy companies, as well as research institutions that develop sustainable energy solutions. Work environments for power engineers often involve power plants and industrial facilities, while renewable energy engineers frequently operate in field sites, laboratories, and project development offices dedicated to green technology implementation.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Power Engineers typically have career growth opportunities in traditional energy sectors such as utilities, oil and gas, and manufacturing, with roles advancing from technical specialist to project manager and operations director. Renewable Energy Engineers experience rapid career advancement driven by the expanding clean energy market, with increasing demand for expertise in solar, wind, and battery technologies leading to roles in research, development, and policy advisory positions. Both paths offer strong potential, but Renewable Energy Engineering aligns closely with global sustainability goals and government incentives, often resulting in faster industry growth and innovation-driven promotion.
Salary Comparison and Job Demand
Power engineers typically earn a median salary of $85,000 to $110,000 annually, while renewable energy engineers tend to have salaries ranging from $70,000 to $100,000 depending on experience and location. Job demand for renewable energy engineers is growing rapidly, driven by increasing investment in solar, wind, and green technologies, whereas power engineers maintain steady demand in traditional energy sectors such as utilities and manufacturing. Career growth prospects are stronger in renewable energy fields due to global shifts toward sustainable power solutions, making this sector highly attractive for future job security.
Impact on Sustainability and Environmental Goals
Power engineers specialize in designing and maintaining traditional energy systems such as fossil fuel and nuclear plants, often focusing on efficiency and reliability but with higher carbon emissions. Renewable energy engineers develop innovative technologies like solar, wind, and hydro systems that significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support global sustainability targets. Their work accelerates the transition to low-carbon energy, directly advancing environmental goals and combating climate change.
Challenges Faced in Each Engineering Field
Power engineers frequently confront challenges related to maintaining and upgrading aging electrical infrastructure while ensuring grid reliability and stability under increasing demand. Renewable energy engineers face technical difficulties in integrating variable energy sources like solar and wind into existing power systems, alongside overcoming storage limitations and intermittency issues. Both fields require innovative solutions to address environmental regulations and the transition towards sustainable energy models.
Future Trends in Power and Renewable Energy Engineering
Power engineers are advancing smart grid technologies and modernizing existing energy infrastructure to enhance reliability and efficiency. Renewable energy engineers are driving innovations in solar, wind, and energy storage systems to support the global transition to sustainable power sources. Future trends emphasize integration of AI-driven grid management, increased use of distributed energy resources, and development of green hydrogen technologies to meet rising energy demands and reduce carbon emissions.
Power Engineer vs Renewable Energy Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com