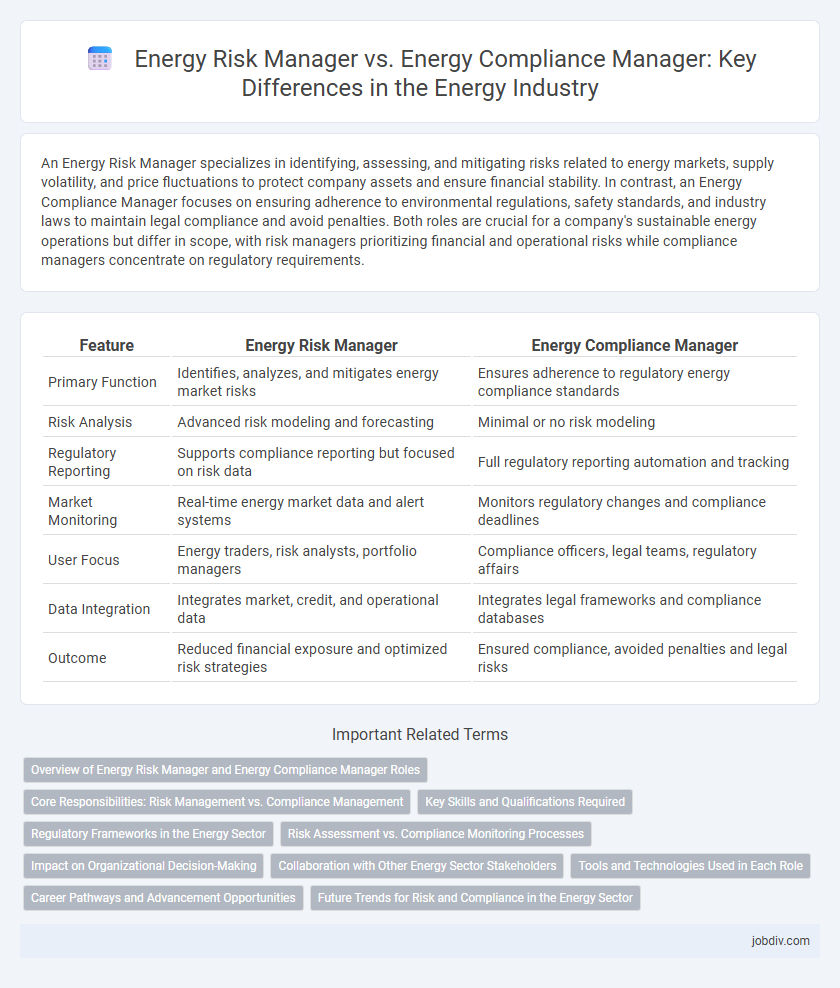
An Energy Risk Manager specializes in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to energy markets, supply volatility, and price fluctuations to protect company assets and ensure financial stability. In contrast, an Energy Compliance Manager focuses on ensuring adherence to environmental regulations, safety standards, and industry laws to maintain legal compliance and avoid penalties. Both roles are crucial for a company's sustainable energy operations but differ in scope, with risk managers prioritizing financial and operational risks while compliance managers concentrate on regulatory requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Energy Risk Manager | Energy Compliance Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Identifies, analyzes, and mitigates energy market risks | Ensures adherence to regulatory energy compliance standards |
| Risk Analysis | Advanced risk modeling and forecasting | Minimal or no risk modeling |
| Regulatory Reporting | Supports compliance reporting but focused on risk data | Full regulatory reporting automation and tracking |
| Market Monitoring | Real-time energy market data and alert systems | Monitors regulatory changes and compliance deadlines |
| User Focus | Energy traders, risk analysts, portfolio managers | Compliance officers, legal teams, regulatory affairs |
| Data Integration | Integrates market, credit, and operational data | Integrates legal frameworks and compliance databases |
| Outcome | Reduced financial exposure and optimized risk strategies | Ensured compliance, avoided penalties and legal risks |
Overview of Energy Risk Manager and Energy Compliance Manager Roles
Energy Risk Managers analyze market trends, manage exposure to price volatility, and develop strategies to mitigate financial risks associated with energy trading and procurement. Energy Compliance Managers ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, oversee reporting protocols, and implement policies to maintain operational compliance within energy markets. Both roles are critical in balancing risk management with regulatory obligations to optimize company performance and safeguard against legal penalties.
Core Responsibilities: Risk Management vs. Compliance Management
Energy Risk Managers specialize in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential financial and operational risks associated with energy markets and assets through risk assessment models and hedging strategies. Energy Compliance Managers focus on ensuring adherence to regulatory standards, environmental laws, and industry-specific guidelines by developing compliance programs and conducting audits. While Risk Managers prioritize minimizing exposure to volatile market conditions and supply disruptions, Compliance Managers safeguard the organization against legal penalties and reputational damage by maintaining strict regulatory conformity.
Key Skills and Qualifications Required
Energy Risk Managers require expertise in risk assessment, quantitative analysis, and market modeling to identify and mitigate energy price volatility and operational risks, often holding certifications like FRM or PRM. Energy Compliance Managers need a deep understanding of regulatory frameworks, environmental laws, and industry standards, with qualifications such as Certified Compliance and Ethics Professional (CCEP) or related legal expertise. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in energy sector regulations and market dynamics.
Regulatory Frameworks in the Energy Sector
Energy Risk Managers focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential financial and operational risks within the energy sector, emphasizing adherence to regulatory frameworks such as the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) guidelines and the European Union's Clean Energy Package. Energy Compliance Managers ensure strict compliance with laws and regulations, including environmental standards like the EPA's Clean Air Act and industry-specific mandates such as the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) standards. Both roles require deep expertise in evolving regulatory landscapes to maintain organizational integrity and avoid penalties in complex energy markets.
Risk Assessment vs. Compliance Monitoring Processes
Energy Risk Managers specialize in risk assessment by identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential threats to energy assets and market volatility through quantitative modeling and scenario analysis. Energy Compliance Managers focus on compliance monitoring processes by ensuring adherence to regulatory standards, conducting audits, and maintaining reporting protocols aligned with energy industry regulations. The risk assessment process emphasizes predictive analytics to manage uncertainties, while compliance monitoring centers on verification and enforcement of legal requirements.
Impact on Organizational Decision-Making
Energy Risk Managers analyze market volatility, price fluctuations, and regulatory changes to guide strategic risk mitigation, directly influencing financial planning and investment decisions. Energy Compliance Managers enforce regulatory standards, ensuring operational practices align with laws, thereby reducing legal liabilities and promoting sustainable governance. Their combined roles enhance organizational decision-making by balancing risk exposure with regulatory adherence, optimizing both financial stability and corporate responsibility.
Collaboration with Other Energy Sector Stakeholders
Energy Risk Managers collaborate closely with traders, analysts, and regulatory bodies to identify, assess, and mitigate market risks, ensuring portfolio stability and regulatory adherence. Energy Compliance Managers engage with legal teams, environmental agencies, and internal audit functions to enforce regulatory frameworks and maintain operational standards across energy projects. Effective collaboration between these roles enhances comprehensive risk management and regulatory compliance within the energy sector.
Tools and Technologies Used in Each Role
Energy Risk Managers utilize advanced risk modeling software, real-time market analytics platforms, and predictive algorithms to assess and mitigate financial exposure in energy trading and asset management. Energy Compliance Managers rely heavily on regulatory reporting systems, compliance management software, and automated audit tools to ensure adherence to environmental regulations, industry standards, and legal requirements. Both roles integrate data visualization technologies and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to support decision-making and internal communication.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Energy Risk Managers specialize in identifying and mitigating financial and operational risks related to energy markets, often advancing into senior risk advisory or chief risk officer roles due to their expertise in risk analysis and strategy development. Energy Compliance Managers focus on ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards, progressing towards senior compliance officer or regulatory affairs director positions by mastering policy interpretation and organizational governance. Career pathways for both roles involve continuous skill enhancement in energy markets, regulatory landscapes, and technology implementation to meet evolving industry demands.
Future Trends for Risk and Compliance in the Energy Sector
Energy Risk Managers are increasingly leveraging AI-driven analytics and real-time data monitoring to anticipate and mitigate market volatility and operational hazards. Energy Compliance Managers are focusing on integrating blockchain technology and automated reporting systems to ensure transparent adherence to evolving environmental regulations and sustainability standards. Both roles are converging towards a digital-first approach, emphasizing proactive risk identification and compliance in a rapidly transforming energy landscape.
Energy Risk Manager vs Energy Compliance Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com