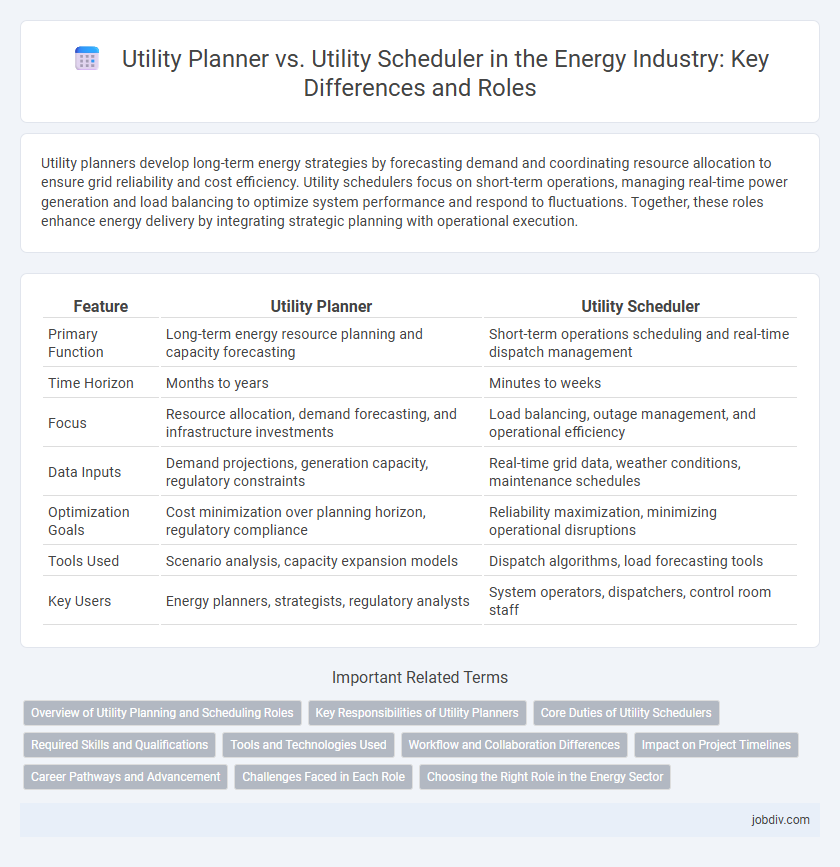
Utility planners develop long-term energy strategies by forecasting demand and coordinating resource allocation to ensure grid reliability and cost efficiency. Utility schedulers focus on short-term operations, managing real-time power generation and load balancing to optimize system performance and respond to fluctuations. Together, these roles enhance energy delivery by integrating strategic planning with operational execution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Utility Planner | Utility Scheduler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Long-term energy resource planning and capacity forecasting | Short-term operations scheduling and real-time dispatch management |
| Time Horizon | Months to years | Minutes to weeks |
| Focus | Resource allocation, demand forecasting, and infrastructure investments | Load balancing, outage management, and operational efficiency |
| Data Inputs | Demand projections, generation capacity, regulatory constraints | Real-time grid data, weather conditions, maintenance schedules |
| Optimization Goals | Cost minimization over planning horizon, regulatory compliance | Reliability maximization, minimizing operational disruptions |
| Tools Used | Scenario analysis, capacity expansion models | Dispatch algorithms, load forecasting tools |
| Key Users | Energy planners, strategists, regulatory analysts | System operators, dispatchers, control room staff |
Overview of Utility Planning and Scheduling Roles
Utility planners analyze long-term energy demand patterns and develop strategic plans to ensure reliable power supply and resource allocation. Utility schedulers coordinate daily operations by managing generation schedules, monitoring grid stability, and adjusting load dispatch in real time. Both roles are critical for optimizing energy resources, minimizing costs, and maintaining grid reliability within power utilities.
Key Responsibilities of Utility Planners
Utility Planners focus on long-term resource allocation, demand forecasting, and infrastructure development to ensure reliable energy supply and cost efficiency. They analyze consumption patterns, evaluate generation capacity, and coordinate with stakeholders to develop strategic energy plans. These responsibilities enable utilities to optimize grid performance and support sustainable energy integration.
Core Duties of Utility Schedulers
Utility schedulers primarily manage the real-time dispatch of electricity generation, ensuring supply meets demand while maintaining grid reliability. They coordinate outage schedules, monitor system conditions, and adjust generation plans to respond to fluctuations and emergencies. Their core duties emphasize operational control and immediate decision-making within the utility's control center environment.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility Planners require strong analytical skills, proficiency in energy market regulations, and expertise in forecasting demand and resource allocation to develop long-term energy plans. Utility Schedulers must excel in real-time decision-making, operational coordination, and knowledge of grid management software to efficiently balance supply and demand during daily operations. Both roles demand a solid understanding of electrical systems, data analysis, and communication skills to ensure reliable energy delivery.
Tools and Technologies Used
Utility planners utilize advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS), load forecasting software, and asset management platforms to optimize resource allocation and long-term infrastructure development. Utility schedulers rely heavily on real-time Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, workforce management tools, and outage management software to coordinate daily operations and maintenance activities efficiently. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies increasingly enhances both roles by improving predictive analytics and decision-making accuracy.
Workflow and Collaboration Differences
Utility Planners focus on long-term resource allocation and strategic project planning, ensuring capacity meets future demand through scenario analysis and load forecasting. Utility Schedulers manage daily operations by coordinating real-time generation dispatch, outage schedules, and field crew activities to maintain grid reliability. Collaboration differences arise as planners provide forecasts and plans that schedulers adapt on a daily basis, requiring seamless information exchange via integrated software platforms for optimal workflow efficiency.
Impact on Project Timelines
Utility Planners develop comprehensive resource allocation strategies that ensure the availability of materials and labor, directly influencing project start dates and minimizing delays. Utility Schedulers focus on sequencing tasks and coordinating workflows to optimize daily operations, which enhances on-site efficiency and adherence to planned milestones. The combined effectiveness of both roles significantly reduces project timeline risks by aligning strategic planning with tactical execution in energy infrastructure projects.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Utility planners focus on long-term infrastructure development and resource allocation, requiring strong analytical skills and strategic foresight for project management roles. Utility schedulers manage daily operational tasks, ensuring efficient workforce deployment and real-time system reliability, often advancing into supervisory or operations manager positions. Career pathways for planners typically lead to senior engineering or planning director roles, while schedulers may progress into field operations management or system control leadership.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Utility planners face challenges in accurately forecasting energy demand and integrating renewable resources into long-term infrastructure plans. Utility schedulers must manage real-time grid stability while balancing fluctuating supply and demand, often navigating unexpected outages or generation variability. Both roles require advanced data analytics and coordination to optimize grid reliability and cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Role in the Energy Sector
Utility Planners focus on long-term energy resource management and demand forecasting to optimize infrastructure investments and ensure reliable power supply. Utility Schedulers handle real-time grid operations, balancing supply and demand by coordinating generation dispatch and maintenance activities. Choosing the right role depends on expertise in strategic planning for system expansion or operational skills for managing daily energy distribution.
Utility Planner vs Utility Scheduler Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com