Energy Risk Managers analyze market trends and operational risks to develop strategies that protect organizations from price volatility and supply disruptions. Energy Procurement Specialists concentrate on sourcing and negotiating contracts for energy supplies to ensure reliable and cost-effective access. Both roles are critical for balancing risk mitigation with securing energy resources efficiently in dynamic markets.
Table of Comparison
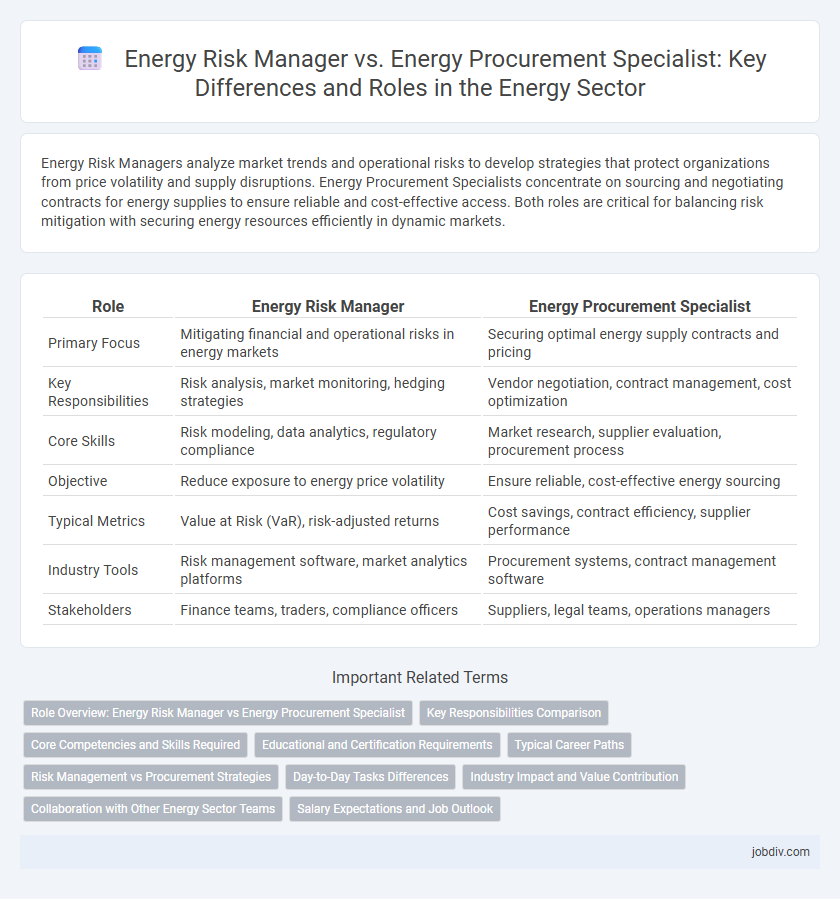
| Role | Energy Risk Manager | Energy Procurement Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Mitigating financial and operational risks in energy markets | Securing optimal energy supply contracts and pricing |
| Key Responsibilities | Risk analysis, market monitoring, hedging strategies | Vendor negotiation, contract management, cost optimization |
| Core Skills | Risk modeling, data analytics, regulatory compliance | Market research, supplier evaluation, procurement process |
| Objective | Reduce exposure to energy price volatility | Ensure reliable, cost-effective energy sourcing |
| Typical Metrics | Value at Risk (VaR), risk-adjusted returns | Cost savings, contract efficiency, supplier performance |
| Industry Tools | Risk management software, market analytics platforms | Procurement systems, contract management software |
| Stakeholders | Finance teams, traders, compliance officers | Suppliers, legal teams, operations managers |
Role Overview: Energy Risk Manager vs Energy Procurement Specialist
Energy Risk Managers specialize in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating financial risks associated with energy markets, using quantitative models and market data to safeguard an organization's energy investments. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on sourcing and purchasing energy supplies, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to ensure cost-effective and reliable energy delivery. Both roles require deep knowledge of energy markets, but Risk Managers prioritize risk mitigation strategies while Procurement Specialists emphasize supplier negotiation and contract execution.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Energy Risk Managers identify, assess, and mitigate risks related to market volatility, regulatory changes, and operational disruptions by developing risk management strategies and monitoring energy portfolios. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on sourcing and purchasing energy supplies, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to ensure cost-effective and reliable energy procurement. Both roles require deep market analysis but differ as Risk Managers emphasize risk mitigation while Procurement Specialists prioritize supply acquisition and cost optimization.
Core Competencies and Skills Required
Energy Risk Managers excel in identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks associated with energy markets, utilizing strong analytical skills, quantitative modeling, and knowledge of market regulations. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring cost-effective energy acquisitions, requiring expertise in vendor management, contract law, and market trends analysis. Both roles demand proficiency in energy market dynamics, strategic decision-making, and regulatory compliance but prioritize risk assessment versus procurement execution.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Energy Risk Managers typically require advanced degrees in finance, economics, or energy management, accompanied by certifications such as Financial Risk Manager (FRM) or Professional Risk Manager (PRM) to demonstrate expertise in market risk analysis and mitigation. Energy Procurement Specialists often hold degrees in supply chain management, business administration, or environmental science, with certifications like Certified Professional in Supply Management (CPSM) or Certified Energy Manager (CEM) emphasizing strategic sourcing and contract negotiation in the energy sector. Both roles benefit from industry-specific knowledge, but certification paths highlight distinct skill sets: risk assessment for Energy Risk Managers and procurement strategy for Energy Procurement Specialists.
Typical Career Paths
Energy Risk Managers often progress from roles in risk analysis or trading, leveraging expertise in market volatility, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation strategies to advance into senior risk management or executive positions. Energy Procurement Specialists typically begin in supply chain or contract negotiation roles, developing skills in supplier management, cost optimization, and procurement strategy before moving into leadership roles within procurement or strategic sourcing departments. Both career paths may intersect at senior management levels where energy market knowledge and strategic decision-making are critical.
Risk Management vs Procurement Strategies
Energy Risk Managers prioritize identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with market volatility, regulatory changes, and operational hazards to safeguard financial stability. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on developing strategic sourcing plans, negotiating contracts, and optimizing supplier relationships to ensure cost-effective energy acquisition. While risk management emphasizes minimizing exposure to uncertainties, procurement strategies concentrate on securing reliable energy supply at optimal terms.
Day-to-Day Tasks Differences
Energy Risk Managers analyze market trends, monitor price fluctuations, and implement strategies to minimize financial exposure to volatile energy markets. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on sourcing energy supplies, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to secure cost-effective and reliable energy resources. While Risk Managers prioritize risk assessment and mitigation, Procurement Specialists handle supplier coordination and contract execution within the energy sector.
Industry Impact and Value Contribution
Energy Risk Managers play a critical role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks associated with market volatility, regulatory changes, and supply chain disruptions, thereby protecting company assets and ensuring operational stability. Energy Procurement Specialists focus on negotiating and securing energy contracts, optimizing supply costs, and managing supplier relationships to guarantee a reliable and cost-effective energy supply. Both positions drive significant industry impact by enhancing organizational resilience and financial performance, with Energy Risk Managers emphasizing risk reduction and Energy Procurement Specialists maximizing procurement efficiency.
Collaboration with Other Energy Sector Teams
Energy Risk Managers collaborate closely with trading teams, finance departments, and regulatory compliance units to identify, assess, and mitigate market and operational risks tied to energy supply and price volatility. Energy Procurement Specialists work in tandem with supply chain managers, contracts teams, and sustainability experts to secure cost-effective, reliable energy sources while aligning procurement strategies with corporate energy goals and regulatory requirements. Both roles require seamless communication and data sharing across risk analysis, procurement planning, and operational execution to optimize overall energy portfolio performance and ensure business continuity.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Energy Risk Managers typically command higher salaries, averaging $95,000 to $130,000 annually, due to their critical role in identifying and mitigating financial risks in volatile energy markets. Energy Procurement Specialists earn between $70,000 and $100,000, focusing primarily on securing cost-effective energy contracts and supplier relationships. Job outlook for both positions remains strong, with Energy Risk Managers experiencing faster growth driven by increasing regulatory complexities and market uncertainties.
Energy Risk Manager vs Energy Procurement Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com