Renewable energy engineers specialize in designing and implementing sustainable energy systems using resources like solar, wind, and hydropower, reducing environmental impact and promoting energy efficiency. Conventional energy engineers focus on traditional power sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, optimizing extraction and combustion processes to meet consistent energy demands. Both roles require strong technical expertise, but renewable engineers prioritize innovation in green technologies while conventional engineers emphasize reliability and cost-effectiveness within established infrastructures.
Table of Comparison
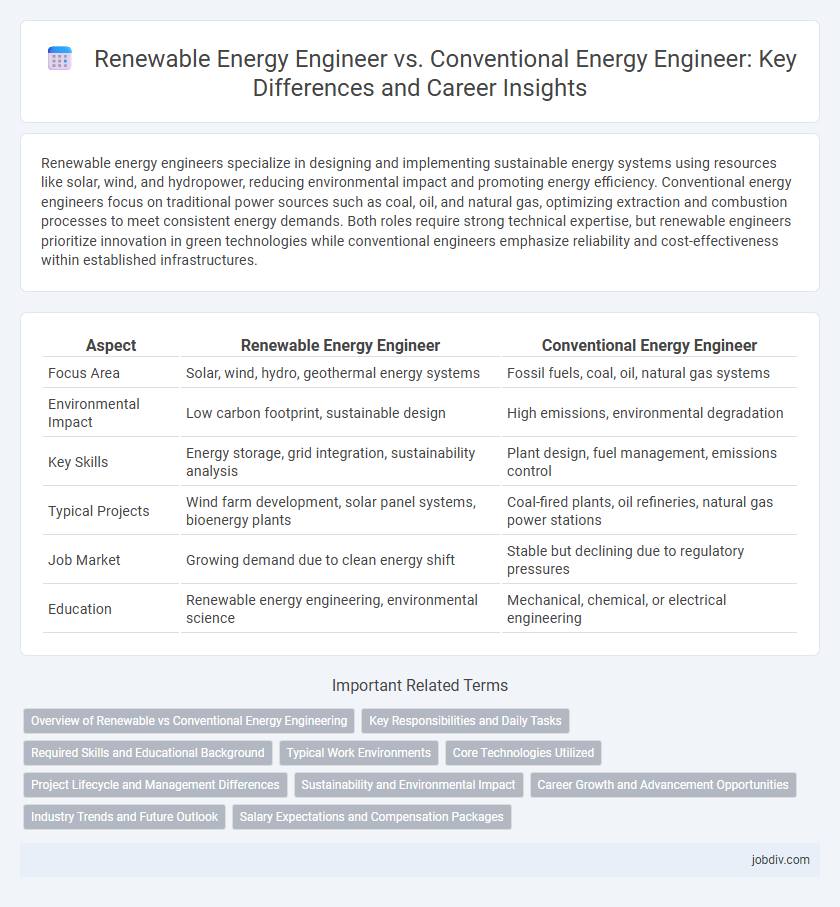
| Aspect | Renewable Energy Engineer | Conventional Energy Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Solar, wind, hydro, geothermal energy systems | Fossil fuels, coal, oil, natural gas systems |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable design | High emissions, environmental degradation |
| Key Skills | Energy storage, grid integration, sustainability analysis | Plant design, fuel management, emissions control |
| Typical Projects | Wind farm development, solar panel systems, bioenergy plants | Coal-fired plants, oil refineries, natural gas power stations |
| Job Market | Growing demand due to clean energy shift | Stable but declining due to regulatory pressures |
| Education | Renewable energy engineering, environmental science | Mechanical, chemical, or electrical engineering |
Overview of Renewable vs Conventional Energy Engineering
Renewable energy engineers specialize in designing and implementing systems that harness natural resources like solar, wind, and geothermal power to create sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions. Conventional energy engineers focus on traditional energy sources such as coal, natural gas, and oil, emphasizing extraction, refinement, and efficiency improvements within established fossil fuel infrastructures. The primary distinction lies in renewable energy engineering's commitment to reducing carbon footprints and promoting environmental sustainability, while conventional energy engineering centers on optimizing existing energy production methods.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Renewable Energy Engineers design and implement sustainable energy systems such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, focusing on optimizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. They conduct feasibility studies, analyze energy yields, and collaborate on integrating smart grid technologies. Conventional Energy Engineers manage fossil fuel-based power generation, oversee plant maintenance, monitor emissions, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards for coal, oil, or natural gas facilities.
Required Skills and Educational Background
Renewable Energy Engineers typically require expertise in sustainable energy technologies, environmental science, and proficiency with solar, wind, and bioenergy systems, often holding degrees in renewable energy engineering or environmental engineering. Conventional Energy Engineers focus on skills related to fossil fuels, thermodynamics, and mechanical systems, with educational backgrounds in petroleum engineering, mechanical engineering, or chemical engineering. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, project management skills, and proficiency in energy modeling software, but the renewable sector emphasizes knowledge of greenhouse gas reduction and energy policy compliance.
Typical Work Environments
Renewable Energy Engineers commonly work in dynamic environments such as wind farms, solar power plants, and research laboratories focused on sustainable technologies. Conventional Energy Engineers are typically found in traditional settings like oil refineries, coal power plants, and natural gas facilities, where fossil fuel extraction and processing occur. Both roles require collaboration in industrial sites and offices, but Renewable Energy Engineers often engage more in outdoor and field-based project implementation.
Core Technologies Utilized
Renewable energy engineers primarily utilize technologies such as solar photovoltaic systems, wind turbines, biomass conversion, and geothermal energy extraction to harness sustainable power sources. Conventional energy engineers focus on core technologies including fossil fuel extraction, thermal power plants, and nuclear reactors that rely on finite resources. Both roles require expertise in energy storage and grid integration, but renewable engineers emphasize emerging smart grid and energy efficiency innovations.
Project Lifecycle and Management Differences
Renewable Energy Engineers oversee project lifecycles that emphasize sustainable resource integration, from feasibility studies of solar, wind, or bioenergy systems to regulatory compliance and environmental impact assessments. Conventional Energy Engineers manage projects centered on fossil fuel extraction and power generation, with a focus on optimizing efficiency, safety protocols, and emission control throughout construction, operation, and decommissioning phases. Renewable projects often involve iterative management due to technology advancements and policy shifts, while conventional energy projects rely on stable, long-established practices and infrastructure frameworks.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Renewable Energy Engineers specialize in designing and implementing sustainable energy systems such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, significantly reducing carbon footprints and mitigating environmental degradation. Conventional Energy Engineers focus on fossil fuel-based systems like coal, oil, and natural gas, which often contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The shift toward renewable energy engineering promotes long-term ecological balance and supports global efforts to combat climate change.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Renewable Energy Engineers experience rapid career growth fueled by expanding global investments in solar, wind, and bioenergy technologies, leading to diverse advancement opportunities in sustainable project management and innovation. Conventional Energy Engineers maintain steady career paths within established sectors like oil, gas, and coal, with advancement often tied to operational expertise and regulatory compliance roles. The increasing emphasis on decarbonization and clean energy policies positions Renewable Energy Engineers for accelerated progression compared to the more traditional, slower-moving advancement landscape in conventional energy.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Renewable energy engineers focus on designing and implementing technologies such as solar, wind, and bioenergy to meet growing global demand for sustainable power solutions, reflecting industry trends toward decarbonization and energy efficiency. Conventional energy engineers specialize in optimizing fossil fuel-based systems, but shifting regulations and market pressures are driving a decline in new projects within coal and oil sectors. The future outlook favors renewable energy engineers due to increasing government incentives, advancements in storage technologies, and corporate commitments to net-zero emissions targets worldwide.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Packages
Renewable energy engineers typically receive competitive salary packages that reflect the growing demand for sustainable technologies, with median annual earnings around $75,000 to $100,000, often supplemented by benefits like bonuses tied to project success and stock options in green energy firms. Conventional energy engineers generally report comparable base salaries, ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually, but their compensation packages frequently include hazard pay, performance incentives, and allowances associated with fossil fuel industry risks. Salary expectations for both roles are influenced by factors such as geographic location, level of expertise, and employer type, with renewable energy sectors showing stronger growth potential in total compensation over time.
Renewable Energy Engineer vs Conventional Energy Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com