Grid operators oversee the entire electricity network, ensuring balance and stability between supply and demand in real-time. Energy dispatchers manage the operational control of power plants and resources, directing the flow of electricity to meet immediate grid requirements efficiently. Coordination between grid operators and energy dispatchers is critical for maintaining reliable energy delivery and optimizing grid performance.
Table of Comparison
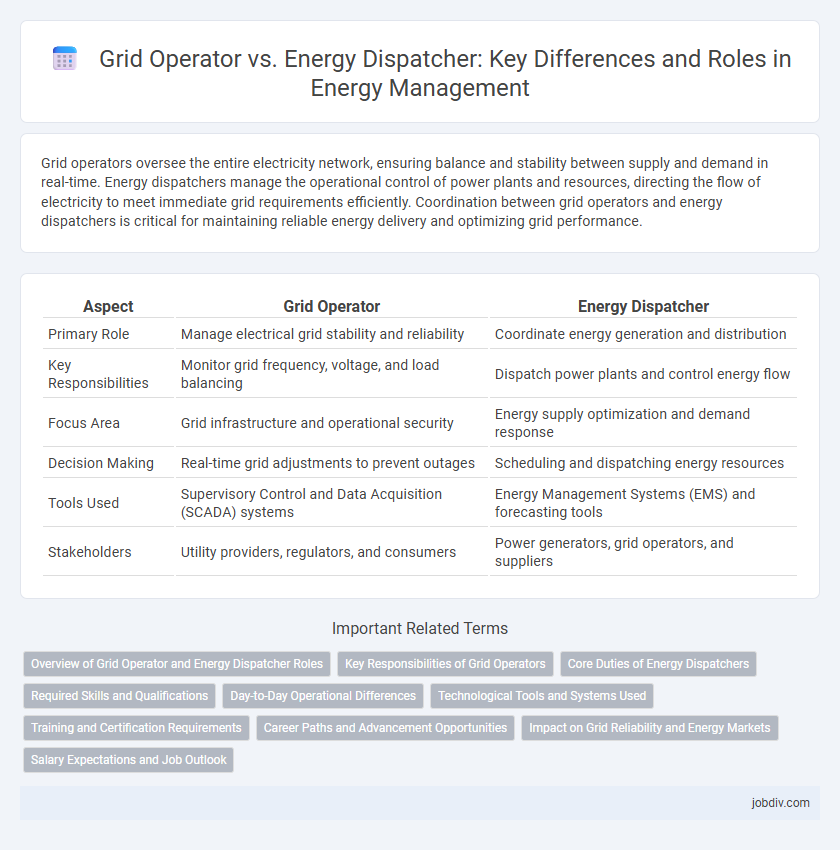
| Aspect | Grid Operator | Energy Dispatcher |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage electrical grid stability and reliability | Coordinate energy generation and distribution |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor grid frequency, voltage, and load balancing | Dispatch power plants and control energy flow |
| Focus Area | Grid infrastructure and operational security | Energy supply optimization and demand response |
| Decision Making | Real-time grid adjustments to prevent outages | Scheduling and dispatching energy resources |
| Tools Used | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems | Energy Management Systems (EMS) and forecasting tools |
| Stakeholders | Utility providers, regulators, and consumers | Power generators, grid operators, and suppliers |
Overview of Grid Operator and Energy Dispatcher Roles
Grid operators maintain the stability and reliability of electrical power systems by monitoring grid conditions, managing power flows, and coordinating with power generators and consumers. Energy dispatchers execute real-time instructions from grid operators to control generation units and balance supply with demand on the energy grid. Both roles are critical for ensuring uninterrupted electricity supply and efficient grid management in complex power networks.
Key Responsibilities of Grid Operators
Grid Operators manage the real-time stability and reliability of the electrical grid by balancing supply and demand, monitoring grid conditions, and coordinating with power plants and substations. They ensure continuous electricity delivery by controlling voltage levels, preventing outages, and responding to emergencies with rapid decision-making. Their key responsibilities include grid frequency regulation, congestion management, and implementation of system protection schemes to maintain overall grid integrity.
Core Duties of Energy Dispatchers
Energy dispatchers manage real-time electricity flow by coordinating power generation and distribution to maintain grid stability and meet demand fluctuations. They monitor system performance, respond to outages or faults, and implement load balancing to prevent blackouts. Unlike grid operators who oversee broader network operations, dispatchers focus on immediate control and operational adjustments within the energy grid.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Grid operators require strong analytical skills, deep knowledge of power systems, and proficiency in SCADA systems to monitor and control electricity flow in real-time. Energy dispatchers must possess excellent decision-making abilities, familiarity with energy market operations, and expertise in load forecasting to efficiently allocate resources and balance supply-demand. Both roles demand technical certifications such as NERC reliability standards and experience with emergency response protocols.
Day-to-Day Operational Differences
Grid operators monitor and control the overall electricity grid to ensure stability and reliability, managing real-time power flows and grid frequency. Energy dispatchers specifically schedule and direct power generation from various sources to meet demand, optimizing cost and resource allocation moment by moment. While grid operators focus on system-wide balance, dispatchers concentrate on executing generation orders within the operator's framework.
Technological Tools and Systems Used
Grid operators utilize advanced SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems and real-time monitoring platforms to oversee electricity transmission networks, ensuring grid stability and load balancing. Energy dispatchers employ sophisticated energy management systems (EMS) and predictive analytics tools to optimize power generation schedules, integrating renewable energy sources and responding to demand fluctuations. Both roles rely on smart grid technologies and IoT sensors to enhance operational efficiency and improve decision-making accuracy.
Training and Certification Requirements
Grid operators require specialized training in real-time grid management, electrical systems, and regulatory compliance, often necessitating certifications like NERC System Operator Certification in North America. Energy dispatchers undergo focused training in load forecasting, energy market operations, and dispatch software, with certifications such as the Certified Energy Dispatcher (CED) enhancing professional credibility. Both roles demand continuous education to keep pace with evolving grid technologies and reliability standards.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Grid Operators manage the real-time coordination and stability of electrical grids, requiring strong skills in system monitoring and emergency response, often leading to advancement into senior operator or control center manager roles. Energy Dispatchers focus on scheduling and dispatching power resources to meet demand efficiently, with career paths advancing toward energy market analysts or dispatch supervisors. Both roles offer progression into specialized positions within energy management, regulatory compliance, or grid modernization projects.
Impact on Grid Reliability and Energy Markets
Grid operators maintain overall power system stability by coordinating real-time electricity flow and managing grid frequency, which directly influences grid reliability and prevents blackouts. Energy dispatchers execute the operational decisions by controlling generation units and load dispatch, affecting energy market efficiency through effective resource allocation and cost optimization. Their combined functions ensure a balanced supply-demand relationship, stabilizing energy prices and supporting market transparency.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Grid Operators typically earn an average salary ranging from $60,000 to $85,000 annually, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade due to increasing grid modernization efforts. Energy Dispatchers usually have a salary range between $55,000 and $75,000, with steady demand driven by the need for real-time energy distribution and crisis management. Both roles offer stable employment opportunities, but Grid Operators may experience higher salary potential linked to advanced technical responsibilities and regulatory compliance.
Grid Operator vs Energy Dispatcher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com