HVAC specialists concentrate on the installation, maintenance, and repair of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to optimize indoor climate control and energy efficiency. Energy auditors assess a building's overall energy consumption, identify inefficiencies, and recommend improvements to reduce energy costs and environmental impact. While HVAC specialists focus on system-specific solutions, energy auditors provide a comprehensive evaluation of energy use across all systems in a facility.
Table of Comparison
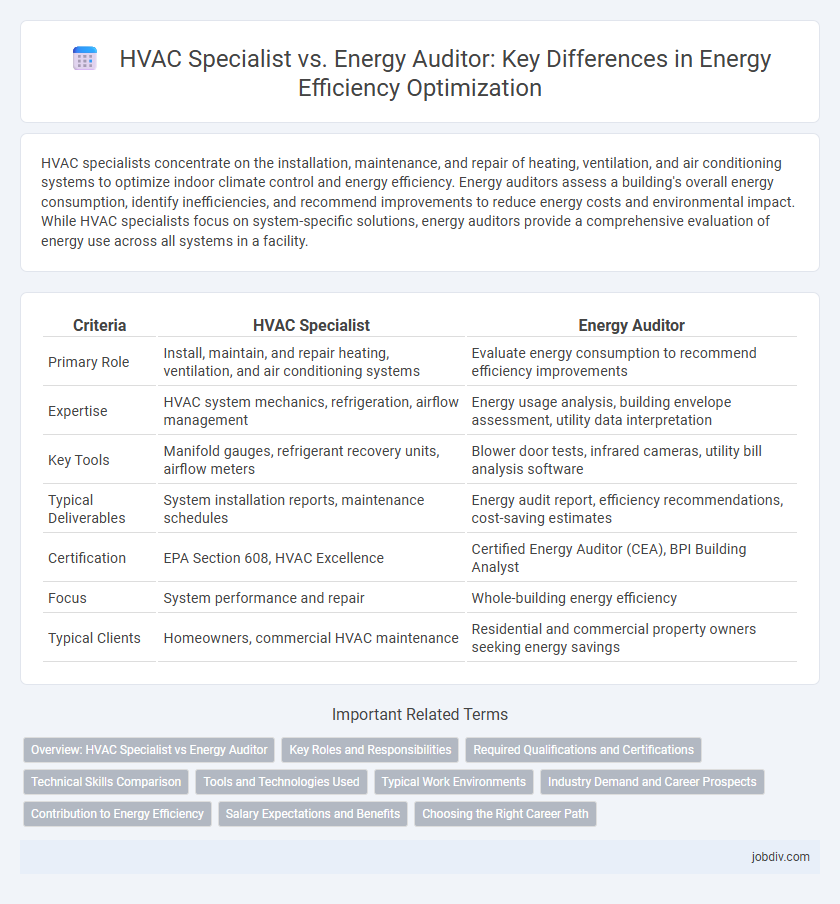
| Criteria | HVAC Specialist | Energy Auditor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Install, maintain, and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems | Evaluate energy consumption to recommend efficiency improvements |
| Expertise | HVAC system mechanics, refrigeration, airflow management | Energy usage analysis, building envelope assessment, utility data interpretation |
| Key Tools | Manifold gauges, refrigerant recovery units, airflow meters | Blower door tests, infrared cameras, utility bill analysis software |
| Typical Deliverables | System installation reports, maintenance schedules | Energy audit report, efficiency recommendations, cost-saving estimates |
| Certification | EPA Section 608, HVAC Excellence | Certified Energy Auditor (CEA), BPI Building Analyst |
| Focus | System performance and repair | Whole-building energy efficiency |
| Typical Clients | Homeowners, commercial HVAC maintenance | Residential and commercial property owners seeking energy savings |
Overview: HVAC Specialist vs Energy Auditor
HVAC specialists focus on designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to optimize indoor climate control and energy efficiency. Energy auditors analyze building energy consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and recommend improvements to reduce overall energy costs and environmental impact. Both roles contribute to energy management but differ in scope, with HVAC specialists handling system-specific tasks and energy auditors providing comprehensive facility-wide energy assessments.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
HVAC specialists focus on the installation, maintenance, and repair of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to optimize indoor climate control and energy efficiency. Energy auditors analyze energy consumption patterns in buildings, identifying inefficiencies and recommending cost-effective measures to reduce energy usage and environmental impact. Both roles contribute to sustainable energy management, with HVAC specialists emphasizing system performance and energy auditors prioritizing overall energy savings strategies.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
HVAC specialists typically require certifications such as EPA Section 608 and Certified HVAC Technician credentials, along with hands-on experience in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Energy auditors generally hold certifications like Building Performance Institute (BPI) Analyst or Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET) HERS Rater, emphasizing skills in energy assessment and efficiency analysis. Both professions demand a strong understanding of energy systems, but auditors focus more on building energy performance while HVAC specialists concentrate on system installation and maintenance.
Technical Skills Comparison
HVAC specialists possess advanced expertise in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, including installation, repair, and maintenance, with proficiency in mechanical diagnostics and system optimization. Energy auditors specialize in energy efficiency assessments, utilizing tools like blower doors and infrared cameras to analyze building envelopes and identify energy loss areas. While HVAC specialists focus on system-level technical skills, energy auditors emphasize comprehensive energy usage analysis and recommendation of cost-effective improvements.
Tools and Technologies Used
HVAC specialists utilize advanced diagnostic tools such as thermal imaging cameras, refrigerant analyzers, and airflow meters to optimize heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for maximum efficiency. Energy auditors employ technologies like blower doors, infrared thermography, and energy modeling software to assess building energy performance and identify opportunities for conservation. Both professionals leverage data analytics platforms to interpret results and recommend improvements tailored to specific energy consumption patterns.
Typical Work Environments
HVAC specialists predominantly work on-site in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, performing installation, maintenance, and repairs of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Energy auditors often operate in a variety of environments including offices, manufacturing plants, and homes, conducting energy assessments and analyzing utility data to recommend efficiency improvements. Both professionals collaborate within buildings but focus on different aspects: HVAC specialists handle mechanical systems, while energy auditors evaluate overall energy consumption and system performance.
Industry Demand and Career Prospects
HVAC specialists are in high demand due to the growing need for efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in residential and commercial buildings, driven by stricter energy codes and sustainability goals. Energy auditors are increasingly sought after as organizations emphasize energy conservation and cost reduction, creating opportunities in energy consulting and sustainability assessments. Both careers offer strong growth prospects, but energy auditors often benefit from expanding roles in renewable energy integration and climate compliance sectors.
Contribution to Energy Efficiency
HVAC specialists optimize heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to enhance building energy performance by ensuring efficient equipment operation and proper system maintenance. Energy auditors conduct comprehensive evaluations of energy use, identifying inefficiencies and recommending targeted improvements across lighting, insulation, and appliance systems. Both roles crucially contribute to reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs, promoting sustainable building management.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
HVAC specialists typically earn a median annual salary of $50,000 to $70,000, benefiting from hands-on technical roles and opportunities for overtime pay. Energy auditors command a similar salary range, often between $55,000 and $75,000, with the advantage of growing demand in energy efficiency consulting and potential bonuses linked to energy savings. Both careers offer benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, but energy auditors may enjoy greater job stability due to increasing regulatory focus on sustainability.
Choosing the Right Career Path
HVAC specialists focus on designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, requiring hands-on technical skills and certifications in system mechanics. Energy auditors analyze buildings' energy consumption to identify efficiency improvements, utilizing knowledge in energy modeling and sustainability standards. Choosing between these careers depends on whether one prefers practical system work or data-driven energy optimization strategies.
HVAC Specialist vs Energy Auditor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com