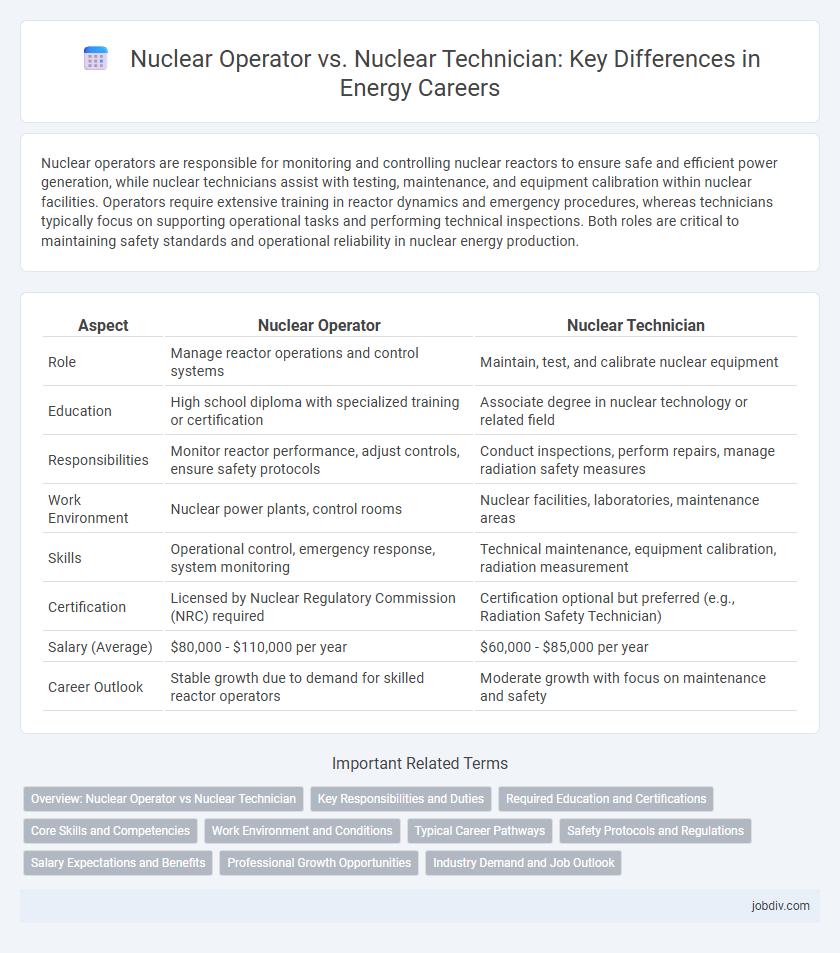
Nuclear operators are responsible for monitoring and controlling nuclear reactors to ensure safe and efficient power generation, while nuclear technicians assist with testing, maintenance, and equipment calibration within nuclear facilities. Operators require extensive training in reactor dynamics and emergency procedures, whereas technicians typically focus on supporting operational tasks and performing technical inspections. Both roles are critical to maintaining safety standards and operational reliability in nuclear energy production.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nuclear Operator | Nuclear Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manage reactor operations and control systems | Maintain, test, and calibrate nuclear equipment |
| Education | High school diploma with specialized training or certification | Associate degree in nuclear technology or related field |
| Responsibilities | Monitor reactor performance, adjust controls, ensure safety protocols | Conduct inspections, perform repairs, manage radiation safety measures |
| Work Environment | Nuclear power plants, control rooms | Nuclear facilities, laboratories, maintenance areas |
| Skills | Operational control, emergency response, system monitoring | Technical maintenance, equipment calibration, radiation measurement |
| Certification | Licensed by Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) required | Certification optional but preferred (e.g., Radiation Safety Technician) |
| Salary (Average) | $80,000 - $110,000 per year | $60,000 - $85,000 per year |
| Career Outlook | Stable growth due to demand for skilled reactor operators | Moderate growth with focus on maintenance and safety |
Overview: Nuclear Operator vs Nuclear Technician
Nuclear Operators manage the control room operations of nuclear power plants, ensuring safe and efficient reactor performance through monitoring and adjustments. Nuclear Technicians support these activities by performing routine maintenance, data collection, and technical inspections to maintain system integrity. Both roles require specialized training in nuclear safety protocols but differ in operational focus, with Operators handling real-time reactor controls and Technicians emphasizing technical support and equipment maintenance.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Nuclear Operators oversee reactor controls, monitor system parameters, and ensure safe plant operations, adhering strictly to regulatory standards and emergency protocols. Nuclear Technicians support operators by conducting routine maintenance, performing equipment inspections, and assisting with testing and calibration of nuclear instruments. Both roles require comprehensive knowledge of nuclear safety procedures, yet operators hold primary responsibility for reactor performance and system integrity.
Required Education and Certifications
Nuclear operators typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, with extensive on-the-job training and certifications such as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) operator license. Nuclear technicians generally need an associate degree in nuclear technology or a related field, along with certifications like the Nuclear Uniform Curriculum Program (NUCP). Both roles demand adherence to strict safety standards and continued education to maintain certification validity.
Core Skills and Competencies
Nuclear Operators excel in reactor operation, safety protocol adherence, and system monitoring, ensuring efficient power generation and regulatory compliance. Nuclear Technicians specialize in equipment maintenance, radiation detection, and data analysis to support reactor stability and minimize environmental impact. Both roles demand strong technical knowledge, attention to detail, and adherence to strict safety standards within nuclear power facilities.
Work Environment and Conditions
Nuclear operators typically work in control rooms within nuclear power plants, managing reactor operations under strict safety protocols and high-pressure environments. Nuclear technicians often perform hands-on maintenance and testing in various plant locations, including radiation-controlled areas, requiring adherence to rigorous safety standards and protective gear. Both roles demand continuous monitoring of radiation levels and compliance with regulatory guidelines to ensure a safe and secure nuclear facility.
Typical Career Pathways
Nuclear Operators typically begin their careers as trainees in power plants, advancing through positions such as control room operator, shift supervisor, and plant manager, often requiring extensive on-the-job training and licensing by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). Nuclear Technicians usually start with an associate degree in nuclear technology or a related field, gaining experience in radiological monitoring, equipment maintenance, and instrumentation calibration, progressing to senior technician or specialist roles in research labs, reactor facilities, or support services. Both career pathways emphasize safety protocols, technical expertise, and regulatory compliance, with opportunities for specialization in reactor operations, health physics, or nuclear instrumentation.
Safety Protocols and Regulations
Nuclear operators strictly adhere to safety protocols outlined by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), ensuring reactor stability and preventing radiation exposure through constant monitoring and control of nuclear systems. Nuclear technicians implement these regulations by conducting routine equipment inspections, radiation measurements, and maintenance tasks to uphold operational safety and compliance standards. Both roles require rigorous training in emergency procedures and regulatory updates to maintain a secure nuclear facility environment.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Nuclear Operators typically earn higher salaries than Nuclear Technicians, with median annual wages around $90,000 compared to $70,000, reflecting their greater responsibility in controlling and monitoring nuclear reactors. Benefits for both roles often include comprehensive health insurance, retirement plans, and paid training, but Operators may receive additional performance bonuses and hazard pay due to the critical nature of their tasks. Salary and benefits vary by region and employer, with opportunities for advancement and overtime pay influencing total compensation in nuclear energy facilities.
Professional Growth Opportunities
Nuclear operators often advance through structured certification programs leading to supervisory roles, plant management, or specialized technical positions within power generation facilities. Nuclear technicians typically experience growth by obtaining additional education or certifications, transitioning into engineering support, radiation protection, or quality assurance roles. Both careers offer pathways to increased responsibility and expertise, with nuclear operators focusing more on operational leadership and technicians on technical problem-solving and regulatory compliance.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Nuclear operators and nuclear technicians both play crucial roles in the energy sector, with nuclear operators primarily responsible for controlling and monitoring nuclear reactors, while nuclear technicians assist in maintenance and technical support tasks. Industry demand for nuclear operators is steady due to strict regulatory requirements and the specialized skills needed to manage reactor safety, resulting in a job outlook aligned closely with the operational status of nuclear power plants. Nuclear technicians face growing opportunities driven by advancements in nuclear technology and decommissioning projects, reflecting a positive employment trend influenced by energy transition efforts and increased investment in nuclear safety and innovation.
Nuclear Operator vs Nuclear Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com