Grip tape provides strong traction and durability, making it ideal for pets' indoor playgrounds or agility courses where secure footing is crucial. Gaffer tape offers a matte finish with strong adhesive properties but is easier to remove without damaging surfaces, suitable for temporary setups or securing decorations during pet events. Choosing between grip and gaffer tape depends on whether long-lasting grip or surface protection and easy removal are priorities in your pet entertainment environment.
Table of Comparison
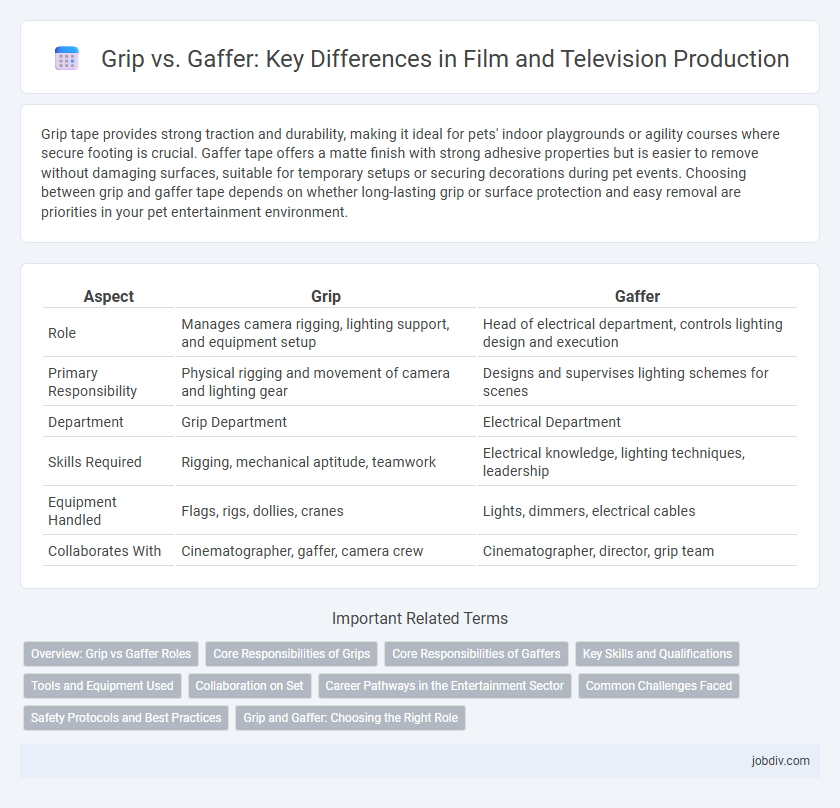
| Aspect | Grip | Gaffer |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages camera rigging, lighting support, and equipment setup | Head of electrical department, controls lighting design and execution |
| Primary Responsibility | Physical rigging and movement of camera and lighting gear | Designs and supervises lighting schemes for scenes |
| Department | Grip Department | Electrical Department |
| Skills Required | Rigging, mechanical aptitude, teamwork | Electrical knowledge, lighting techniques, leadership |
| Equipment Handled | Flags, rigs, dollies, cranes | Lights, dimmers, electrical cables |
| Collaborates With | Cinematographer, gaffer, camera crew | Cinematographer, director, grip team |
Overview: Grip vs Gaffer Roles
Grips are primarily responsible for setting up, adjusting, and maintaining equipment that supports the camera, such as tripods, dollies, and rigs, ensuring smooth camera movements and safety on set. Gaffers handle the lighting design and electrical aspects, managing light setup, power distribution, and ensuring the director's vision for visual tone and mood is achieved. Both roles are essential in film and television production, collaborating closely to enhance the visual storytelling through precise camera and lighting coordination.
Core Responsibilities of Grips
Grips specialize in the physical aspects of film production, managing and maintaining equipment that supports cameras, such as dollies, tracks, and cranes, to ensure smooth and stable shots. They handle rigging, lighting modifications, and safety protocols on set, collaborating closely with the gaffer who is responsible for electrical lighting. Their expertise in setting up and adjusting mechanical equipment is essential for achieving precise camera movements and enhancing overall production quality.
Core Responsibilities of Gaffers
Gaffers are primarily responsible for the design and execution of the lighting plan on film and television sets, ensuring the desired mood and visual aesthetics are achieved through precise control of lighting instruments. They manage the electrical distribution and coordinate with the director of photography to adjust intensity, color, and placement of lights. Their expertise in rigging, power management, and safety protocols is critical for creating an efficient and visually compelling production environment.
Key Skills and Qualifications
Grips require expertise in camera rigging, lighting modification, and equipment safety to ensure smooth on-set operations, emphasizing physical strength and technical problem-solving skills. Gaffers specialize in electrical knowledge, lighting design, and power distribution, holding certifications in electrical safety and experience with various lighting instruments. Both roles demand strong communication, teamwork abilities, and a thorough understanding of film production workflows to collaborate effectively with directors and cinematographers.
Tools and Equipment Used
Grips use tools such as C-clamps, dolly tracks, and rigging hardware to manipulate camera movement and support lighting setups on set. Gaffers rely on electrical equipment like dimmers, cable snakes, and various lighting instruments to control intensity, color, and direction of the lights. Both roles require specialized gear tailored to their distinct functions in film and television production.
Collaboration on Set
The grip and gaffer collaborate closely on set to ensure seamless lighting and camera movement, optimizing the visual storytelling process. Grips handle rigging and equipment support, coordinating with the gaffer who controls the lighting design and electrical needs. This teamwork enhances efficiency, safety, and creative execution during film and television production.
Career Pathways in the Entertainment Sector
Careers as a grip or gaffer in the entertainment sector offer distinct pathways, with grips specializing in camera rigging, lighting support, and equipment setup, while gaffers focus on the design and execution of lighting plans for film productions. Grip roles often require hands-on technical skills and experience with rigging equipment, progressing from key grip positions to departmental leadership, whereas gaffers advance through lighting technician roles to become chief lighting electricians, collaborating closely with directors of photography. Both pathways demand strong technical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and teamwork within film crews, offering numerous opportunities in film, television, and commercial productions.
Common Challenges Faced
Grips and gaffers often face common challenges such as managing complex lighting setups and ensuring seamless coordination on set to maintain visual continuity. Both roles require quick problem-solving skills to adapt to unexpected changes in equipment or environment, which can impact production schedules. Efficient communication and technical expertise are crucial to overcoming obstacles related to rigging, power distribution, and lighting adjustments in dynamic filming environments.
Safety Protocols and Best Practices
Grips and gaffers play crucial roles in entertainment production, each adhering to strict safety protocols to prevent on-set injuries and equipment damage. Grips focus on rigging and camera support systems, following best practices such as regular equipment inspections and secure load management to ensure stability during shooting. Gaffers manage lighting setups with emphasis on electrical safety, proper cable organization, and using protective gear to minimize risks associated with high-voltage equipment.
Grip and Gaffer: Choosing the Right Role
Grips are responsible for setting up, maintaining, and operating camera rigs and lighting supports, ensuring smooth camera movement and safety on set. Gaffers specialize in designing and executing the lighting plan, controlling the intensity, color, and placement of lights to achieve the director's visual vision. Selecting between a Grip and a Gaffer depends on whether the project's priority lies in camera stabilization or lighting design expertise.
Grip vs Gaffer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com