A Location Manager oversees site logistics, securing permits, coordinating with property owners, and managing on-site operations to ensure smooth production flow. In contrast, a Scout specializes in identifying and recommending potential filming locations that fit the creative vision and practical requirements of the project. Both roles are essential in entertainment production, with the Scout focusing on location discovery and the Location Manager handling execution and management on set.
Table of Comparison
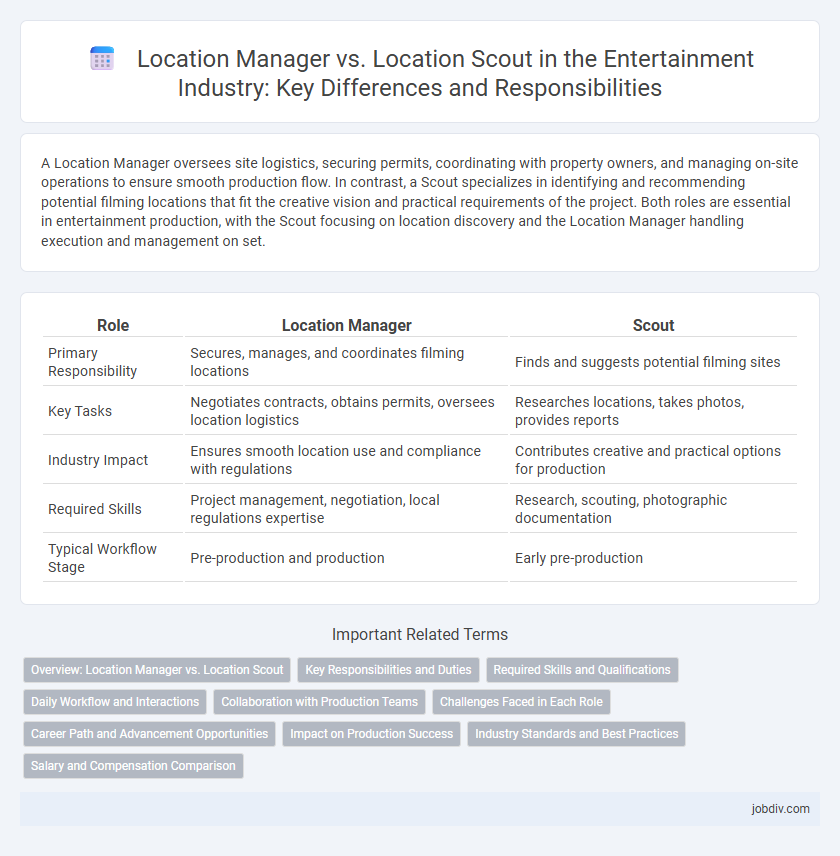
| Role | Location Manager | Scout |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Secures, manages, and coordinates filming locations | Finds and suggests potential filming sites |
| Key Tasks | Negotiates contracts, obtains permits, oversees location logistics | Researches locations, takes photos, provides reports |
| Industry Impact | Ensures smooth location use and compliance with regulations | Contributes creative and practical options for production |
| Required Skills | Project management, negotiation, local regulations expertise | Research, scouting, photographic documentation |
| Typical Workflow Stage | Pre-production and production | Early pre-production |
Overview: Location Manager vs. Location Scout
Location Managers oversee the entire logistics and coordination of film or television shoot locations, ensuring permits, contracts, and on-site needs are managed efficiently. Location Scouts specialize in finding and recommending suitable shooting locations that match the director's vision, often conducting extensive research and site visits. Both roles are crucial in production, with Scouts focusing on discovery and creative input, while Managers handle administrative and operational execution.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Location Managers secure filming sites, handle permits, and coordinate logistics to ensure seamless production flow, while Location Scouts primarily identify and propose potential locations that fit the director's vision. Location Managers oversee site management during shoots, troubleshoot on-site issues, and liaise with local authorities, whereas Scouts focus on researching environments, taking preliminary photos, and presenting options for approval. Both roles require extensive knowledge of geography and regulations, but Location Managers emphasize operational execution while Scouts prioritize creative location discovery.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Location Managers require strong organizational skills, project management experience, and in-depth knowledge of local regulations and permits for film production sites. Location Scouts focus on creativity, excellent research abilities, and keen observational skills to identify and evaluate potential filming locations. Both roles benefit from strong communication, negotiation skills, and familiarity with the entertainment industry's spatial and logistical demands.
Daily Workflow and Interactions
Location Managers oversee site logistics, coordinate with property owners, and manage permits to ensure smooth daily operations on set. Scouts dedicate their workflow to researching, visiting, and photographing potential filming sites, presenting options aligned with the director's vision. Both roles maintain constant communication with production teams, but Location Managers handle on-site problem-solving while Scouts focus on pre-production scouting and evaluation.
Collaboration with Production Teams
Location Managers and Scouts play crucial roles in entertainment production by working closely with production teams to identify and secure ideal filming sites. Location Managers coordinate logistics, permits, and schedules to ensure seamless integration with the production timeline and budget constraints. Scouts provide creative input by presenting diverse options that match the director's vision, enhancing the overall aesthetic and narrative impact of the project.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Location Managers coordinate logistics, secure permits, and manage on-site challenges such as weather disruptions and local regulations, requiring strong negotiation and problem-solving skills. Location Scouts face pressure to find visually compelling, accessible sites within budget constraints and tight schedules while anticipating potential production issues. Both roles demand adaptability and thorough knowledge of the filming environment to ensure seamless production workflows.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
A Location Manager oversees site logistics and coordinates with production teams, requiring experience in location scouting and project management. Scouts focus on discovering and assessing potential filming sites, serving as an entry point into the location department. Advancement opportunities often lead from scouting roles into location management, production supervision, or broader logistics positions within the entertainment industry.
Impact on Production Success
A Location Manager plays a pivotal role in securing and managing film sites, ensuring logistical feasibility and compliance with permits, which directly influences production efficiency. In contrast, a Location Scout concentrates on discovering visually compelling and narrative-enhancing locations, shaping the film's aesthetic and storytelling impact. Both roles significantly affect production success, with the Manager optimizing operational workflow while the Scout enhances creative vision.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Location Managers oversee site logistics, negotiate permits, and ensure compliance with local regulations, establishing industry standards for operational efficiency in film production. Scouts specialize in identifying visually compelling and technically feasible locations, adhering to best practices in scouting for safety, accessibility, and creative alignment with the script. Collaboration between these roles upholds production quality, budget constraints, and legal requirements, crucial for smooth on-set execution.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Location Managers typically earn a median annual salary of $67,000, with potential bonuses and overtime pay increasing total compensation, while Location Scouts generally receive lower base salaries averaging around $45,000 per year but may benefit from per diem and travel reimbursements. Salary variations depend on production budget, geographic location, and industry experience, with union contracts sometimes influencing wages for both roles. Differences in compensation reflect the distinct responsibilities, where managers oversee logistics and contracts, and scouts focus on site discovery and preliminary approvals.
Location Manager vs Scout Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com