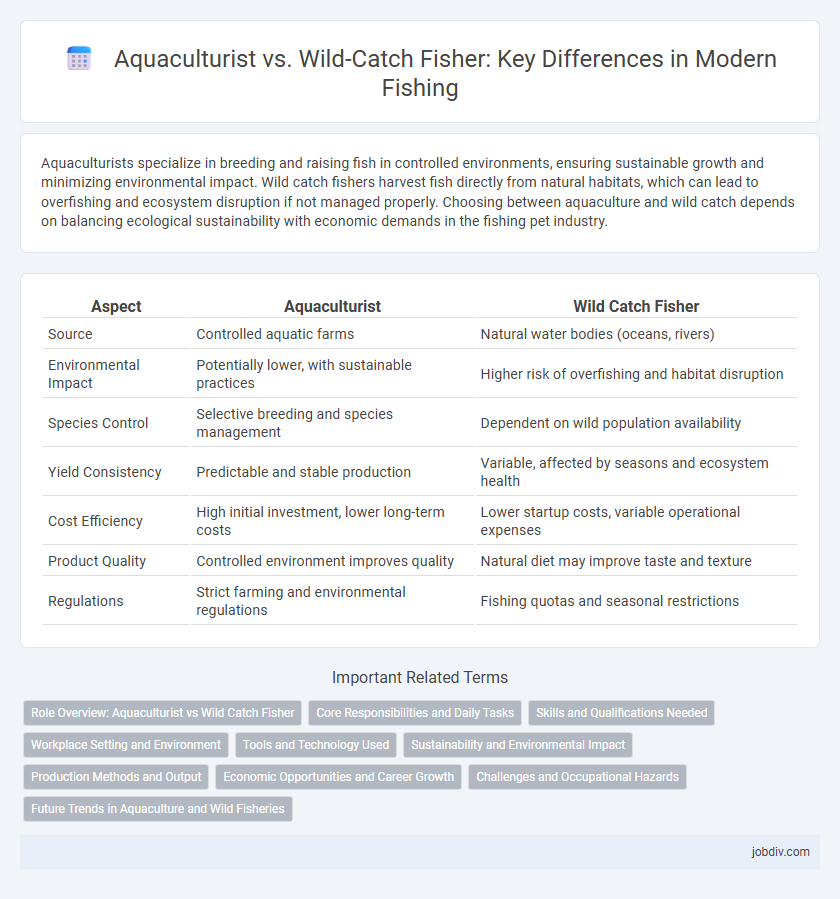
Aquaculturists specialize in breeding and raising fish in controlled environments, ensuring sustainable growth and minimizing environmental impact. Wild catch fishers harvest fish directly from natural habitats, which can lead to overfishing and ecosystem disruption if not managed properly. Choosing between aquaculture and wild catch depends on balancing ecological sustainability with economic demands in the fishing pet industry.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aquaculturist | Wild Catch Fisher |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Controlled aquatic farms | Natural water bodies (oceans, rivers) |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower, with sustainable practices | Higher risk of overfishing and habitat disruption |
| Species Control | Selective breeding and species management | Dependent on wild population availability |
| Yield Consistency | Predictable and stable production | Variable, affected by seasons and ecosystem health |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment, lower long-term costs | Lower startup costs, variable operational expenses |
| Product Quality | Controlled environment improves quality | Natural diet may improve taste and texture |
| Regulations | Strict farming and environmental regulations | Fishing quotas and seasonal restrictions |
Role Overview: Aquaculturist vs Wild Catch Fisher
Aquaculturists specialize in breeding, raising, and harvesting fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments such as tanks, ponds, or ocean enclosures, ensuring sustainable seafood production. Wild catch fishers focus on harvesting fish and other marine species directly from natural water bodies like oceans, rivers, and lakes, often relying on traditional or commercial fishing methods. Both roles contribute significantly to the seafood supply chain but differ in their impact on ecosystems and resource management practices.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Aquaculturists manage the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of aquatic organisms in controlled environments, ensuring optimal water quality and nutrition for species like fish, shellfish, and algae. Wild catch fishers focus on locating, capturing, and preserving marine life in natural habitats using various fishing gear such as nets, lines, and traps while adhering to sustainable fishing regulations. Both roles require monitoring environmental conditions and maintaining equipment to maximize yield and promote ecological balance.
Skills and Qualifications Needed
Aquaculturists require expertise in aquatic biology, water quality management, and sustainable farming techniques, often holding degrees in marine science or aquaculture. Wild catch fishers need strong navigation skills, knowledge of fish behavior, and proficiency with fishing gear, typically acquired through hands-on experience and certifications in marine safety. Both professions demand physical endurance and awareness of environmental regulations to ensure responsible fishing practices.
Workplace Setting and Environment
Aquaculturists typically work in controlled environments such as hatcheries, ponds, or tanks where water quality, temperature, and species breeding conditions are carefully monitored to optimize aquatic life growth. Wild catch fishers operate primarily in open water settings including oceans, rivers, and lakes, facing unpredictable weather, varying sea conditions, and the physical demands of navigating and harvesting fish in natural habitats. The workplace setting for aquaculturists is generally more stable and regulated, whereas wild catch fishers encounter dynamic and often hazardous conditions requiring specialized vessels and equipment for sustainable harvesting.
Tools and Technology Used
Aquaculturists utilize advanced technologies such as automated feeding systems, water quality sensors, and selective breeding tools to enhance fish growth and health within controlled environments. Wild catch fishers rely on traditional gear like nets, traps, hooks, and increasingly employ GPS, sonar, and fish finders to locate and harvest fish efficiently. The integration of modern technology in both sectors aims to optimize yield while promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aquaculturists promote sustainability by cultivating fish in controlled environments, reducing pressure on wild populations and minimizing habitat destruction. Wild catch fishers often face challenges with overfishing and bycatch, which can deplete marine ecosystems and disrupt biodiversity. Sustainable aquaculture practices, such as using eco-friendly feed and avoiding chemical pollutants, contribute to lower environmental impact compared to conventional wild fishing methods.
Production Methods and Output
Aquaculturists cultivate aquatic organisms in controlled environments, enabling consistent production and efficient resource use, often leading to higher yields per area compared to wild catch fishing. Wild catch fishers rely on harvesting fish from natural habitats, resulting in variable output influenced by seasonal and environmental factors, often leading to fluctuating supply levels. Production methods in aquaculture emphasize sustainability and disease control, whereas wild capture techniques face challenges like overfishing and habitat degradation.
Economic Opportunities and Career Growth
Aquaculturists benefit from a rapidly expanding global industry valued at over $250 billion, offering stable employment and opportunities in sustainable seafood production. Wild catch fishers face fluctuating income due to variable fish stocks and regulatory constraints, limiting long-term economic security. Career growth in aquaculture includes advancements in biotechnology, environmental management, and supply chain logistics, contrasting with the traditional roles and seasonal nature of wild fishing.
Challenges and Occupational Hazards
Aquaculturists face challenges such as disease outbreaks, water quality management, and the need for continuous monitoring of fish health to ensure sustainable production. Wild catch fishers encounter occupational hazards including unpredictable weather conditions, physical injuries from handling heavy equipment, and risks of drowning during extended hours at sea. Both professions require specialized skills to mitigate environmental and safety risks inherent to their respective practices.
Future Trends in Aquaculture and Wild Fisheries
Rapid advancements in aquaculture technology, including recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) and genetic improvements, are driving sustainable seafood production to meet global demand. Wild catch fisheries face increasing challenges from overfishing, climate change, and habitat degradation, prompting stricter regulations and conservation efforts. Integrating ecosystem-based management and digital monitoring tools is essential for balancing productivity and environmental health in both industries.
Aquaculturist vs Wild Catch Fisher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com