Purse seiners target large schools of fish like tuna using a massive wall of netting to encircle and capture them efficiently, while lobster fishers employ traps or pots baited to attract lobsters crawling on the ocean floor. Purse seining is a fast-paced method focused on pelagic species, whereas lobster fishing relies on patience and knowledge of benthic habitats. Both techniques require specialized equipment and skills tailored to their distinct marine environments and target species.
Table of Comparison
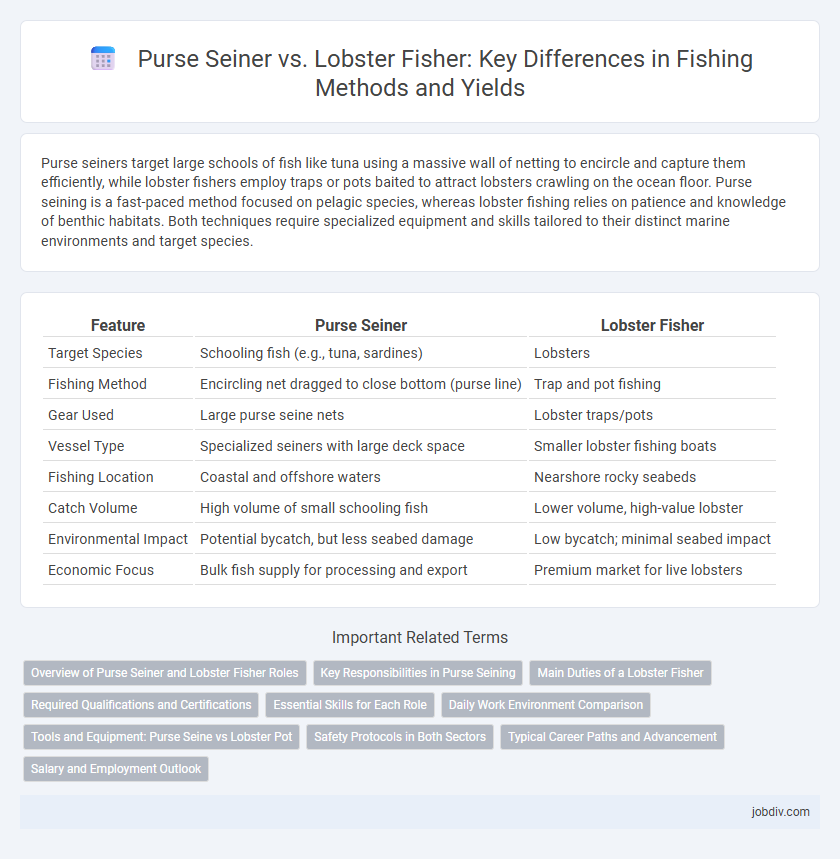
| Feature | Purse Seiner | Lobster Fisher |
|---|---|---|
| Target Species | Schooling fish (e.g., tuna, sardines) | Lobsters |
| Fishing Method | Encircling net dragged to close bottom (purse line) | Trap and pot fishing |
| Gear Used | Large purse seine nets | Lobster traps/pots |
| Vessel Type | Specialized seiners with large deck space | Smaller lobster fishing boats |
| Fishing Location | Coastal and offshore waters | Nearshore rocky seabeds |
| Catch Volume | High volume of small schooling fish | Lower volume, high-value lobster |
| Environmental Impact | Potential bycatch, but less seabed damage | Low bycatch; minimal seabed impact |
| Economic Focus | Bulk fish supply for processing and export | Premium market for live lobsters |
Overview of Purse Seiner and Lobster Fisher Roles
Purse seiners deploy large nets to encircle entire schools of pelagic fish like tuna and sardines, targeting massive catches for commercial markets. Lobster fishers use traps or pots baited to attract lobsters, prioritizing sustainable harvesting from the sea floor. Both roles demand specialized knowledge of marine ecosystems but differ significantly in gear, target species, and fishing techniques.
Key Responsibilities in Purse Seining
Purse seiners primarily focus on deploying large nets around schools of fish, typically targeting species like tuna and sardines, to efficiently encircle and capture them in bulk. Their key responsibilities include setting and hauling the seine net, strategically coordinating with crew members to maximize catch, and ensuring the integrity of the net to prevent losses. Precision in navigation and understanding fish behavior are critical for purse seiners to optimize catch rates and maintain sustainable fishing practices.
Main Duties of a Lobster Fisher
A lobster fisher primarily focuses on setting, checking, and retrieving lobster traps to harvest lobsters while ensuring sustainable practices to protect the marine ecosystem. They must navigate and operate boats in coastal waters, maintain and repair traps, and comply with seasonal regulations and quotas to maximize lobster yield. Unlike purse seiners who capture large quantities of fish using nets, lobster fishers rely on specialized gear and manual labor to trap individual lobsters, emphasizing species-specific knowledge and careful handling.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Purse seiners typically require certification in marine safety, vessel operation, and fish handling, often needing a Commercial Fishing License and endorsements specific to net fishing techniques. Lobster fishers must possess a Lobster Trap Certificate or similar permits, alongside training in trap setting, retrieval, and compliance with local fisheries regulations to ensure sustainable harvesting. Both roles demand knowledge of navigation, maritime safety, and adherence to environmental protection laws to meet industry standards.
Essential Skills for Each Role
Purse seiners require precise boat maneuvering, expert net deployment, and strong teamwork to efficiently encircle and capture large schools of fish like sardines or tuna. Lobster fishers must master trap setting, baiting techniques, and navigation of rough coastal waters to locate and retrieve traps while ensuring sustainable catch practices. Both roles demand keen observation, physical endurance, and knowledge of maritime safety protocols to operate effectively.
Daily Work Environment Comparison
Purse seiners operate primarily on large fishing vessels navigating open waters, often enduring long hours with exposure to harsh weather and the physical demands of handling heavy nets to catch schooling fish. Lobster fishers work from smaller boats closer to shore, frequently managing traps and lines in more confined spaces while contending with cold, wet conditions and the repetitive manual labor of hauling lobster pots. Both professions require resilience and expertise but differ markedly in vessel size, methods, and the types of physical challenges encountered daily.
Tools and Equipment: Purse Seine vs Lobster Pot
Purse seiners rely on large, fine mesh nets called purse seines, designed to encircle and capture schools of fish efficiently in open waters. Lobster fishers use sturdy lobster pots or traps made from wire or wood with bait compartments to lure and capture lobsters on the ocean floor. The equipment in purse seining emphasizes rapid deployment and retrieval, while lobster fishing gear focuses on durability and selective trapping.
Safety Protocols in Both Sectors
Purse seiners implement safety protocols including regular equipment inspections, life jacket mandates, and emergency drills to mitigate risks associated with net handling and vessel maneuvering. Lobster fishers emphasize protective gear, communication systems, and strict adherence to weather advisories to prevent accidents during trap retrieval in rough seas. Both sectors prioritize crew training and emergency preparedness to enhance safety outcomes and reduce injury rates on board.
Typical Career Paths and Advancement
Purse seiners often begin their careers as deckhands, progressing to skiff skippers or net tenders before advancing to captain roles managing entire vessels and coordinating large-scale pelagic fish harvests, with opportunities to transition into fisheries management or vessel ownership. Lobster fishers typically start as crew members learning crab and trap setting techniques, moving up to captains who plan trap deployments and oversee seasonal harvesting of benthic species, with potential advancement into quota leasing, processing, or regulatory positions within the shellfish industry. Both careers demand extensive knowledge of maritime navigation, gear operation, and local marine ecosystems, fostering progression through hands-on experience and industry networking.
Salary and Employment Outlook
Purse seiners typically earn between $40,000 and $70,000 annually, with employment opportunities concentrated in coastal regions with abundant schooling fish, reflecting steady demand in commercial fishing industries. Lobster fishers often make higher incomes, ranging from $50,000 to over $100,000 per year due to premium market prices for lobster, though their employment outlook is more seasonal and geographically limited to colder Atlantic waters. Both careers face challenges such as regulatory changes and environmental factors, but lobster fishing offers greater earning potential with fluctuating seasonal work, while purse seining provides more consistent year-round employment.
Purse Seiner vs Lobster Fisher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com