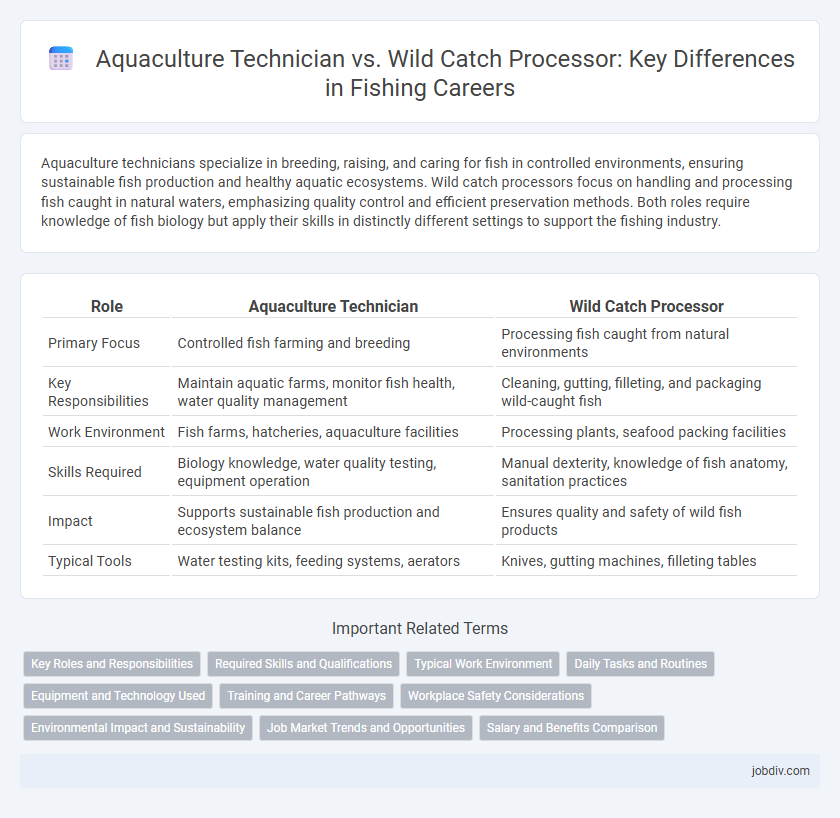
Aquaculture technicians specialize in breeding, raising, and caring for fish in controlled environments, ensuring sustainable fish production and healthy aquatic ecosystems. Wild catch processors focus on handling and processing fish caught in natural waters, emphasizing quality control and efficient preservation methods. Both roles require knowledge of fish biology but apply their skills in distinctly different settings to support the fishing industry.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Aquaculture Technician | Wild Catch Processor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Controlled fish farming and breeding | Processing fish caught from natural environments |
| Key Responsibilities | Maintain aquatic farms, monitor fish health, water quality management | Cleaning, gutting, filleting, and packaging wild-caught fish |
| Work Environment | Fish farms, hatcheries, aquaculture facilities | Processing plants, seafood packing facilities |
| Skills Required | Biology knowledge, water quality testing, equipment operation | Manual dexterity, knowledge of fish anatomy, sanitation practices |
| Impact | Supports sustainable fish production and ecosystem balance | Ensures quality and safety of wild fish products |
| Typical Tools | Water testing kits, feeding systems, aerators | Knives, gutting machines, filleting tables |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Aquaculture technicians manage the breeding, nurturing, and health monitoring of farmed fish and aquatic organisms, ensuring optimal water quality and disease control for sustainable production. Wild catch processors handle the sorting, cleaning, and packaging of seafood harvested from natural habitats, emphasizing quality control and regulatory compliance. Both roles require knowledge of marine biology and seafood safety standards but differ in operational environments and specific technical tasks.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Aquaculture Technicians require knowledge in aquatic biology, water quality management, and fish health monitoring, often needing certifications in aquaculture practices and equipment operation. Wild Catch Processors must have skills in fish handling, sorting, and preservation techniques, with qualifications typically emphasizing food safety standards and seafood processing regulations. Both roles demand physical stamina and attention to detail, but Aquaculture Technicians focus more on environmental controls while Wild Catch Processors prioritize efficient product handling.
Typical Work Environment
Aquaculture Technicians typically work in controlled environments such as hatcheries, fish farms, and aquatic laboratories where water quality and fish health are closely monitored. Wild Catch Processors operate in more variable conditions including fish processing plants, docks, and sometimes aboard fishing vessels, handling freshly caught seafood under strict time constraints. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols, but the Aquaculture Technician environment emphasizes biotechnological control, while Wild Catch Processors deal with high-volume, fast-paced processing settings.
Daily Tasks and Routines
Aquaculture technicians monitor water quality, feed aquatic species, and maintain breeding tanks in controlled environments to ensure optimal growth and health. Wild catch processors handle the receipt, inspection, cleaning, gutting, and packaging of fish caught from natural habitats, following strict safety and quality standards. Both roles require attention to detail and adherence to industry regulations but differ significantly in their focus on cultivating versus handling wild seafood.
Equipment and Technology Used
Aquaculture Technicians primarily utilize advanced monitoring systems such as water quality sensors, automated feeders, and biofiltration units to maintain optimal conditions in controlled aquatic environments. Wild Catch Processors rely on specialized machinery like fish graders, automated filleting machines, and refrigeration technology to efficiently process and preserve freshly caught seafood. The integration of IoT devices in aquaculture enhances precision farming, while wild catch operations emphasize rapid sorting and cold chain management for product quality.
Training and Career Pathways
Aquaculture Technicians typically undergo specialized training in hatchery management, water quality control, and aquatic animal health, often earning certifications or degrees in aquaculture or marine biology. Wild Catch Processors usually receive on-the-job training focused on fish handling, processing techniques, and safety protocols to ensure product quality and compliance with regulations. Career pathways for Aquaculture Technicians often lead to roles in fish farm management or aquatic research, while Wild Catch Processors may advance to supervisory positions within seafood processing plants or quality control.
Workplace Safety Considerations
Aquaculture Technicians primarily work in controlled environments such as fish farms, where they implement biosecurity measures and monitor water quality to prevent contamination and ensure aquatic health, reducing exposure to environmental hazards. Wild Catch Processors operate in dynamic, often harsh conditions on fishing vessels or docks, facing risks like heavy machinery, slippery surfaces, and unpredictable weather, requiring stringent adherence to safety protocols and protective gear. Both roles demand specialized training in workplace safety, but the controlled nature of aquaculture generally offers a more stable and regulated safety environment compared to the variable and high-risk settings of wild catch processing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aquaculture technicians contribute to sustainable seafood production by managing fish farms that reduce overfishing and habitat destruction, employing eco-friendly practices like water recycling and disease control. Wild catch processors handle fish from natural habitats, often facing challenges related to bycatch, overexploitation, and ecosystem disruption, which can negatively impact marine biodiversity. Emphasizing responsible aquaculture techniques can mitigate environmental impacts more effectively than conventional wild catch processing methods.
Job Market Trends and Opportunities
Aquaculture technicians benefit from the expanding global aquaculture industry, which is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% through 2030 due to rising demand for sustainable seafood. Wild catch processors face more fluctuating job opportunities influenced by regulatory measures and environmental changes affecting wild fish stocks, with job growth in this sector expected to remain steady but limited. Emerging technologies and stricter sustainability practices in aquaculture are driving increased investment and hiring in aquaculture technician roles compared to the more traditional wild catch processing jobs.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Aquaculture Technicians typically earn between $30,000 and $45,000 annually, benefiting from structured work schedules, health insurance, and opportunities for skill development in controlled aquatic environments. Wild Catch Processors often receive hourly wages ranging from $12 to $20, with seasonal employment leading to less job stability but sometimes benefiting from overtime pay and hazard pay due to physically demanding and unpredictable fishing conditions. Salary and benefits for Aquaculture Technicians generally provide more consistency and long-term career advancement, while Wild Catch Processors experience variable income influenced by catch volume and fishing seasons.
Aquaculture Technician vs Wild Catch Processor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com