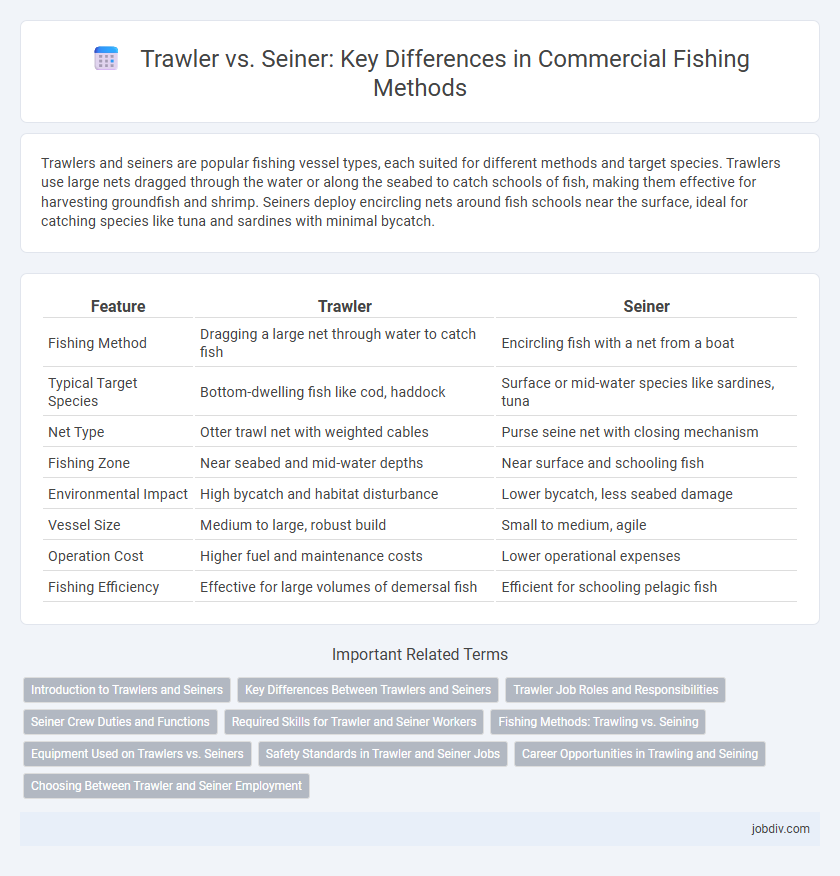
Trawlers and seiners are popular fishing vessel types, each suited for different methods and target species. Trawlers use large nets dragged through the water or along the seabed to catch schools of fish, making them effective for harvesting groundfish and shrimp. Seiners deploy encircling nets around fish schools near the surface, ideal for catching species like tuna and sardines with minimal bycatch.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Trawler | Seiner |
|---|---|---|
| Fishing Method | Dragging a large net through water to catch fish | Encircling fish with a net from a boat |
| Typical Target Species | Bottom-dwelling fish like cod, haddock | Surface or mid-water species like sardines, tuna |
| Net Type | Otter trawl net with weighted cables | Purse seine net with closing mechanism |
| Fishing Zone | Near seabed and mid-water depths | Near surface and schooling fish |
| Environmental Impact | High bycatch and habitat disturbance | Lower bycatch, less seabed damage |
| Vessel Size | Medium to large, robust build | Small to medium, agile |
| Operation Cost | Higher fuel and maintenance costs | Lower operational expenses |
| Fishing Efficiency | Effective for large volumes of demersal fish | Efficient for schooling pelagic fish |
Introduction to Trawlers and Seiners
Trawlers are fishing vessels equipped with large nets that are dragged through the water or along the seabed to catch fish and other marine species, optimizing catch volume in both deep and shallow waters. Seiners, on the other hand, use seine nets that encircle schools of fish near the surface or midwater, enabling selective and efficient harvesting of species like tuna and sardines. These two methods differ primarily in their net deployment techniques and target species, impacting fishing efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Key Differences Between Trawlers and Seiners
Trawlers use large nets dragged along the sea floor or midwater to catch fish, targeting species like cod, haddock, and shrimp, while seiners deploy encircling nets that trap schooling fish such as sardines, mackerel, and tuna. Trawler fishing generally results in higher bycatch and habitat disturbance due to bottom contact, whereas seiner methods are more selective and cause less seabed damage. The operational costs, fuel consumption, and catch efficiency also differ significantly, with trawlers requiring more power and producing larger catches compared to the more energy-efficient seiner vessels adapted for pelagic fishing.
Trawler Job Roles and Responsibilities
Trawler job roles focus on operating large fishing vessels equipped with heavy nets that drag along the sea floor or midwater to catch various fish species, such as cod, haddock, and pollock. Crew members are responsible for deploying, retrieving, and maintaining trawl nets, monitoring fish catch quality, and ensuring compliance with fishing regulations and safety protocols. Effective teamwork and technical knowledge of winches, navigation, and fish storage systems are essential for maximizing catch efficiency and vessel operation.
Seiner Crew Duties and Functions
Seiner crew members specialize in operating purse seine nets to encircle fish schools, requiring precise teamwork for deploying, setting, and hauling the nets efficiently. Roles include skippers managing navigation and fishing strategy, deckhands handling net operations, and engineers maintaining vessel machinery to ensure uninterrupted fishing activities. Effective coordination among the crew maximizes catch yield while minimizing environmental impact and bycatch.
Required Skills for Trawler and Seiner Workers
Trawler workers must possess skills in navigation, heavy machinery operation, and deep-sea fishing techniques to manage large nets and equipment effectively. Seiner workers require expertise in deploying and retrieving seine nets swiftly, precise teamwork for encircling fish schools, and knowledge of fish behavior to optimize catch efficiency. Both roles demand physical endurance and safety awareness, but trawlers emphasize mechanical proficiency while seiners focus on coordination and timing.
Fishing Methods: Trawling vs. Seining
Trawling involves dragging a large net through the water or along the seabed to catch fish, primarily targeting species like cod, haddock, and shrimp, whereas seining uses a vertical net deployed in a circle around a school of fish such as sardines or mackerel. Trawlers often operate in deeper waters and have a higher bycatch rate due to the indiscriminate nature of the drag net, while seiners typically fish in shallower areas with more selective capture, reducing unintended catch. The efficiency of seining relies on locating dense fish schools, whereas trawling covers broader areas, making both methods pivotal yet distinct in commercial fishing operations.
Equipment Used on Trawlers vs. Seiners
Trawlers utilize large, heavy nets called otter trawls, equipped with otter boards that keep the net open horizontally while dragged along the seabed, targeting bottom-dwelling fish. Seiners operate with seine nets, including purse seines and Danish seines, designed to encircle schools of fish near the surface or midwater, using a series of ropes and floats to close and secure the catch. The specialized equipment on trawlers is optimized for benthic fishing, while seiners employ gear suited for pelagic species, reflecting their distinct fishing methods and target species.
Safety Standards in Trawler and Seiner Jobs
Trawlers and seiners operate under stringent maritime safety standards, but differences in gear and fishing methods influence their risk profiles. Trawlers, using heavy nets dragged through the water, require reinforced deck structures and safety protocols to manage large machinery and prevent entanglement accidents. Seiners rely on encircling nets and must prioritize rapid response to potential net snags and crew falls overboard, with enhanced personal flotation devices and emergency communication systems mandated for safer operations.
Career Opportunities in Trawling and Seining
Trawling offers extensive career opportunities in vessel operation, maintenance, and fish processing, with roles such as trawl master, deckhand, and marine engineer in commercial fishing fleets worldwide. Seining provides specialized positions including seine skipper, deck crew, and fish grader, emphasizing teamwork and precise net handling in coastal fisheries. Both methods require knowledge of fish behavior, sustainable practices, and navigation skills, crucial for long-term career growth in the fishing industry.
Choosing Between Trawler and Seiner Employment
When choosing between trawler and seiner employment, consider the targeted fish species and fishing environment. Trawlers use large nets dragged along the sea floor or midwater, ideal for catching groundfish or schooling species, while seiners encircle schools with a purse seine net, often targeting pelagic fish like tuna or sardines. Employment in trawler operations often requires experience with heavy machinery and longer trips, whereas seiner work emphasizes teamwork and rapid net handling in coastal or offshore waters.
Trawler vs Seiner Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com