Fire Lookouts serve as vigilant sentinels in remote forest areas, using visual observation to detect early signs of wildfire and communicate potential threats to firefighting teams. Fire Management Officers coordinate and implement strategic plans for wildfire prevention, suppression, and resource allocation, ensuring safety and ecological balance across forest landscapes. Both roles are crucial for effective wildfire response, combining on-the-ground monitoring with strategic oversight to protect natural resources and communities.
Table of Comparison
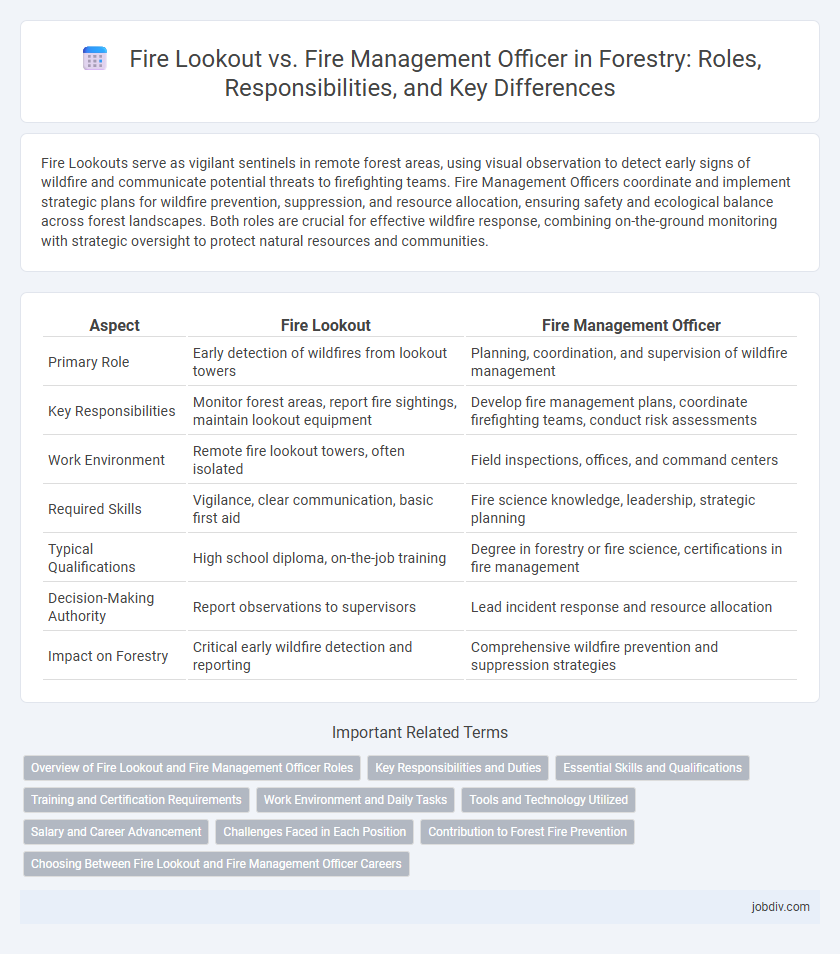
| Aspect | Fire Lookout | Fire Management Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Early detection of wildfires from lookout towers | Planning, coordination, and supervision of wildfire management |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor forest areas, report fire sightings, maintain lookout equipment | Develop fire management plans, coordinate firefighting teams, conduct risk assessments |
| Work Environment | Remote fire lookout towers, often isolated | Field inspections, offices, and command centers |
| Required Skills | Vigilance, clear communication, basic first aid | Fire science knowledge, leadership, strategic planning |
| Typical Qualifications | High school diploma, on-the-job training | Degree in forestry or fire science, certifications in fire management |
| Decision-Making Authority | Report observations to supervisors | Lead incident response and resource allocation |
| Impact on Forestry | Critical early wildfire detection and reporting | Comprehensive wildfire prevention and suppression strategies |
Overview of Fire Lookout and Fire Management Officer Roles
Fire Lookouts are stationed in elevated towers or remote locations to provide early detection of forest fires by continuously monitoring vast forested areas for signs of smoke or fire. Fire Management Officers coordinate fire suppression strategies, oversee resource allocation, and lead firefighting teams to effectively control and manage wildfire incidents. Both roles are critical for ensuring rapid response and minimizing the impact of wildfires on forest ecosystems and surrounding communities.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Fire Lookout's key responsibility involves vigilant surveillance of forested areas to detect early signs of wildfire, using observation towers and communication tools to report potential threats promptly. In contrast, a Fire Management Officer oversees strategic planning and coordination of fire prevention, suppression, and mitigation activities, including resource allocation, incident command, and safety protocols. Both roles are critical in wildfire management, with Fire Lookouts prioritizing frontline detection and Fire Management Officers focusing on operational control and decision-making.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Fire Lookouts require keen observational skills, the ability to identify smoke and fire patterns, and proficiency with communication tools for timely reporting. Fire Management Officers must possess strong leadership abilities, expertise in fire behavior analysis, and knowledge of firefighting tactics and safety regulations. Both roles demand physical fitness, attention to detail, and certification in wildfire suppression and emergency response protocols.
Training and Certification Requirements
Fire Lookouts require specialized training in wildfire observation, communication protocols, and basic safety procedures, often certified through state forestry agencies or wildfire training programs such as S-130/S-190. Fire Management Officers undergo advanced training including incident command systems (ICS), fire behavior analysis, resource management, and leadership certifications like NWCG S-420 or equivalent. Both roles demand ongoing education to stay current with evolving fire management techniques and regulatory standards.
Work Environment and Daily Tasks
Fire Lookouts primarily work in remote, elevated locations such as towers or ridges to monitor and identify wildfire activity, often spending long hours in solitude with harsh weather conditions. Fire Management Officers operate in more dynamic environments, including field sites, command centers, and offices, coordinating wildfire response, planning controlled burns, and liaising with multiple agencies. Daily tasks for Fire Lookouts focus on observation and reporting, while Fire Management Officers engage in strategic decision-making, resource allocation, and overseeing fire suppression efforts.
Tools and Technology Utilized
Fire Lookouts rely primarily on optical tools such as high-powered binoculars, telescopes, and fire-finder devices to detect and report smoke or fire outbreaks from observation towers. Fire Management Officers utilize advanced technologies including Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing data from satellites and drones, and predictive modeling software to strategize fire suppression and resource deployment effectively. The integration of real-time communication systems further enhances coordination between on-ground personnel and command centers in wildfire management.
Salary and Career Advancement
Fire Lookouts typically earn between $30,000 and $45,000 annually, focusing on early wildfire detection through constant surveillance in remote forest locations. Fire Management Officers command higher salaries, ranging from $60,000 to $90,000, reflecting their advanced responsibilities in strategic planning, resource allocation, and coordination of firefighting efforts. Career advancement for Fire Lookouts often leads to roles such as Fire Management Officers or Forestry Technicians, while Fire Management Officers may progress into senior positions like Regional Fire Chiefs or Forestry Program Directors.
Challenges Faced in Each Position
Fire Lookouts face the challenge of maintaining constant vigilance in remote, often isolated locations, requiring acute observational skills to detect early signs of wildfire under harsh weather conditions. Fire Management Officers confront complex decision-making pressures involving resource allocation, interagency coordination, and strategizing effective response plans amid rapidly changing fire behavior. Both roles demand resilience, but the tactical immediacy for Lookouts contrasts with the strategic oversight burdening Management Officers.
Contribution to Forest Fire Prevention
Fire Lookouts play a crucial role in forest fire prevention by providing early detection through continuous monitoring of high-risk areas, enabling rapid reporting of smoke or fire signs to firefighting teams. Fire Management Officers contribute strategically by developing comprehensive fire prevention plans, coordinating resource allocation, and implementing community education programs that reduce fire risks. Together, their efforts enhance forest resilience by combining real-time surveillance with proactive management and public awareness initiatives.
Choosing Between Fire Lookout and Fire Management Officer Careers
Choosing between a Fire Lookout and a Fire Management Officer career depends on the desired level of field engagement and decision-making responsibility in forestry fire prevention. Fire Lookouts primarily focus on early detection and continuous observation of forest fires from remote towers, providing real-time data essential for rapid response. Fire Management Officers oversee strategic planning, resource allocation, and coordination of firefighting efforts, requiring advanced skills in leadership and incident command within forest fire management operations.
Fire Lookout vs Fire Management Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com