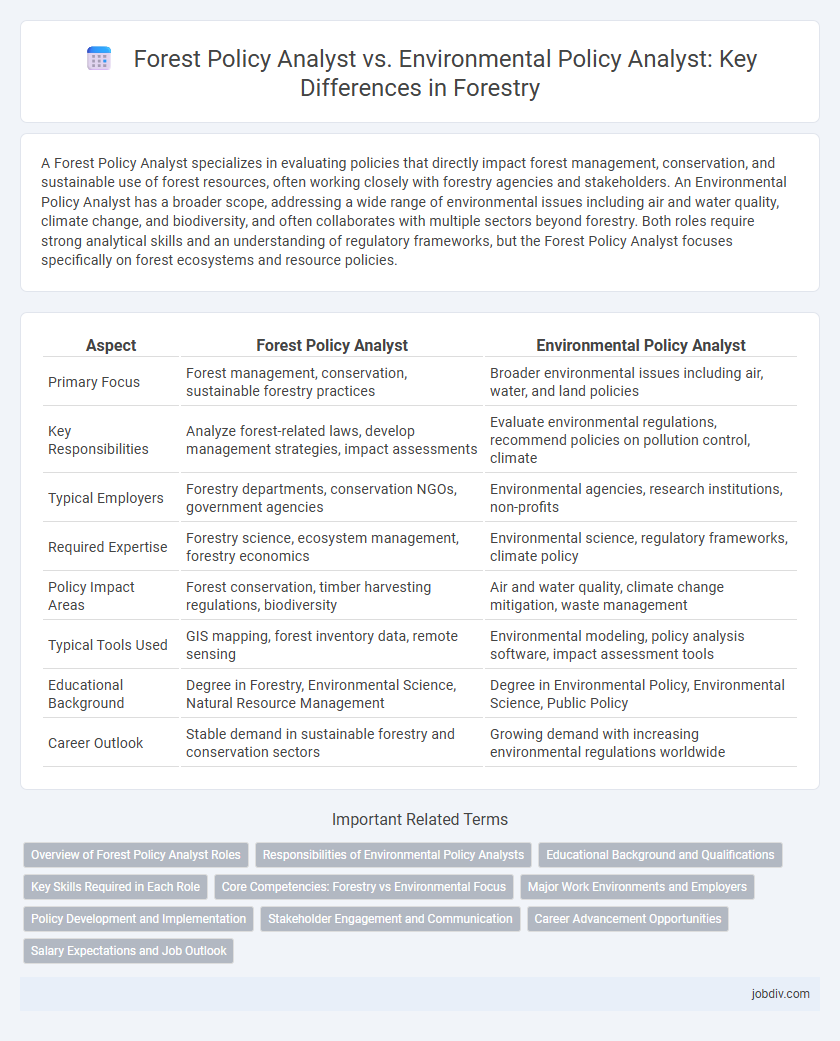
A Forest Policy Analyst specializes in evaluating policies that directly impact forest management, conservation, and sustainable use of forest resources, often working closely with forestry agencies and stakeholders. An Environmental Policy Analyst has a broader scope, addressing a wide range of environmental issues including air and water quality, climate change, and biodiversity, and often collaborates with multiple sectors beyond forestry. Both roles require strong analytical skills and an understanding of regulatory frameworks, but the Forest Policy Analyst focuses specifically on forest ecosystems and resource policies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Forest Policy Analyst | Environmental Policy Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Forest management, conservation, sustainable forestry practices | Broader environmental issues including air, water, and land policies |
| Key Responsibilities | Analyze forest-related laws, develop management strategies, impact assessments | Evaluate environmental regulations, recommend policies on pollution control, climate |
| Typical Employers | Forestry departments, conservation NGOs, government agencies | Environmental agencies, research institutions, non-profits |
| Required Expertise | Forestry science, ecosystem management, forestry economics | Environmental science, regulatory frameworks, climate policy |
| Policy Impact Areas | Forest conservation, timber harvesting regulations, biodiversity | Air and water quality, climate change mitigation, waste management |
| Typical Tools Used | GIS mapping, forest inventory data, remote sensing | Environmental modeling, policy analysis software, impact assessment tools |
| Educational Background | Degree in Forestry, Environmental Science, Natural Resource Management | Degree in Environmental Policy, Environmental Science, Public Policy |
| Career Outlook | Stable demand in sustainable forestry and conservation sectors | Growing demand with increasing environmental regulations worldwide |
Overview of Forest Policy Analyst Roles
Forest Policy Analysts evaluate and develop strategies to manage forest resources sustainably, focusing on timber production, conservation, reforestation, and wildlife habitat protection. They analyze regulations, monitor environmental impacts, and advise government agencies, industry stakeholders, and conservation groups on policy implementation specific to forestry. Their expertise informs decisions on land use planning, forest health, climate change adaptation, and economic benefits from forest ecosystems.
Responsibilities of Environmental Policy Analysts
Environmental Policy Analysts assess the impacts of policies on natural resources, biodiversity, and ecosystem services, providing data-driven recommendations to promote sustainable development. They evaluate regulations related to air and water quality, pollution control, and climate change mitigation, ensuring environmental protection goals align with economic and social objectives. Their responsibilities include analyzing environmental legislation, conducting impact assessments, and advising stakeholders on compliance and conservation strategies within forestry and broader ecological contexts.
Educational Background and Qualifications
Forest Policy Analysts typically hold degrees in forestry, environmental science, or natural resource management, often requiring specialized training in ecosystem management and forest ecology. Environmental Policy Analysts usually possess broader academic backgrounds in environmental studies, public policy, or environmental law, emphasizing understanding regulatory frameworks and sustainability principles. Both professions demand strong analytical skills, proficiency in data interpretation, and familiarity with environmental regulations, but forest policy roles prioritize expertise in forest-specific sciences.
Key Skills Required in Each Role
Forest Policy Analysts require expertise in sustainable forestry practices, ecosystem management, and knowledge of forestry regulations and timber markets. Environmental Policy Analysts focus on environmental impact assessment, climate change mitigation strategies, and regulatory compliance across diverse ecosystems. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, stakeholder engagement skills, and proficiency in policy development and evaluation.
Core Competencies: Forestry vs Environmental Focus
Forest Policy Analysts possess expert knowledge in silviculture, forest ecology, and sustainable timber management, enabling them to develop policies that balance economic interests with conservation. Environmental Policy Analysts emphasize ecosystem services, biodiversity protection, and climate change mitigation strategies, applying broader environmental science principles across multiple ecosystems. Both roles require strong data analysis, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory understanding, but Forest Policy Analysts prioritize forestry-specific practices and resource management, while Environmental Policy Analysts focus on cross-sectoral environmental impacts and sustainability frameworks.
Major Work Environments and Employers
Forest Policy Analysts predominantly work for government agencies such as the U.S. Forest Service, state forestry departments, and environmental NGOs focused on forest conservation. Environmental Policy Analysts have a broader range of employers including federal and state environmental protection agencies, international organizations, and private consulting firms specializing in environmental impact assessments. Both roles often operate in office settings but also engage in fieldwork, collaborating with land managers and community stakeholders to develop sustainable policies.
Policy Development and Implementation
Forest Policy Analysts specialize in developing and implementing policies that promote sustainable forest management, conservation, and biodiversity protection, often working with government agencies and stakeholders directly involved in forestry. Environmental Policy Analysts focus more broadly on environmental regulations, addressing issues like climate change, pollution control, and natural resource management, influencing policies beyond just forests. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Forest Policy Analysts bring specialized knowledge of forest ecosystems and timber industry dynamics, while Environmental Policy Analysts integrate a wider range of environmental factors into policy frameworks.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Forest Policy Analysts specialize in engaging stakeholders such as local communities, logging companies, and conservation groups to balance timber production with ecosystem preservation. Environmental Policy Analysts communicate complex regulations and environmental impacts to policymakers, advocacy groups, and the public, fostering collaboration on broader sustainability goals. Both roles require advanced skills in stakeholder communication, but Forest Policy Analysts emphasize sector-specific dialogue related to forestry practices and resource management.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Forest Policy Analysts often advance by specializing in sustainable forestry management and gaining expertise in timber regulations, which can lead to senior roles in government agencies or conservation organizations. Environmental Policy Analysts typically broaden their scope to include climate change, pollution control, and ecosystem restoration, positioning themselves for leadership roles in environmental planning, advocacy groups, or international agencies. Career growth in both fields depends heavily on experience with policy analysis, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory frameworks specific to forestry or broader environmental issues.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Forest Policy Analysts typically command salaries ranging from $60,000 to $90,000 annually, reflecting specialized expertise in forestry management, conservation strategies, and sustainable resource use. Environmental Policy Analysts, with a broader focus on climate change, pollution control, and environmental regulations, earn between $55,000 and $85,000, with demand growing steadily due to increasing environmental awareness and regulatory measures. Job outlook for both roles is promising, but Forest Policy Analysts may experience niche growth tied to forestry sector advancements, while Environmental Policy Analysts benefit from wider opportunities across various industries addressing ecological challenges.
Forest Policy Analyst vs Environmental Policy Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com