Riparian specialists thrive in wet, streamside environments where they manage vegetation to protect water quality and provide habitat diversity. Upland specialists focus on drier, elevated areas, promoting species adapted to well-drained soils and reducing wildfire risks through strategic thinning. Both roles complement each other by maintaining ecosystem balance across forest landscapes.
Table of Comparison
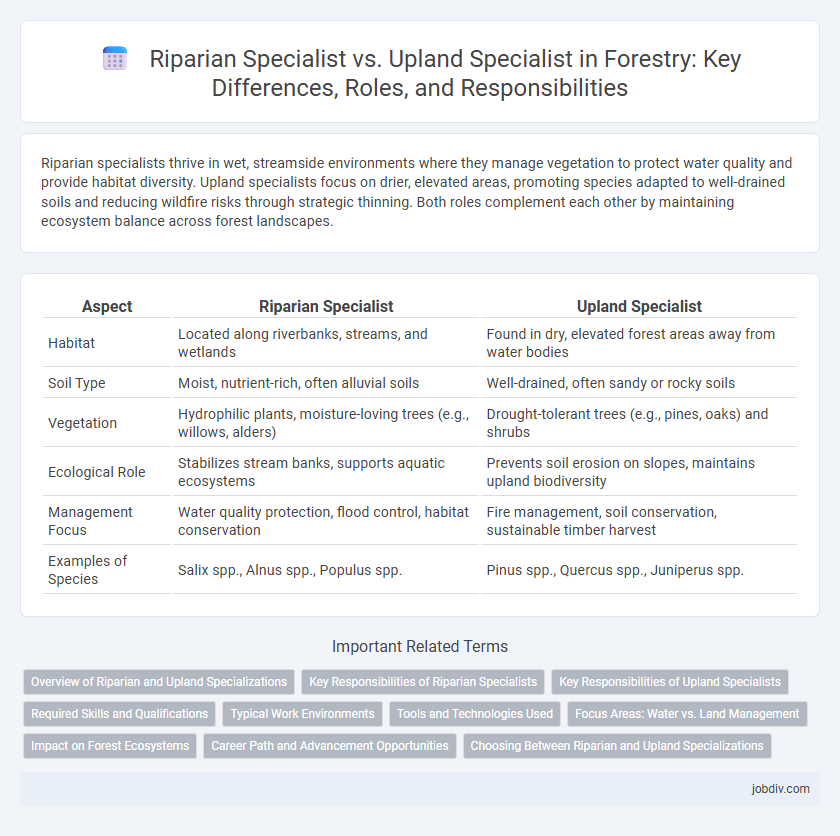
| Aspect | Riparian Specialist | Upland Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Located along riverbanks, streams, and wetlands | Found in dry, elevated forest areas away from water bodies |
| Soil Type | Moist, nutrient-rich, often alluvial soils | Well-drained, often sandy or rocky soils |
| Vegetation | Hydrophilic plants, moisture-loving trees (e.g., willows, alders) | Drought-tolerant trees (e.g., pines, oaks) and shrubs |
| Ecological Role | Stabilizes stream banks, supports aquatic ecosystems | Prevents soil erosion on slopes, maintains upland biodiversity |
| Management Focus | Water quality protection, flood control, habitat conservation | Fire management, soil conservation, sustainable timber harvest |
| Examples of Species | Salix spp., Alnus spp., Populus spp. | Pinus spp., Quercus spp., Juniperus spp. |
Overview of Riparian and Upland Specializations
Riparian specialists focus on managing and restoring ecosystems adjacent to water bodies, emphasizing water quality, bank stabilization, and habitat preservation for aquatic and semi-aquatic species. Upland specialists manage forested areas away from water edges, prioritizing soil conservation, wildlife habitat diversity, and sustainable timber production. Both specializations require distinct knowledge of vegetation types, hydrology, and ecosystem functions critical to maintaining overall forest health.
Key Responsibilities of Riparian Specialists
Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring ecosystems along riverbanks and wetlands, ensuring water quality and habitat preservation for aquatic and terrestrial species. They conduct assessments of stream bank stability, vegetation health, and erosion control measures while collaborating with landowners and regulatory agencies to implement conservation plans. Their expertise in hydrology and soil science is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and mitigating the impacts of land use on riparian zones.
Key Responsibilities of Upland Specialists
Upland Specialists primarily focus on managing forest ecosystems away from water bodies, emphasizing soil conservation, wildlife habitat improvement, and timber stand management. Their key responsibilities include monitoring soil health, implementing erosion control measures, and planning reforestation activities tailored to upland conditions. They also analyze forest composition and work to enhance biodiversity while sustaining timber production on elevated terrains.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Riparian specialists require expertise in hydrology, soil science, and wetland ecology to manage and restore water-adjacent forest ecosystems effectively. Upland specialists focus on knowledge of dryland tree species, soil conservation, and fire management practices to sustain forest health in drier, higher elevation areas. Both roles demand proficiency in GIS mapping, ecosystem assessment, and strong communication skills for stakeholder collaboration.
Typical Work Environments
Riparian specialists typically work in environments adjacent to rivers, streams, and wetlands, focusing on the conservation and restoration of aquatic ecosystems and floodplain management. Upland specialists operate primarily in forested areas away from water bodies, concentrating on soil conservation, timber harvest planning, and habitat improvement for terrestrial wildlife. Both roles require fieldwork in diverse terrains but differ in their emphasis on water-related versus upland forest ecosystems.
Tools and Technologies Used
Riparian specialists utilize tools such as soil moisture sensors, water quality monitoring devices, and GIS mapping software to assess and manage streamside vegetation and aquatic habitats. Upland specialists often employ drones, remote sensing technology, and GIS for terrain analysis, wildfire risk assessment, and forest stand inventory. Both specialists rely on GPS units and data management systems to optimize site-specific forest management practices.
Focus Areas: Water vs. Land Management
Riparian specialists concentrate on water resource management, emphasizing streambank stabilization, watershed health, and aquatic habitat restoration to enhance water quality and biodiversity. Upland specialists focus on terrestrial land management practices such as soil conservation, forest regeneration, and wildlife habitat improvement to maintain ecosystem stability and productivity. Both roles are essential for integrated natural resource management, ensuring balanced ecosystems through targeted interventions in water or land environments.
Impact on Forest Ecosystems
Riparian specialists enhance forest ecosystems by stabilizing stream banks, improving water quality, and providing critical habitats for aquatic and terrestrial species. Upland specialists contribute to soil conservation, promote biodiversity through diverse tree species, and support wildlife adapted to drier, elevated environments. Both specialists play crucial roles in maintaining ecosystem resilience, but riparian specialists more directly influence hydrological processes, while upland specialists drive nutrient cycling and forest regeneration.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Riparian specialists focus on managing and restoring water-adjacent ecosystems, offering career advancement through roles in watershed management, ecological restoration, and environmental compliance monitoring. Upland specialists concentrate on forested and terrestrial habitats, advancing by gaining expertise in silviculture, wildlife habitat management, and timber resource planning. Both paths provide opportunities for leadership in environmental consulting, government forestry agencies, and natural resource conservation organizations.
Choosing Between Riparian and Upland Specializations
Selecting between riparian and upland specializations in forestry hinges on the targeted ecosystem management goals. Riparian specialists focus on protecting water quality, enhancing habitat for aquatic and semi-aquatic species, and managing floodplain vegetation, while upland specialists concentrate on soil conservation, timber production, and wildfire risk reduction in drier, elevated areas. Understanding the distinct ecological functions and management techniques of each specialization ensures optimized forest health and biodiversity conservation.
Riparian Specialist vs Upland Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com