Physicians diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions through non-surgical methods, focusing on patient care, preventive medicine, and medical management. Surgeons specialize in performing operative procedures to correct or manage diseases, injuries, and deformities. Both roles require extensive medical training but differ significantly in their approach to treatment and patient care.
Table of Comparison
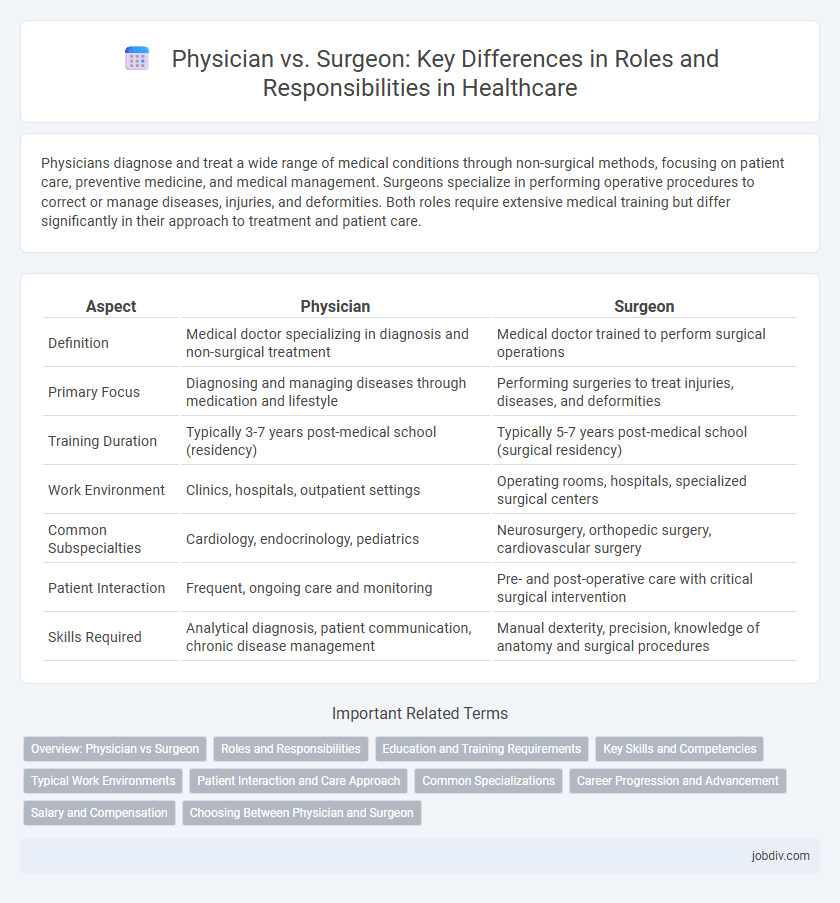
| Aspect | Physician | Surgeon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medical doctor specializing in diagnosis and non-surgical treatment | Medical doctor trained to perform surgical operations |
| Primary Focus | Diagnosing and managing diseases through medication and lifestyle | Performing surgeries to treat injuries, diseases, and deformities |
| Training Duration | Typically 3-7 years post-medical school (residency) | Typically 5-7 years post-medical school (surgical residency) |
| Work Environment | Clinics, hospitals, outpatient settings | Operating rooms, hospitals, specialized surgical centers |
| Common Subspecialties | Cardiology, endocrinology, pediatrics | Neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, cardiovascular surgery |
| Patient Interaction | Frequent, ongoing care and monitoring | Pre- and post-operative care with critical surgical intervention |
| Skills Required | Analytical diagnosis, patient communication, chronic disease management | Manual dexterity, precision, knowledge of anatomy and surgical procedures |
Overview: Physician vs Surgeon
Physicians specialize in diagnosing and managing a wide range of medical conditions through non-surgical treatments and patient care, whereas surgeons focus on performing operative procedures to treat injuries, diseases, or deformities. While both require extensive medical education and training, surgeons typically undergo additional years specializing in surgical techniques and hands-on practice. Collaborative patient management often involves both physicians and surgeons to ensure comprehensive treatment and recovery.
Roles and Responsibilities
Physicians diagnose illnesses, manage chronic conditions, and provide preventive care through patient consultations and medical testing. Surgeons perform operative procedures to treat injuries, diseases, and deformities, often specializing in specific body systems or techniques. Both roles require extensive medical training, but surgeons focus primarily on hands-on interventions, while physicians emphasize medical management and patient monitoring.
Education and Training Requirements
Physicians complete a minimum of four years of medical school followed by a residency program lasting three to seven years, depending on their specialty. Surgeons undergo similar foundational training but require additional specialized surgical residencies that typically extend from five to seven years. Both professions demand rigorous board certification and continuing medical education to maintain clinical competency and stay updated with advances in medical and surgical techniques.
Key Skills and Competencies
Physicians require strong diagnostic abilities, patient communication skills, and expertise in disease management to provide comprehensive care. Surgeons must possess advanced manual dexterity, precision, and in-depth knowledge of surgical procedures and anatomy. Both roles demand critical thinking, medical knowledge, and adherence to safety protocols to ensure effective treatment outcomes.
Typical Work Environments
Physicians typically work in outpatient clinics, hospitals, and private practices, providing diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care across a broad range of medical conditions. Surgeons are primarily found in hospital operating rooms, surgical centers, and trauma units where they perform procedures requiring specialized surgical skills and sterile environments. Both professionals often collaborate in multidisciplinary teams to ensure comprehensive patient care and recovery planning.
Patient Interaction and Care Approach
Physicians often emphasize long-term patient interaction and holistic care management, focusing on diagnosing and treating medical conditions through comprehensive evaluation and follow-up. Surgeons prioritize procedural interventions, with patient care centered around preoperative preparation, precise surgical execution, and postoperative recovery monitoring. Effective communication and empathy are critical for both roles to ensure patient trust and optimal health outcomes.
Common Specializations
Physicians commonly specialize in areas such as internal medicine, pediatrics, cardiology, and family medicine, focusing on diagnosing and managing a wide range of medical conditions through non-surgical treatments. Surgeons specialize in fields like general surgery, orthopedic surgery, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular surgery, performing operative procedures to treat injuries, diseases, and deformities. Both roles require extensive medical training but differ primarily in the emphasis on surgical versus non-surgical patient care.
Career Progression and Advancement
Physicians typically begin their careers with a residency in specialties like internal medicine or pediatrics, offering diverse opportunities for subspecialization and research roles. Surgeons undergo extensive surgical residency programs, often followed by fellowships in areas such as cardiovascular or orthopedic surgery, focusing on procedural expertise and operative skills. Career advancement for physicians can include leadership in clinical practice or academia, while surgeons may progress to chief surgeon roles or specialized surgical research positions.
Salary and Compensation
Surgeons generally earn higher average salaries compared to physicians due to the specialized nature and complexity of surgical procedures. According to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023, surgeons report an average annual income ranging from $400,000 to $600,000, while non-surgical physicians typically earn between $250,000 and $350,000. Factors influencing compensation include years of experience, geographic location, and subspecialty demand within the healthcare market.
Choosing Between Physician and Surgeon
Choosing between a physician and a surgeon depends on the type of medical care required; physicians focus on diagnosing and treating internal illnesses, while surgeons perform operative procedures to address physical conditions. Patients with chronic diseases or general health concerns typically consult physicians, whereas those needing corrective, emergency, or cosmetic surgeries seek surgeons. Understanding the specific medical condition and desired treatment outcome is crucial for selecting the appropriate healthcare specialist.
Physician vs Surgeon Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com