Radiologic Technologists specialize in performing imaging examinations using X-rays and other radiation-based methods to assist in diagnosing medical conditions. Ultrasound Technologists, also known as sonographers, use high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues, often focusing on prenatal care or cardiovascular health. Both professions require specialized training and certification, yet they differ significantly in the technology and techniques employed for patient imaging.
Table of Comparison
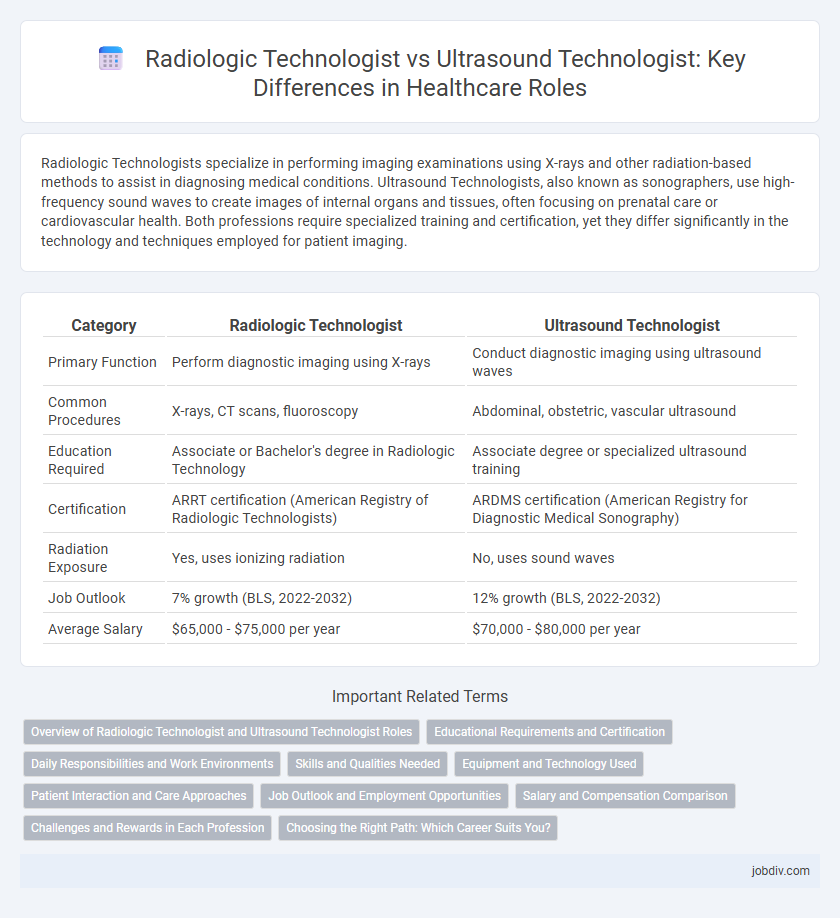
| Category | Radiologic Technologist | Ultrasound Technologist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Perform diagnostic imaging using X-rays | Conduct diagnostic imaging using ultrasound waves |
| Common Procedures | X-rays, CT scans, fluoroscopy | Abdominal, obstetric, vascular ultrasound |
| Education Required | Associate or Bachelor's degree in Radiologic Technology | Associate degree or specialized ultrasound training |
| Certification | ARRT certification (American Registry of Radiologic Technologists) | ARDMS certification (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography) |
| Radiation Exposure | Yes, uses ionizing radiation | No, uses sound waves |
| Job Outlook | 7% growth (BLS, 2022-2032) | 12% growth (BLS, 2022-2032) |
| Average Salary | $65,000 - $75,000 per year | $70,000 - $80,000 per year |
Overview of Radiologic Technologist and Ultrasound Technologist Roles
Radiologic Technologists specialize in performing diagnostic imaging exams such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to aid in disease detection and treatment planning. Ultrasound Technologists operate high-frequency sound wave equipment to capture real-time images of organs, tissues, and blood flow, primarily used in prenatal care and cardiovascular assessments. Both roles require expertise in patient positioning, safety protocols, and image quality but differ in imaging technology and diagnostic applications.
Educational Requirements and Certification
Radiologic technologists typically require an associate degree in radiologic technology, along with certification from the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). Ultrasound technologists usually obtain a specialized associate degree or postsecondary certificate in diagnostic medical sonography and pursue certification through the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Both professions demand clinical training and passing specific exams to achieve credentialing and ensure competence in their respective imaging techniques.
Daily Responsibilities and Work Environments
Radiologic Technologists perform diagnostic imaging examinations using X-rays and radiation therapy equipment primarily in hospitals and outpatient clinics, focusing on capturing clear images for physician analysis. Ultrasound Technologists utilize high-frequency sound waves to produce images of organs and tissues, often working in specialized imaging centers, obstetrics, and cardiology departments. Both professionals ensure patient safety and operate complex imaging technology but differ in radiation use and specific clinical settings.
Skills and Qualities Needed
Radiologic technologists require strong technical skills to operate X-ray and CT scan equipment, combined with a thorough understanding of anatomy and radiation safety protocols to ensure accurate imaging and patient protection. Ultrasound technologists must possess excellent hand-eye coordination and detailed knowledge of sonographic techniques to capture high-quality images while demonstrating strong interpersonal skills for patient communication during sensitive procedures. Both professions demand critical thinking, attention to detail, and the ability to work under pressure in fast-paced healthcare environments.
Equipment and Technology Used
Radiologic Technologists primarily operate X-ray machines, computed tomography (CT) scanners, and fluoroscopy equipment to capture detailed images of bones and internal organs. Ultrasound Technologists utilize high-frequency sound wave devices, such as transducers and Doppler ultrasound machines, to create real-time images of soft tissues and blood flow. Both specialties require proficiency in advanced imaging technology, but Radiologic Technologists rely on ionizing radiation, whereas Ultrasound Technologists use non-ionizing sound waves for diagnostic purposes.
Patient Interaction and Care Approaches
Radiologic technologists primarily focus on obtaining diagnostic images using X-rays, requiring precise positioning and patient cooperation to ensure image quality while minimizing discomfort. Ultrasound technologists engage in real-time imaging, often necessitating ongoing communication and patient reassurance during procedures to address anxiety and improve image accuracy. Both roles emphasize patient-centered care, but ultrasound technologists typically have more direct and extended interaction due to the nature of the imaging process.
Job Outlook and Employment Opportunities
Radiologic technologists have a projected job growth of 9% from 2022 to 2032, with employment opportunities concentrated in hospitals, outpatient care centers, and diagnostic laboratories. Ultrasound technologists are expected to experience a higher growth rate of 14% during the same period, driven by advancements in prenatal care, cardiology, and musculoskeletal imaging. Both professions offer strong job prospects, but ultrasound technologists may encounter more opportunities due to expanding applications of sonographic technology.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Radiologic technologists typically earn a median annual salary of approximately $65,000, while ultrasound technologists often command a slightly higher median pay around $70,000 due to specialized skills in diagnostic imaging. Compensation packages for ultrasound technologists may also include additional benefits and bonuses tied to their expertise in non-invasive procedures. Salary variations depend on geographic location, years of experience, and the healthcare facility's size and type.
Challenges and Rewards in Each Profession
Radiologic Technologists face challenges such as exposure to ionizing radiation and the need for precise positioning to obtain accurate diagnostic images, while their work is rewarded by contributing to early disease detection and patient care. Ultrasound Technologists encounter difficulties managing patient discomfort and ensuring image clarity amid varying tissue densities, yet they benefit from a safer, radiation-free environment and real-time imaging capabilities that aid in immediate diagnoses. Both professions offer fulfilling careers with opportunities for specialization, professional growth, and impactful patient interaction.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Career Suits You?
Radiologic Technologists specialize in using X-rays and CT scans to diagnose medical conditions, requiring strong technical skills and comfort with radiation exposure, while Ultrasound Technologists utilize sound waves to create images, offering a non-invasive, radiation-free alternative ideal for those seeking patient interaction and dynamic imaging environments. Consider factors such as work environment, job growth projected at 7% for Radiologic Technologists and 12% for Ultrasound Technologists by 2031, and educational requirements--a typical associate degree plus certification versus more specialized ultrasound training--to determine which aligns best with your career goals. Understanding the physical demands, technological proficiency, and patient care aspects of each role will guide you in choosing the path that suits your skills and lifestyle preferences.
Radiologic Technologist vs Ultrasound Technologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com