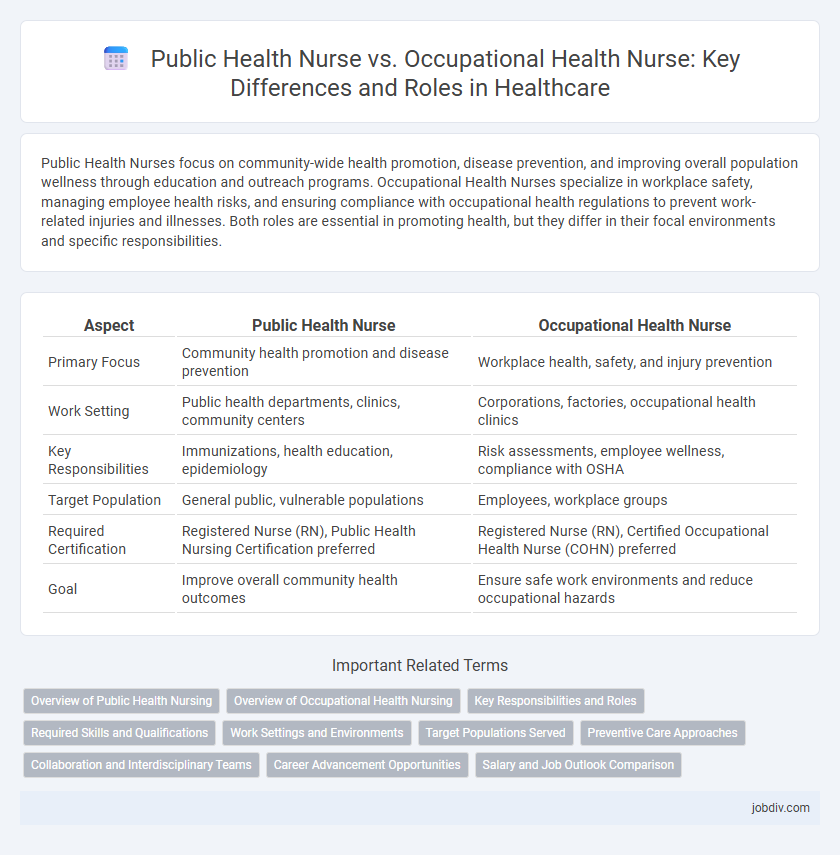
Public Health Nurses focus on community-wide health promotion, disease prevention, and improving overall population wellness through education and outreach programs. Occupational Health Nurses specialize in workplace safety, managing employee health risks, and ensuring compliance with occupational health regulations to prevent work-related injuries and illnesses. Both roles are essential in promoting health, but they differ in their focal environments and specific responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Health Nurse | Occupational Health Nurse |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Community health promotion and disease prevention | Workplace health, safety, and injury prevention |
| Work Setting | Public health departments, clinics, community centers | Corporations, factories, occupational health clinics |
| Key Responsibilities | Immunizations, health education, epidemiology | Risk assessments, employee wellness, compliance with OSHA |
| Target Population | General public, vulnerable populations | Employees, workplace groups |
| Required Certification | Registered Nurse (RN), Public Health Nursing Certification preferred | Registered Nurse (RN), Certified Occupational Health Nurse (COHN) preferred |
| Goal | Improve overall community health outcomes | Ensure safe work environments and reduce occupational hazards |
Overview of Public Health Nursing
Public Health Nursing focuses on improving community health through disease prevention, health education, and wellness promotion across diverse populations. Public Health Nurses assess community needs, plan and implement public health programs, and collaborate with organizations to address social determinants of health. Their role contrasts with Occupational Health Nurses, who prioritize workplace health and safety, injury prevention, and employee health management within specific occupational settings.
Overview of Occupational Health Nursing
Occupational health nursing focuses on the prevention, management, and treatment of work-related injuries and illnesses, emphasizing employee health and safety within various workplace environments. These nurses perform health risk assessments, implement injury prevention programs, and ensure compliance with occupational safety regulations to promote a safe work environment. Unlike public health nurses who address community-wide health issues, occupational health nurses specialize in tailored interventions that support workforce health, productivity, and regulatory adherence.
Key Responsibilities and Roles
Public Health Nurses focus on community-wide health promotion, disease prevention, and managing public health programs to improve population well-being. Occupational Health Nurses specialize in workplace health, ensuring employee safety, injury prevention, and compliance with occupational health regulations. Both roles collaborate with healthcare teams but differ in their primary settings and target populations.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Public Health Nurses require strong community assessment skills, knowledge of epidemiology, and experience in preventive care to effectively address population health issues, holding a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and state licensure as Registered Nurses (RNs). Occupational Health Nurses need expertise in workplace hazard identification, injury prevention, and compliance with occupational safety regulations, often supplemented by certifications such as the Certified Occupational Health Nurse (COHN) credential, alongside a BSN and RN licensure. Both roles demand critical thinking, excellent communication abilities, and proficiency in health education to promote wellness in their respective environments.
Work Settings and Environments
Public Health Nurses primarily operate within community health settings such as clinics, schools, and public health departments, focusing on disease prevention and health education across diverse populations. Occupational Health Nurses work predominantly in industrial and corporate environments, including manufacturing plants and office settings, where they manage workplace safety, injury prevention, and employee wellness programs. Both roles require specialized knowledge of health promotion but differ significantly in their work environments and target populations.
Target Populations Served
Public Health Nurses focus primarily on community-wide populations, including vulnerable groups such as children, elderly, and underserved families, aiming to improve overall community health outcomes. Occupational Health Nurses serve employees within specific workplaces, targeting worker health and safety, injury prevention, and maintaining productivity in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and corporate settings. Both roles emphasize disease prevention and health promotion but differ in their primary target populations and settings of care delivery.
Preventive Care Approaches
Public Health Nurses emphasize community-wide preventive care through health education, vaccination programs, and disease surveillance to reduce population risks. Occupational Health Nurses specialize in workplace safety, conducting hazard assessments, implementing injury prevention strategies, and promoting employee wellness. Both roles prioritize early detection and health promotion but target different environments for disease prevention and health improvement.
Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Teams
Public Health Nurses collaborate with community organizations and healthcare providers to implement population-wide health strategies, while Occupational Health Nurses work closely with employers, safety specialists, and medical staff to ensure workplace wellness and injury prevention. Both roles emphasize interdisciplinary teamwork to address complex health challenges by integrating clinical care, education, and policy development. Effective collaboration between these nursing specialties enhances holistic health outcomes by combining expertise in community health and occupational safety.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Public Health Nurses often advance by specializing in community health education, epidemiology, or health policy development, leading to roles such as public health program managers or directors. Occupational Health Nurses typically progress by gaining expertise in workplace safety, industrial hygiene, and regulatory compliance, moving into positions like occupational health managers or corporate wellness coordinators. Both career paths require continuous education and certifications, such as Certified Occupational Health Nurse (COHN) for occupational roles or public health nursing specialty certifications, to enhance opportunities for leadership and advanced practice.
Salary and Job Outlook Comparison
Public Health Nurses earn an average annual salary of approximately $75,000, with job growth projected at 7% through 2032, driven by community health initiatives and preventive care programs. Occupational Health Nurses typically have a higher median salary around $80,000, benefiting from employment in corporate or industrial settings focused on workplace safety, with a job outlook growth rate of 6% over the next decade. Both professions experience steady demand, but Public Health Nurses often work in public sectors while Occupational Health Nurses are more prevalent in private industries.
Public Health Nurse vs Occupational Health Nurse Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com