A pharmacologist studies the effects and mechanisms of drugs at the molecular and cellular levels to understand their impact on the human body, driving drug development and safety assessments. A pharmacist dispenses medications, provides patient counseling, and ensures proper drug use to promote health and prevent adverse effects. Both professions play crucial roles in healthcare but focus on different aspects of medication management and therapy optimization.
Table of Comparison
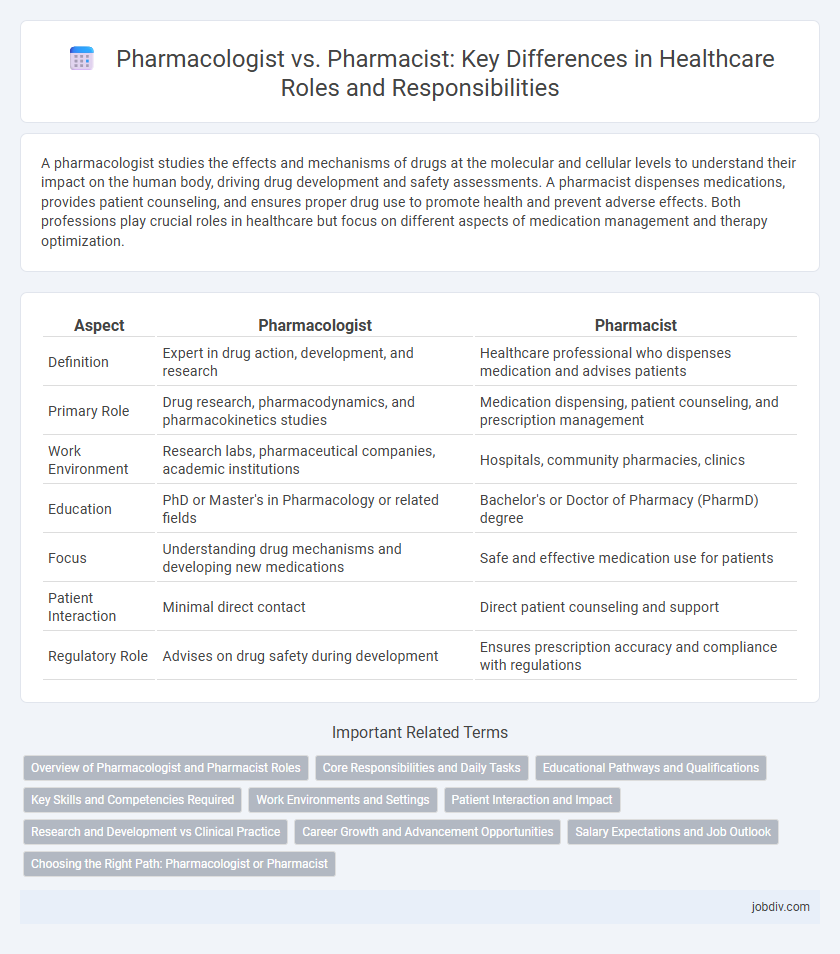
| Aspect | Pharmacologist | Pharmacist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expert in drug action, development, and research | Healthcare professional who dispenses medication and advises patients |
| Primary Role | Drug research, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics studies | Medication dispensing, patient counseling, and prescription management |
| Work Environment | Research labs, pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions | Hospitals, community pharmacies, clinics |
| Education | PhD or Master's in Pharmacology or related fields | Bachelor's or Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) degree |
| Focus | Understanding drug mechanisms and developing new medications | Safe and effective medication use for patients |
| Patient Interaction | Minimal direct contact | Direct patient counseling and support |
| Regulatory Role | Advises on drug safety during development | Ensures prescription accuracy and compliance with regulations |
Overview of Pharmacologist and Pharmacist Roles
Pharmacologists study drug actions and interactions at the molecular and systemic levels, conducting research to develop new medications and improve therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacists specialize in dispensing medications, providing patient counseling, and ensuring the safe and effective use of prescriptions in clinical settings. Both professionals play vital roles in healthcare, with pharmacologists focused on drug discovery and mechanism, while pharmacists emphasize medication management and patient care.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Pharmacologists conduct research to understand drug actions and develop new medications, focusing on biochemical mechanisms and clinical trials. Pharmacists dispense prescribed medications, provide patient counseling, and manage medication therapies to ensure proper usage and safety. Both professionals play crucial roles in healthcare, with pharmacologists driving drug innovation and pharmacists ensuring effective patient treatment.
Educational Pathways and Qualifications
Pharmacologists typically hold a PhD in pharmacology or related biomedical sciences, focusing on drug research, development, and the study of drug interactions at the molecular level. Pharmacists must complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) program, which emphasizes clinical practice, patient care, and medication management, followed by licensure exams to practice. While both professions require extensive knowledge of medications, pharmacologists are primarily research-oriented, and pharmacists are healthcare providers specializing in dispensing and counseling on medications.
Key Skills and Competencies Required
Pharmacologists require strong analytical skills, expertise in drug interactions, and proficiency in laboratory research to study the effects of medications. Pharmacists need excellent communication abilities, attention to detail, and in-depth knowledge of medication dispensing and patient counseling. Both professions demand a solid understanding of pharmacology, but pharmacologists focus on drug development while pharmacists emphasize clinical application and patient safety.
Work Environments and Settings
Pharmacologists primarily work in research laboratories, pharmaceutical companies, and academic institutions where they study drug actions and develop new medications. Pharmacists commonly operate in community pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics, directly engaging with patients to dispense medications and provide drug-related advice. Both professionals contribute to healthcare, but their environments differ significantly, with pharmacologists focusing on drug discovery and pharmacists on medication management and patient care.
Patient Interaction and Impact
Pharmacists engage directly with patients by providing medication counseling, managing prescriptions, and ensuring safe drug use, which enhances patient adherence and health outcomes. Pharmacologists conduct research on drug actions and interactions, contributing to the development of safer and more effective medications but have limited direct patient contact. The patient impact of pharmacists is immediate and practical, while pharmacologists influence healthcare through scientific advancements and drug innovation.
Research and Development vs Clinical Practice
Pharmacologists specialize in research and development, studying drug interactions, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics to create new medications and improve existing treatments. Pharmacists focus on clinical practice, ensuring proper medication dispensing, patient counseling, and monitoring therapeutic outcomes to optimize drug efficacy and safety. Both roles are essential in healthcare, bridging the gap between drug innovation and patient care.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Pharmacologists primarily engage in research and drug development, offering career growth through roles in pharmaceutical companies, academia, and regulatory agencies, often leading to positions in research management or clinical trials oversight. Pharmacists focus on patient care and medication dispensing, with advancement opportunities in clinical pharmacy, hospital administration, and specialized areas such as oncology or pediatrics pharmacy. Both careers demand continuous education and certifications, but pharmacologists typically experience growth through scientific innovation, while pharmacists advance via clinical expertise and patient-oriented services.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Pharmacologists typically earn higher salaries than pharmacists due to their specialized research roles, with average annual salaries ranging from $90,000 to $130,000 compared to pharmacists' $120,000 to $140,000 depending on location and experience. The job outlook for pharmacists shows slower growth, around 2%, primarily due to automation and retail pharmacy consolidation, while pharmacologists can expect faster growth near 6% driven by expanding pharmaceutical research and development sectors. Salary and employment prospects vary significantly based on education level, with pharmacologists often requiring a Ph.D. and pharmacists holding a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree.
Choosing the Right Path: Pharmacologist or Pharmacist
Pharmacologists specialize in researching drug actions and developing new medications, focusing on laboratory work and clinical trials to enhance drug efficacy and safety. Pharmacists are healthcare professionals who dispense medications, provide patient counseling, and ensure proper drug use in clinical settings. Choosing the right path depends on whether one prefers scientific research and drug development or direct patient care and medication management.
Pharmacologist vs Pharmacist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com