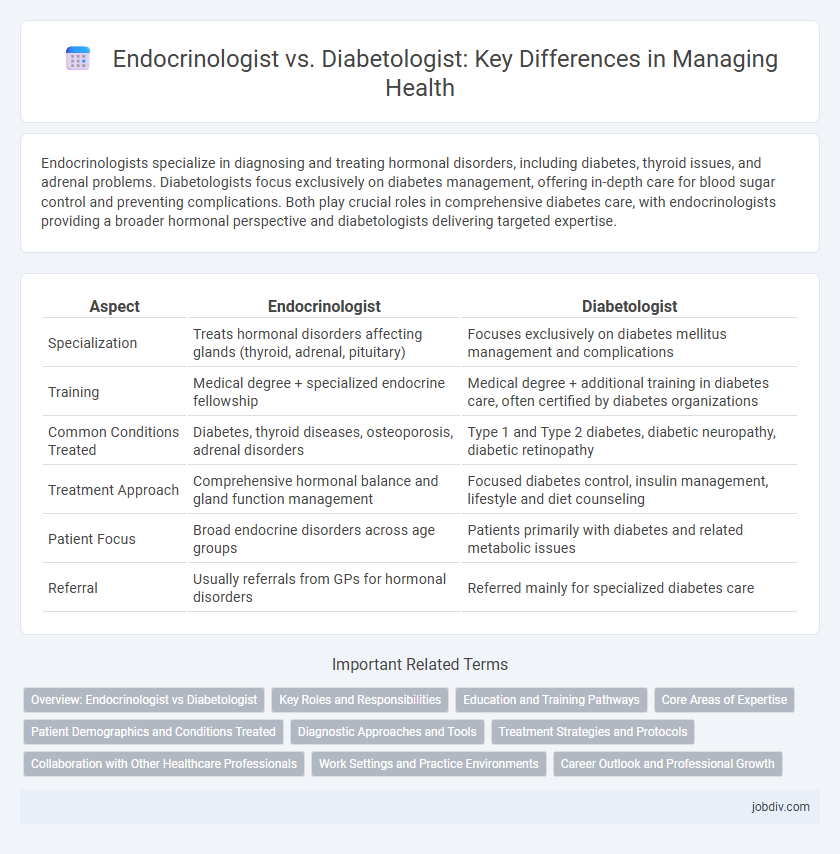
Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormonal disorders, including diabetes, thyroid issues, and adrenal problems. Diabetologists focus exclusively on diabetes management, offering in-depth care for blood sugar control and preventing complications. Both play crucial roles in comprehensive diabetes care, with endocrinologists providing a broader hormonal perspective and diabetologists delivering targeted expertise.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Endocrinologist | Diabetologist |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Treats hormonal disorders affecting glands (thyroid, adrenal, pituitary) | Focuses exclusively on diabetes mellitus management and complications |
| Training | Medical degree + specialized endocrine fellowship | Medical degree + additional training in diabetes care, often certified by diabetes organizations |
| Common Conditions Treated | Diabetes, thyroid diseases, osteoporosis, adrenal disorders | Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy |
| Treatment Approach | Comprehensive hormonal balance and gland function management | Focused diabetes control, insulin management, lifestyle and diet counseling |
| Patient Focus | Broad endocrine disorders across age groups | Patients primarily with diabetes and related metabolic issues |
| Referral | Usually referrals from GPs for hormonal disorders | Referred mainly for specialized diabetes care |
Overview: Endocrinologist vs Diabetologist
Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormone-related disorders, including diabetes, thyroid diseases, and adrenal gland issues, providing comprehensive care for a range of endocrine system conditions. Diabetologists focus specifically on managing diabetes mellitus, offering expertise in blood sugar control, insulin therapy, and prevention of diabetes-related complications. Both specialists work to optimize patient outcomes, but endocrinologists have a broader scope, while diabetologists zero in on diabetes management.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances and disorders such as thyroid disease, osteoporosis, and adrenal insufficiency, managing conditions related to the endocrine system. Diabetologists focus specifically on diabetes mellitus, emphasizing glycemic control, insulin management, and prevention of diabetes-related complications like neuropathy and retinopathy. Both specialists coordinate patient care, but endocrinologists address a broader range of metabolic conditions while diabetologists provide targeted diabetes treatment and education.
Education and Training Pathways
Endocrinologists complete medical school followed by a residency in internal medicine and a fellowship specializing in endocrinology, covering a broad range of hormone-related disorders. Diabetologists may pursue specialized training through fellowships or certifications focused specifically on diabetes management, often after internal medicine or pediatrics residency. Both professionals require extensive education, but endocrinologists have a wider scope of hormone-related expertise, while diabetologists concentrate deeply on diabetes care.
Core Areas of Expertise
Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormone-related disorders such as thyroid diseases, adrenal gland issues, and pituitary gland problems. Diabetologists focus specifically on managing diabetes mellitus, including blood sugar regulation, insulin therapy, and prevention of diabetes-related complications. Both experts contribute to metabolic health, but endocrinologists have a broader hormonal expertise beyond diabetes care.
Patient Demographics and Conditions Treated
Endocrinologists specialize in a broad range of hormonal and metabolic disorders affecting patients of all ages, including thyroid diseases, adrenal disorders, and pituitary problems, while diabetologists focus specifically on managing diabetes mellitus across diverse populations. Patient demographics for endocrinologists often include individuals with complex endocrine conditions requiring comprehensive hormonal evaluation, whereas diabetologists primarily treat adults and children with type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. The tailored care provided by each specialist ensures targeted treatment plans based on distinct patient needs and disease presentations.
Diagnostic Approaches and Tools
Endocrinologists utilize comprehensive hormonal assays, imaging techniques like MRI and ultrasound, and specialized blood tests to diagnose a wide range of endocrine disorders affecting glands such as the thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary. Diabetologists focus primarily on glycemic control assessments including HbA1c testing, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) to diagnose and manage diabetes mellitus. Both specialists employ advanced diagnostic tools, but endocrinologists have a broader scope encompassing multiple hormonal conditions, whereas diabetologists specialize in detailed diabetes-specific evaluations.
Treatment Strategies and Protocols
Endocrinologists specialize in treating hormonal disorders such as thyroid diseases, adrenal insufficiencies, and pituitary abnormalities using comprehensive hormonal replacement and regulation protocols. Diabetologists focus exclusively on diabetes management, implementing tailored glycemic control strategies, including insulin therapy, diet modification, and continuous glucose monitoring. Both specialists employ evidence-based treatment algorithms but differ in scope, with endocrinologists addressing broader endocrine dysfunctions and diabetologists specializing in optimizing diabetes outcomes.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Endocrinologists and diabetologists often collaborate closely with primary care physicians, dietitians, and diabetes educators to provide comprehensive patient care. This multidisciplinary approach ensures precise management of complex hormonal disorders and diabetes, enhancing patient outcomes through coordinated treatment plans. Effective communication among these specialists is crucial for addressing both metabolic control and associated complications.
Work Settings and Practice Environments
Endocrinologists commonly work in hospital settings, academic medical centers, and specialized endocrine clinics, managing complex hormonal disorders including diabetes, thyroid diseases, and metabolic conditions. Diabetologists primarily practice in outpatient clinics and diabetes care centers, focusing exclusively on diabetes management, patient education, and insulin therapy optimization. Both specialists collaborate with multidisciplinary teams in varied environments to provide tailored chronic disease management and improve patient outcomes.
Career Outlook and Professional Growth
Endocrinologists specialize in hormone-related disorders, experiencing steady career growth driven by rising cases of thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary diseases, while diabetologists focus exclusively on diabetes management amid a growing global diabetes epidemic. Both fields offer strong demand, but endocrinology provides broader opportunities due to its wider scope, including metabolic disorders and osteoporosis. Advances in medical technology and personalized treatment methods further enhance professional growth prospects in these specialties.
Endocrinologist vs Diabetologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com