Public health nurses specialize in community-wide health promotion and disease prevention through education, outreach, and vaccination programs. Clinical nurses provide direct patient care in healthcare settings, managing treatments, administering medications, and monitoring patient recovery. Both roles are critical in improving health outcomes but differ in focus, with public health nurses addressing population health and clinical nurses concentrating on individual patient care.
Table of Comparison
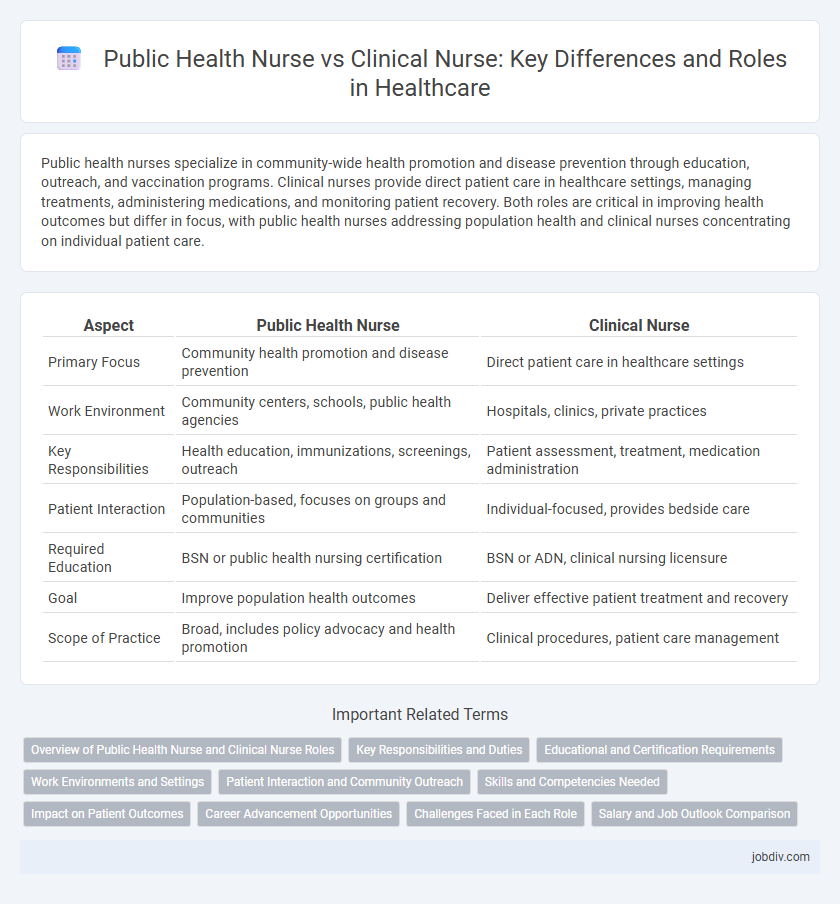
| Aspect | Public Health Nurse | Clinical Nurse |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Community health promotion and disease prevention | Direct patient care in healthcare settings |
| Work Environment | Community centers, schools, public health agencies | Hospitals, clinics, private practices |
| Key Responsibilities | Health education, immunizations, screenings, outreach | Patient assessment, treatment, medication administration |
| Patient Interaction | Population-based, focuses on groups and communities | Individual-focused, provides bedside care |
| Required Education | BSN or public health nursing certification | BSN or ADN, clinical nursing licensure |
| Goal | Improve population health outcomes | Deliver effective patient treatment and recovery |
| Scope of Practice | Broad, includes policy advocacy and health promotion | Clinical procedures, patient care management |
Overview of Public Health Nurse and Clinical Nurse Roles
Public Health Nurses focus on community-wide health promotion, disease prevention, and resource coordination, addressing social determinants of health and providing education at the population level. Clinical Nurses deliver direct patient care in hospitals or healthcare settings, managing treatments, monitoring patient conditions, and supporting recovery. Both roles require specialized nursing knowledge but differ primarily in settings and scope, with Public Health Nurses emphasizing community health and Clinical Nurses concentrating on individual patient care.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Public Health Nurses focus on community-wide health promotion, disease prevention, and health education, often coordinating vaccination programs and conducting epidemiological research. Clinical Nurses provide direct patient care in healthcare facilities, managing treatments, monitoring symptoms, and administering medications at the bedside. Both roles require strong communication skills, but Public Health Nurses emphasize population health strategies, while Clinical Nurses prioritize individualized patient care.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Public Health Nurses typically require a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) with additional certification in community health or public health nursing, such as the Certified Public Health Nurse (CPHN) credential. Clinical Nurses also generally hold a BSN but may pursue specialized certifications like the Certified Registered Nurse (CRN) or specialty-specific credentials depending on their clinical focus. Both roles mandate licensure as Registered Nurses (RN) and ongoing continuing education to maintain certification and stay current with healthcare standards.
Work Environments and Settings
Public Health Nurses primarily work in community settings such as schools, health departments, and home health agencies, focusing on population-based care and health promotion. Clinical Nurses operate mainly in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities, delivering direct patient care and managing acute medical conditions. The distinct work environments influence their responsibilities, with Public Health Nurses emphasizing preventive care and Clinical Nurses providing hands-on clinical treatment.
Patient Interaction and Community Outreach
Public health nurses emphasize community outreach by providing education, preventive care, and resource connections to improve overall population health. Clinical nurses focus on direct patient interaction within healthcare settings, delivering personalized medical care, monitoring patient progress, and managing treatment plans. Both roles require strong communication skills, but public health nurses engage broader populations while clinical nurses concentrate on individual patient needs.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Public Health Nurses require strong community assessment skills, epidemiology knowledge, and health promotion expertise to address population health needs and implement preventive care programs. Clinical Nurses need advanced clinical skills, proficiency in patient assessment, and the ability to manage acute and chronic medical conditions in hospital or clinical settings. Both roles demand excellent communication, critical thinking, and patient-centered care competencies, but Public Health Nurses emphasize population-level interventions while Clinical Nurses focus on direct patient care.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Public health nurses play a critical role in improving community health outcomes through preventive care, health education, and addressing social determinants of health, which reduces hospital admissions and chronic disease prevalence. Clinical nurses directly influence patient outcomes by providing hands-on care, administering treatments, and closely monitoring patient conditions within healthcare settings, ensuring timely interventions and recovery. The combined efforts of public health and clinical nurses enhance overall patient well-being by bridging community health initiatives with individualized clinical care.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Public health nurses often advance by moving into administrative roles, policy development, or community health education, leveraging their expertise in population health management. Clinical nurses typically pursue career growth through specialization in areas such as critical care, pediatrics, or oncology, or by obtaining advanced practice roles like nurse practitioner or clinical nurse specialist. Both paths offer leadership opportunities, but public health nursing emphasizes population-based interventions, while clinical nursing focuses on direct patient care and specialized clinical skills.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Public Health Nurses confront challenges such as managing community-wide disease prevention, addressing health disparities, and navigating limited resources in diverse populations. Clinical Nurses face intense pressure in acute care settings, including high patient acuity, rapid decision-making, and exposure to infectious diseases. Both roles require resilience and adaptability but differ significantly in scope and the nature of patient interactions.
Salary and Job Outlook Comparison
Public Health Nurses typically earn a median annual salary of $75,000, while Clinical Nurses average around $70,000, reflecting variations based on specialization and location. The job outlook for Public Health Nurses is projected to grow by 12% over the next decade due to increasing emphasis on community health initiatives, compared to an 8% growth rate for Clinical Nurses. Demand for Public Health Nurses is rising in response to preventative care programs, whereas Clinical Nurses remain vital in acute care settings with steady employment opportunities.
Public Health Nurse vs Clinical Nurse Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com