A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who can prescribe medication and treat complex mental health disorders through a combination of therapy and medical management. Psychologists specialize in providing psychotherapy and psychological testing but do not prescribe medication, focusing primarily on behavioral interventions and counseling. Understanding the distinct roles of psychiatrists and psychologists helps individuals seek the appropriate mental health care tailored to their specific needs.
Table of Comparison
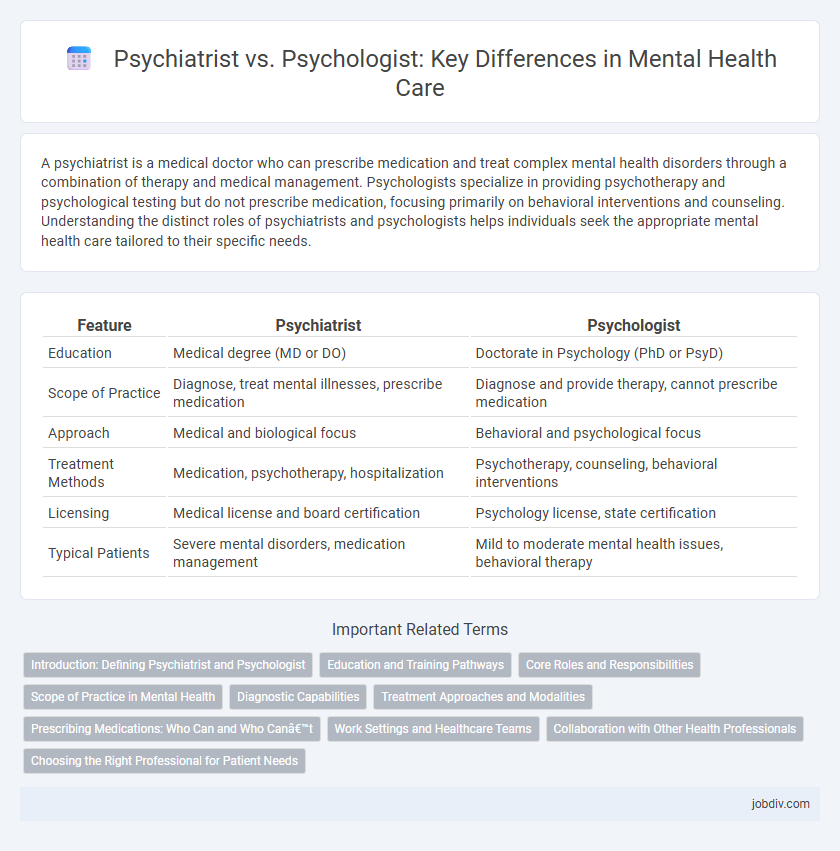
| Feature | Psychiatrist | Psychologist |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Medical degree (MD or DO) | Doctorate in Psychology (PhD or PsyD) |
| Scope of Practice | Diagnose, treat mental illnesses, prescribe medication | Diagnose and provide therapy, cannot prescribe medication |
| Approach | Medical and biological focus | Behavioral and psychological focus |
| Treatment Methods | Medication, psychotherapy, hospitalization | Psychotherapy, counseling, behavioral interventions |
| Licensing | Medical license and board certification | Psychology license, state certification |
| Typical Patients | Severe mental disorders, medication management | Mild to moderate mental health issues, behavioral therapy |
Introduction: Defining Psychiatrist and Psychologist
Psychiatrists are medical doctors specializing in diagnosing and treating mental illnesses through medication and medical interventions, often working with patients requiring complex psychiatric care. Psychologists focus on assessing and treating emotional and behavioral issues using psychotherapy and psychological testing without prescribing medications. Both professions aim to improve mental health but differ fundamentally in education, treatment approaches, and scope of practice.
Education and Training Pathways
Psychiatrists complete medical school followed by a residency in psychiatry, enabling them to prescribe medication and manage complex mental health disorders with a medical approach. Psychologists typically earn a doctoral degree in psychology (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) involving extensive training in psychological testing, therapy, and research, but they typically do not prescribe medication. The distinct education and training pathways reflect their differing roles in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care in mental health.
Core Roles and Responsibilities
Psychiatrists are medical doctors specializing in diagnosing and treating mental illnesses through medication management and medical interventions, often addressing complex psychiatric disorders. Psychologists focus on evaluating cognitive, emotional, and behavioral issues through psychotherapy, psychological testing, and counseling techniques without prescribing medication. Both professions collaborate to improve mental health outcomes but differ fundamentally in training, scope of practice, and treatment approaches.
Scope of Practice in Mental Health
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and provide comprehensive treatment for complex mental health disorders, combining biological and psychological approaches. Psychologists specialize in psychotherapy and behavioral interventions, conducting psychological assessments and counseling but typically cannot prescribe medication. Their scope of practice complements each other in mental health care, with psychiatrists managing medical treatments and psychologists focusing on therapeutic techniques.
Diagnostic Capabilities
Psychiatrists are medical doctors with specialized training in mental health diagnosis, allowing them to perform comprehensive medical evaluations and prescribe medications. Psychologists focus on psychological testing and behavioral assessments to diagnose mental health conditions through clinical interviews and standardized tests. While psychiatrists can integrate medical and psychological data for diagnosis, psychologists emphasize non-medical diagnostic techniques grounded in therapy and cognitive evaluation.
Treatment Approaches and Modalities
Psychiatrists specialize in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders using a combination of medication management and psychotherapy, often addressing biological factors underlying mental illness. Psychologists primarily employ evidence-based psychotherapeutic techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), talk therapy, and behavioral interventions without prescribing medication. Collaboration between psychiatrists and psychologists can enhance treatment efficacy by integrating pharmacological management with psychological support and therapeutic modalities.
Prescribing Medications: Who Can and Who Can’t
Psychiatrists are medical doctors licensed to prescribe medications for mental health conditions, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers. Psychologists, typically holding doctoral degrees in psychology, do not have prescribing privileges but provide therapy and psychological assessments. In some U.S. states, specially trained psychologists may obtain limited prescribing rights under collaborative agreements with physicians.
Work Settings and Healthcare Teams
Psychiatrists primarily work in hospitals, clinics, and private practices as part of multidisciplinary healthcare teams, often collaborating closely with medical doctors and nurses to manage medication and complex mental health disorders. Psychologists typically operate in educational institutions, mental health facilities, and private practices, focusing on psychological testing, therapy, and behavioral interventions while partnering with social workers and counselors. Both professionals play complementary roles in integrated healthcare settings to provide comprehensive mental health care.
Collaboration with Other Health Professionals
Psychiatrists collaborate closely with medical doctors, therapists, and social workers to provide comprehensive mental health care that includes medication management and medical evaluations. Psychologists often work alongside counselors, educators, and healthcare providers to deliver therapy and behavioral assessments tailored to individual patient needs. Interdisciplinary teamwork between psychiatrists and psychologists enhances treatment outcomes by integrating medical and psychological expertise.
Choosing the Right Professional for Patient Needs
Psychiatrists are medical doctors specializing in mental health, able to prescribe medication and manage complex psychiatric conditions, whereas psychologists focus on therapy, behavioral interventions, and psychological testing. Patients with severe mental illnesses, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, may benefit more from a psychiatrist's medical expertise, while those seeking counseling for anxiety, depression, or behavioral issues often find psychologists better suited. Understanding the specific needs, treatment goals, and symptom severity is essential for selecting the most effective mental health professional.
Psychiatrist vs Psychologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com