Public Health Administrators coordinate community health programs and develop policies to improve population health outcomes. Health Services Managers oversee operational aspects of healthcare facilities, ensuring efficient delivery of patient care and resource management. Both roles require strong leadership skills but differ in scope, with administrators focusing on public health initiatives and managers concentrating on healthcare organization performance.
Table of Comparison
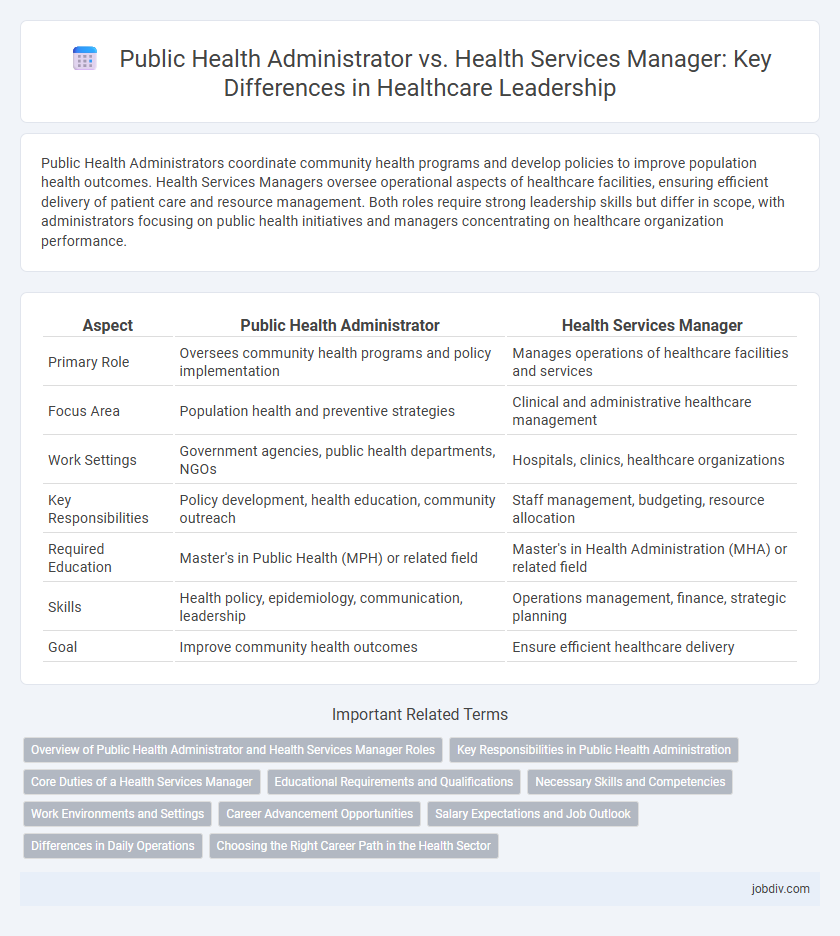
| Aspect | Public Health Administrator | Health Services Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees community health programs and policy implementation | Manages operations of healthcare facilities and services |
| Focus Area | Population health and preventive strategies | Clinical and administrative healthcare management |
| Work Settings | Government agencies, public health departments, NGOs | Hospitals, clinics, healthcare organizations |
| Key Responsibilities | Policy development, health education, community outreach | Staff management, budgeting, resource allocation |
| Required Education | Master's in Public Health (MPH) or related field | Master's in Health Administration (MHA) or related field |
| Skills | Health policy, epidemiology, communication, leadership | Operations management, finance, strategic planning |
| Goal | Improve community health outcomes | Ensure efficient healthcare delivery |
Overview of Public Health Administrator and Health Services Manager Roles
Public Health Administrators oversee community health programs, policy development, and disease prevention initiatives to improve population health outcomes. Health Services Managers coordinate healthcare facility operations, managing budgets, staff, and patient care services to ensure efficient delivery of medical services. Both roles require leadership skills and a strong understanding of healthcare systems, but Public Health Administrators focus on broader public health strategies while Health Services Managers concentrate on organizational management within healthcare settings.
Key Responsibilities in Public Health Administration
Public Health Administrators primarily focus on developing and implementing community-wide health policies, coordinating public health programs, and managing disease prevention initiatives. They oversee compliance with health regulations, collaborate with government agencies, and direct resource allocation to address population health needs. Their responsibilities often include analyzing epidemiological data to inform strategic planning and responding to public health emergencies efficiently.
Core Duties of a Health Services Manager
Health Services Managers oversee the planning, coordination, and supervision of healthcare facilities, ensuring efficient delivery of medical services. They manage budgets, staff operations, and compliance with healthcare regulations to maintain quality standards. Their role emphasizes strategic resource allocation and operational optimization within hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
Educational Requirements and Qualifications
Public Health Administrators typically require a master's degree in public health (MPH) or a related field, emphasizing community health, epidemiology, and health policy. Health Services Managers often hold a bachelor's or master's degree in health administration, business administration, or nursing, focusing on healthcare operations and organizational management. Both roles benefit from certifications like Certified Public Health (CPH) for Public Health Administrators and Certified Professional in Healthcare Management (CPHM) for Health Services Managers to enhance professional qualifications.
Necessary Skills and Competencies
Public Health Administrators require strong skills in policy development, community health assessment, and population health management to effectively design and implement health programs. Health Services Managers must excel in organizational leadership, financial management, and healthcare regulations to oversee healthcare facilities and ensure compliance. Both roles demand competencies in communication, critical thinking, and data analysis to improve health outcomes and manage resources efficiently.
Work Environments and Settings
Public Health Administrators primarily work in government agencies, community health organizations, and non-profit sectors, focusing on population health initiatives and policy implementation. Health Services Managers are commonly employed in hospitals, clinics, and private healthcare facilities, overseeing daily operations and healthcare delivery. Both roles require collaboration with healthcare professionals but differ in their environmental focus, with Public Health Administrators emphasizing community-level impact and Health Services Managers concentrating on facility-based management.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Public Health Administrators often advance by influencing community health policies and leading large-scale public health initiatives, gaining expertise in epidemiology and health education. Health Services Managers typically progress through roles managing healthcare facilities or departments, sharpening skills in operational efficiency and patient care delivery. Both careers offer diverse advancement paths, yet Public Health Administrators lean toward policy impact while Health Services Managers focus on organizational leadership.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Public Health Administrators typically earn between $60,000 and $100,000 annually, with a job outlook growth of 11% through 2031, reflecting increasing demand for community health programs. Health Services Managers often command higher salaries, ranging from $70,000 to $120,000 per year, driven by administrative roles in hospitals and healthcare facilities with a projected job growth of 28%, one of the fastest in healthcare management. Both professions require strong leadership skills, but Health Services Managers benefit from broader employment opportunities and higher median salaries due to their involvement in operational management within diverse healthcare settings.
Differences in Daily Operations
Public Health Administrators primarily focus on policy implementation, community health initiatives, and inter-agency coordination to improve population health outcomes. Health Services Managers oversee daily operations of healthcare facilities, managing staff schedules, budgeting, and patient care services to ensure efficient facility performance. While Public Health Administrators work at a macro-level influencing public health frameworks, Health Services Managers concentrate on micro-level management within specific healthcare settings.
Choosing the Right Career Path in the Health Sector
Public Health Administrators focus on population health initiatives, policy development, and community wellness programs, making them ideal for those passionate about preventive care and health equity. Health Services Managers oversee healthcare facility operations, staffing, and budget management, suited for individuals interested in the administrative functions of hospitals or clinics. Evaluating personal interests in strategic planning versus operational leadership helps determine the optimal career path in the dynamic health sector.
Public Health Administrator vs Health Services Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com