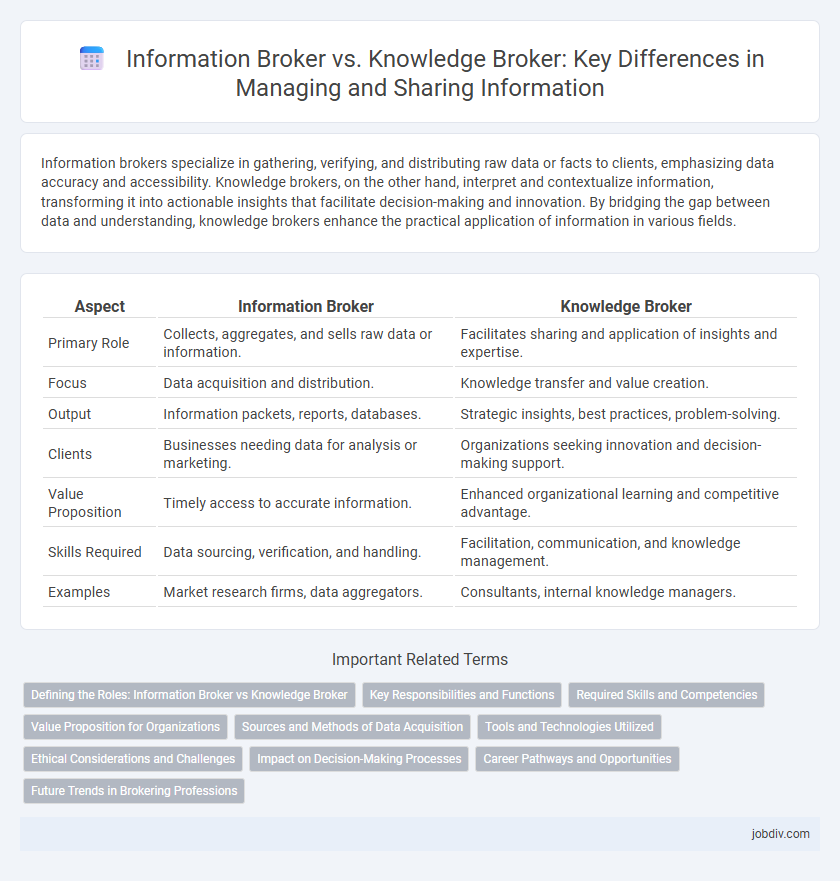
Information brokers specialize in gathering, verifying, and distributing raw data or facts to clients, emphasizing data accuracy and accessibility. Knowledge brokers, on the other hand, interpret and contextualize information, transforming it into actionable insights that facilitate decision-making and innovation. By bridging the gap between data and understanding, knowledge brokers enhance the practical application of information in various fields.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Broker | Knowledge Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Collects, aggregates, and sells raw data or information. | Facilitates sharing and application of insights and expertise. |
| Focus | Data acquisition and distribution. | Knowledge transfer and value creation. |
| Output | Information packets, reports, databases. | Strategic insights, best practices, problem-solving. |
| Clients | Businesses needing data for analysis or marketing. | Organizations seeking innovation and decision-making support. |
| Value Proposition | Timely access to accurate information. | Enhanced organizational learning and competitive advantage. |
| Skills Required | Data sourcing, verification, and handling. | Facilitation, communication, and knowledge management. |
| Examples | Market research firms, data aggregators. | Consultants, internal knowledge managers. |
Defining the Roles: Information Broker vs Knowledge Broker
Information brokers specialize in collecting, verifying, and distributing factual data from diverse sources to support decision-making processes. Knowledge brokers go beyond raw data by synthesizing insights, facilitating knowledge exchange, and promoting the application of expertise across organizations. Defining these roles highlights the difference between managing discrete information and enabling deeper understanding through collaborative knowledge sharing.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Information brokers collect, verify, and distribute raw data from various sources to meet client needs, focusing on accuracy and comprehensiveness. Knowledge brokers analyze, synthesize, and interpret information, transforming data into actionable insights and facilitating knowledge sharing among stakeholders. Both roles enable informed decision-making but differ in emphasis: information brokers prioritize data acquisition, while knowledge brokers emphasize knowledge transfer and application.
Required Skills and Competencies
Information brokers excel in data retrieval, verification, and organization, requiring strong research skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in information management systems. Knowledge brokers emphasize synthesis, interpretation, and communication of complex information, necessitating critical thinking, domain expertise, and excellent interpersonal skills to facilitate knowledge exchange. Both roles demand adaptability and technological literacy but diverge in focus: information brokers prioritize data accuracy, while knowledge brokers drive actionable insights and collaborative learning.
Value Proposition for Organizations
Information brokers aggregate and provide raw data, enabling organizations to quickly access and retrieve relevant facts for decision-making. Knowledge brokers transform information into actionable insights through interpretation, synthesis, and contextual understanding, thereby enhancing organizational learning and innovation. This value proposition empowers companies to leverage not just data availability but strategic wisdom, fostering competitive advantage and informed growth.
Sources and Methods of Data Acquisition
Information brokers primarily gather data from public records, databases, and online platforms using automated tools and data mining techniques. Knowledge brokers focus on acquiring insights through expert networks, interviews, workshops, and collaborative knowledge exchange methods. While information brokers emphasize raw data collection, knowledge brokers prioritize contextualizing information by connecting diverse sources and facilitating meaningful interpretation.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Information brokers leverage advanced data aggregation tools, web scraping software, and database management systems to collect and organize vast amounts of raw data from diverse sources. Knowledge brokers utilize collaborative platforms, knowledge management systems, and artificial intelligence-driven analytics to transform raw data into actionable insights and facilitate knowledge sharing across organizations. Both roles rely on cutting-edge technologies, but information brokers prioritize data acquisition tools, while knowledge brokers emphasize tools that enhance understanding and decision-making.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Information brokers gather, verify, and distribute data, often navigating privacy concerns and data protection regulations to maintain ethical standards. Knowledge brokers facilitate the exchange of expertise and insights between individuals or organizations, emphasizing transparency, consent, and intellectual property rights to uphold trust. Both roles face challenges related to data accuracy, confidentiality, and balancing accessibility with responsible information management.
Impact on Decision-Making Processes
Information brokers gather, verify, and deliver raw data that forms the foundation of decision-making, enabling timely access to relevant facts. Knowledge brokers synthesize and contextualize complex information, transforming it into actionable insights that enhance strategic choices and innovation. The impact on decision-making processes is significant, as knowledge brokers facilitate deeper understanding and more informed decisions compared to mere data provision by information brokers.
Career Pathways and Opportunities
Information brokers specialize in gathering and selling raw data across industries such as market research and competitive intelligence, offering career opportunities in data analysis, sales, and consulting. Knowledge brokers focus on transforming information into actionable insights by facilitating knowledge exchange between experts and organizations, creating roles in project management, innovation strategy, and organizational development. Both career paths demand strong research capabilities and communication skills but differ in their emphasis on data collection versus knowledge synthesis and application.
Future Trends in Brokering Professions
Information brokers increasingly utilize artificial intelligence and big data analytics to enhance data aggregation and real-time insights, driving more precise decision-making processes. Knowledge brokers focus on integrating interdisciplinary expertise and facilitating collaboration across sectors to foster innovation and accelerate knowledge transfer. Future trends indicate a convergence of these roles through advanced digital platforms that combine data curation with strategic knowledge management to deliver holistic solutions.
Information Broker vs Knowledge Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com